forked from fmtlib/fmt
Compare commits
209 Commits
esp-idf-re
...
10.x
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| e69e5f977d | |||
| d88d016e2f | |||
| b169f5be9f | |||
| 67c0c0c09c | |||
| 051b31531c | |||
| b0569451a7 | |||
| ce3161887a | |||
| 1a95e5d1b4 | |||
| e1aac42663 | |||
| 1705600be3 | |||
| 0c345dccd2 | |||
| d33731d202 | |||
| c068c7c622 | |||
| 13fa26745d | |||
| ebd5c8f994 | |||
| f5ca178c12 | |||
| 138a64bfb1 | |||
| a5bacf3fef | |||
| 4aa24f54cd | |||
| e33c1568c3 | |||
| 23826669cf | |||
| 8e6b2541a6 | |||
| 4939d67a83 | |||
| bd3273021b | |||
| 5f9058dbd4 | |||
| 28576b0600 | |||
| 5ddd0cad15 | |||
| 41d31512b7 | |||
| 44b76d88f4 | |||
| 3324152db4 | |||
| 55190dadb5 | |||
| 63e4b93cfc | |||
| c64edcd325 | |||
| 8c520b4fdc | |||
| 2e6bb706bf | |||
| a13d1b12e5 | |||
| 47a0eec2e8 | |||
| a8bed38952 | |||
| e206043d2b | |||
| 4a6f0be5b6 | |||
| 662d784157 | |||
| d5823aae36 | |||
| d83c1b8d4a | |||
| bfba2f9e92 | |||
| a3bf40838f | |||
| ea1066bbe3 | |||
| be57ec7ec0 | |||
| 305747d440 | |||
| 47c8f63d02 | |||
| 76e8f10403 | |||
| 18ca2248df | |||
| 3a25a58482 | |||
| 4cbf6182ea | |||
| 88d19f5de9 | |||
| 62529aad19 | |||
| df62c86783 | |||
| eef6dbafbf | |||
| 41c2433358 | |||
| 0a9d08fefd | |||
| e450b7aeb3 | |||
| c5a85f8d7d | |||
| 1fd093add4 | |||
| c4f2de4933 | |||
| d06921d8d8 | |||
| fc0f84d290 | |||
| 86f2ec5de7 | |||
| a537c39fdf | |||
| 7c240d52c3 | |||
| f64a6a2ecd | |||
| 6f9a816786 | |||
| e7875ae0fa | |||
| 3eb3aef575 | |||
| 56d7a8c157 | |||
| 968fb9d166 | |||
| b5f6b36b00 | |||
| 44dd6c0e09 | |||
| 3a0f4af4e9 | |||
| 1ca1a4a7a9 | |||
| dbd9c89b3c | |||
| 9cd2b87e18 | |||
| d5da9cc40e | |||
| 3a2c50d4ac | |||
| 18c43a214c | |||
| 6b07fff0d9 | |||
| 9165434e5a | |||
| b8f81dede5 | |||
| 923005bd4f | |||
| afa85e46c3 | |||
| 6025bd7c37 | |||
| 5471a2426c | |||
| 7d757cba5d | |||
| 6855bd532b | |||
| bbee753579 | |||
| 89860eb901 | |||
| 274ba2645b | |||
| 9048add999 | |||
| 640e0c02d4 | |||
| 6392dba21c | |||
| 9a6fd11a56 | |||
| dee0dbf07f | |||
| 2fabb43b93 | |||
| 9c3c107c8c | |||
| 4497a2d09a | |||
| 81629e425c | |||
| 6f95000b7a | |||
| 573d74395b | |||
| 5d55375a8a | |||
| 71bd51e6c2 | |||
| f575089243 | |||
| 99b9fbf8ef | |||
| 8f83ee2ad1 | |||
| 2a8a694466 | |||
| 04718008ab | |||
| b87ea22e29 | |||
| 5cfd28d476 | |||
| 73fae91e64 | |||
| 6988be3878 | |||
| 2d1e4bb35e | |||
| 7f8d419115 | |||
| ccc9ab7bf9 | |||
| c4283ec471 | |||
| c3f9a73445 | |||
| 06f1c0d725 | |||
| ffa5b14fe3 | |||
| bea7ecc710 | |||
| 8a39388516 | |||
| dd6f657a79 | |||
| c13753a70c | |||
| 864a8b5f38 | |||
| 649fe0fc8b | |||
| 45e124ee43 | |||
| 045b05d79e | |||
| ec628561c2 | |||
| cbb18c237a | |||
| 6b0082e6c7 | |||
| 52a99a67f7 | |||
| 4548d1eae2 | |||
| 050d41e857 | |||
| 1c023c0087 | |||
| b35d4e40fe | |||
| acaf83f40f | |||
| 05aa783779 | |||
| 05dda9490d | |||
| caf4fcb207 | |||
| e0d3e346d2 | |||
| 19276d7325 | |||
| 2a2c6e676f | |||
| 3b7f58a8b3 | |||
| e9bbd4069e | |||
| 857cce7a83 | |||
| 081d5b0d8b | |||
| baae1ed658 | |||
| 2ac6c5ca8b | |||
| d9063baf22 | |||
| f7542c5761 | |||
| 130cf54cbc | |||
| 8e0ca0589f | |||
| bf497ac068 | |||
| bb8d50f04b | |||
| f76603f21e | |||
| f918289363 | |||
| 72e883e163 | |||
| b3bf23f3c4 | |||
| 349e1c48d1 | |||
| 79dbd3f192 | |||
| 2dd4fa8742 | |||
| 44f3d8a77c | |||
| 06b20387ae | |||
| 649f2460db | |||
| 7529af8f99 | |||
| a3a74fa7f3 | |||
| 8ef4db4b96 | |||
| 492a99c964 | |||
| 3baaa8d899 | |||
| 0e01e46c11 | |||
| f6ca4ea199 | |||
| a8a73da7e4 | |||
| aa3c5a4127 | |||
| bfdf50d183 | |||
| 571a9b7b26 | |||
| 6c088be8ec | |||
| 016b1faede | |||
| e25370093a | |||
| d4987546a4 | |||
| 5bdce181f1 | |||
| a4b7b24b7b | |||
| fac60bd4f5 | |||
| f5be4a8a9a | |||
| 84e6661517 | |||
| ac3240439c | |||
| 8894ae87fe | |||
| ca608547e5 | |||
| 23cf4055a0 | |||
| 46c8301ee9 | |||
| a79a979828 | |||
| 457bb6a98f | |||
| 61aef41110 | |||
| 2a45fd30fe | |||
| 24296cff1c | |||
| 3d1d20a6ac | |||
| 0302c527c6 | |||
| 154eccfeb1 | |||
| 35dc5def30 | |||
| e1fc481d65 | |||
| e8259c5298 | |||
| 6379251554 | |||
| 951fd9e66f | |||
| be89b9a41e | |||
| 28e2d3b640 |
2
.github/dependabot.yml
vendored
2
.github/dependabot.yml
vendored
@ -3,6 +3,6 @@ updates:
|
||||
- package-ecosystem: "github-actions" # Necessary to update action hashs
|
||||
directory: "/"
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
interval: "weekly"
|
||||
interval: "monthly"
|
||||
# Allow up to 3 opened pull requests for github-actions versions
|
||||
open-pull-requests-limit: 3
|
||||
|
||||
6
.github/workflows/cifuzz.yml
vendored
6
.github/workflows/cifuzz.yml
vendored
@ -10,20 +10,20 @@ jobs:
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Build Fuzzers
|
||||
id: build
|
||||
uses: google/oss-fuzz/infra/cifuzz/actions/build_fuzzers@master
|
||||
uses: google/oss-fuzz/infra/cifuzz/actions/build_fuzzers@061583ebb5a96653e42feb3a97ee513eedc18078 # master
|
||||
with:
|
||||
oss-fuzz-project-name: 'fmt'
|
||||
dry-run: false
|
||||
language: c++
|
||||
- name: Run Fuzzers
|
||||
uses: google/oss-fuzz/infra/cifuzz/actions/run_fuzzers@master
|
||||
uses: google/oss-fuzz/infra/cifuzz/actions/run_fuzzers@061583ebb5a96653e42feb3a97ee513eedc18078 # master
|
||||
with:
|
||||
oss-fuzz-project-name: 'fmt'
|
||||
fuzz-seconds: 300
|
||||
dry-run: false
|
||||
language: c++
|
||||
- name: Upload Crash
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@0b7f8abb1508181956e8e162db84b466c27e18ce # v3.1.2
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@c7d193f32edcb7bfad88892161225aeda64e9392 # v4.0.0
|
||||
if: failure() && steps.build.outcome == 'success'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: artifacts
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/doc.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/doc.yml
vendored
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-20.04
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@c85c95e3d7251135ab7dc9ce3241c5835cc595a9 # v3.5.3
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Add ubuntu mirrors
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
26
.github/workflows/lint.yml
vendored
Normal file
26
.github/workflows/lint.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
name: lint
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '**.h'
|
||||
- '**.cc'
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
format_code:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install clang-format
|
||||
uses: aminya/setup-cpp@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
clangformat: 17.0.5
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run clang-format
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
find include src -name '*.h' -o -name '*.cc' | xargs clang-format -i -style=file -fallback-style=none
|
||||
git diff --exit-code
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/linux.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/linux.yml
vendored
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- shared: -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@c85c95e3d7251135ab7dc9ce3241c5835cc595a9 # v3.5.3
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set timezone
|
||||
run: sudo timedatectl set-timezone 'Asia/Yekaterinburg'
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/macos.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/macos.yml
vendored
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: '${{ matrix.os }}'
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@c85c95e3d7251135ab7dc9ce3241c5835cc595a9 # v3.5.3
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set timezone
|
||||
run: sudo systemsetup -settimezone 'Asia/Yekaterinburg'
|
||||
|
||||
8
.github/workflows/scorecard.yml
vendored
8
.github/workflows/scorecard.yml
vendored
@ -29,12 +29,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: "Checkout code"
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@c85c95e3d7251135ab7dc9ce3241c5835cc595a9 # v3.5.3
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0
|
||||
with:
|
||||
persist-credentials: false
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Run analysis"
|
||||
uses: ossf/scorecard-action@08b4669551908b1024bb425080c797723083c031 # v2.2.0
|
||||
uses: ossf/scorecard-action@0864cf19026789058feabb7e87baa5f140aac736 # v2.3.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
results_file: results.sarif
|
||||
results_format: sarif
|
||||
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# Upload the results as artifacts (optional). Commenting out will disable uploads of run results in SARIF
|
||||
# format to the repository Actions tab.
|
||||
- name: "Upload artifact"
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@0b7f8abb1508181956e8e162db84b466c27e18ce # v3.1.2
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@c7d193f32edcb7bfad88892161225aeda64e9392 # v4.0.0
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: SARIF file
|
||||
path: results.sarif
|
||||
@ -60,6 +60,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload the results to GitHub's code scanning dashboard.
|
||||
- name: "Upload to code-scanning"
|
||||
uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@a09933a12a80f87b87005513f0abb1494c27a716 # v2.21.4
|
||||
uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@74483a38d39275f33fcff5f35b679b5ca4a26a99 # v2.22.5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
sarif_file: results.sarif
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/windows.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/windows.yml
vendored
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
standard: 20
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@c85c95e3d7251135ab7dc9ce3241c5835cc595a9 # v3.5.3
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set timezone
|
||||
run: tzutil /s "Ekaterinburg Standard Time"
|
||||
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
release: false
|
||||
msystem: ${{matrix.sys}}
|
||||
pacboy: cc:p cmake:p ninja:p lld:p
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@c85c95e3d7251135ab7dc9ce3241c5835cc595a9 # v3.5.3
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@8ade135a41bc03ea155e62e844d188df1ea18608 # v4.1.0
|
||||
- name: Configure
|
||||
run: cmake -B ../build -DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
|
||||
env: { LDFLAGS: -fuse-ld=lld }
|
||||
|
||||
45
.gitignore
vendored
45
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1,37 +1,24 @@
|
||||
.vscode/
|
||||
.vs/
|
||||
|
||||
*.iml
|
||||
.idea/
|
||||
.externalNativeBuild/
|
||||
.gradle/
|
||||
gradle/
|
||||
gradlew*
|
||||
local.properties
|
||||
build/
|
||||
support/.cxx
|
||||
|
||||
bin/
|
||||
/_CPack_Packages
|
||||
/CMakeScripts
|
||||
/doc/doxyxml
|
||||
/doc/html
|
||||
/doc/node_modules
|
||||
virtualenv
|
||||
/Testing
|
||||
/install_manifest.txt
|
||||
*~
|
||||
*.a
|
||||
*.so*
|
||||
*.xcodeproj
|
||||
*.zip
|
||||
cmake_install.cmake
|
||||
CPack*.cmake
|
||||
fmt-*.cmake
|
||||
CTestTestfile.cmake
|
||||
*~
|
||||
.vscode/
|
||||
/CMakeScripts
|
||||
/Testing
|
||||
/_CPack_Packages
|
||||
/doc/doxyxml
|
||||
/doc/html
|
||||
/doc/node_modules
|
||||
/install_manifest.txt
|
||||
CMakeCache.txt
|
||||
CMakeFiles
|
||||
CPack*.cmake
|
||||
CTestTestfile.cmake
|
||||
FMT.build
|
||||
Makefile
|
||||
run-msbuild.bat
|
||||
bin/
|
||||
build/
|
||||
cmake_install.cmake
|
||||
fmt-*.cmake
|
||||
fmt.pc
|
||||
virtualenv
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8...3.26)
|
||||
|
||||
# Fallback for using newer policies on CMake <3.12.
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_VERSION} VERSION_LESS 3.12)
|
||||
if (${CMAKE_VERSION} VERSION_LESS 3.12)
|
||||
cmake_policy(VERSION ${CMAKE_MAJOR_VERSION}.${CMAKE_MINOR_VERSION})
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine if fmt is built as a subproject (using add_subdirectory)
|
||||
# or if it is the master project.
|
||||
@ -162,10 +162,10 @@ set(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE "")
|
||||
if (FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS)
|
||||
set(FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE SYSTEM)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME STREQUAL "MSDOS")
|
||||
if (CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME STREQUAL "MSDOS")
|
||||
set(FMT_TEST OFF)
|
||||
message(STATUS "MSDOS is incompatible with gtest")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get version from core.h
|
||||
file(READ include/fmt/core.h core_h)
|
||||
@ -283,7 +283,7 @@ if (FMT_OS)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
add_module_library(fmt src/fmt.cc FALLBACK
|
||||
${FMT_SOURCES} ${FMT_HEADERS} README.rst ChangeLog.rst
|
||||
${FMT_SOURCES} ${FMT_HEADERS} README.md ChangeLog.md
|
||||
IF FMT_MODULE)
|
||||
add_library(fmt::fmt ALIAS fmt)
|
||||
if (FMT_MODULE)
|
||||
@ -312,7 +312,15 @@ set(FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX d CACHE STRING "Debug library postfix.")
|
||||
set_target_properties(fmt PROPERTIES
|
||||
VERSION ${FMT_VERSION} SOVERSION ${CPACK_PACKAGE_VERSION_MAJOR}
|
||||
PUBLIC_HEADER "${FMT_HEADERS}"
|
||||
DEBUG_POSTFIX "${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}")
|
||||
DEBUG_POSTFIX "${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}"
|
||||
|
||||
# Workaround for Visual Studio 2017:
|
||||
# Ensure the .pdb is created with the same name and in the same directory
|
||||
# as the .lib. Newer VS versions already do this by default, but there is no
|
||||
# harm in setting it for those too. Ignored by other generators.
|
||||
COMPILE_PDB_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY "${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}"
|
||||
COMPILE_PDB_NAME "fmt"
|
||||
COMPILE_PDB_NAME_DEBUG "fmt${FMT_DEBUG_POSTFIX}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Set FMT_LIB_NAME for pkg-config fmt.pc. We cannot use the OUTPUT_NAME target
|
||||
# property because it's not set by default.
|
||||
@ -326,7 +334,7 @@ if (BUILD_SHARED_LIBS)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
if (FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST)
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt PUBLIC FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
add_library(fmt-header-only INTERFACE)
|
||||
add_library(fmt::fmt-header-only ALIAS fmt-header-only)
|
||||
@ -334,7 +342,8 @@ add_library(fmt::fmt-header-only ALIAS fmt-header-only)
|
||||
target_compile_definitions(fmt-header-only INTERFACE FMT_HEADER_ONLY=1)
|
||||
target_compile_features(fmt-header-only INTERFACE cxx_std_11)
|
||||
|
||||
target_include_directories(fmt-header-only ${FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE} INTERFACE
|
||||
target_include_directories(fmt-header-only
|
||||
${FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERS_ATTRIBUTE} INTERFACE
|
||||
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
|
||||
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:${FMT_INC_DIR}>)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -439,6 +448,6 @@ if (FMT_MASTER_PROJECT AND EXISTS ${gitignore})
|
||||
set(CPACK_SOURCE_IGNORE_FILES ${ignored_files})
|
||||
set(CPACK_SOURCE_PACKAGE_FILE_NAME fmt-${FMT_VERSION})
|
||||
set(CPACK_PACKAGE_NAME fmt)
|
||||
set(CPACK_RESOURCE_FILE_README ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/README.rst)
|
||||
set(CPACK_RESOURCE_FILE_README ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/README.md)
|
||||
include(CPack)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
5533
ChangeLog.md
Normal file
5533
ChangeLog.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
5922
ChangeLog.rst
5922
ChangeLog.rst
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
490
README.md
Normal file
490
README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,490 @@
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/156254208-f5b743a9-88cf-439d-b0c0-923d53e8d551.png" alt="{fmt}" width="25%"/>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows)
|
||||
[](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\%0Acolspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\%0ASummary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
|
||||
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt)
|
||||
[](https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt)
|
||||
|
||||
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
|
||||
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
|
||||
|
||||
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds
|
||||
that help victims of the war in Ukraine: <https://www.stopputin.net/>.
|
||||
|
||||
[Documentation](https://fmt.dev)
|
||||
|
||||
[Cheat Sheets](https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html)
|
||||
|
||||
Q&A: ask questions on [StackOverflow with the tag
|
||||
fmt](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt).
|
||||
|
||||
Try {fmt} in [Compiler Explorer](https://godbolt.org/z/Eq5763).
|
||||
|
||||
# Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Simple [format API](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html) with positional
|
||||
arguments for localization
|
||||
- Implementation of [C++20
|
||||
std::format](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format) and
|
||||
[C++23 std::print](https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/io/print)
|
||||
- [Format string syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) similar
|
||||
to Python\'s
|
||||
[format](https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format)
|
||||
- Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding,
|
||||
shortness and round-trip guarantees using the
|
||||
[Dragonbox](https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox) algorithm
|
||||
- Portable Unicode support
|
||||
- Safe [printf
|
||||
implementation](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#printf-formatting)
|
||||
including the POSIX extension for positional arguments
|
||||
- Extensibility: [support for user-defined
|
||||
types](https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types)
|
||||
- High performance: faster than common standard library
|
||||
implementations of `(s)printf`, iostreams, `to_string` and
|
||||
`to_chars`, see [Speed tests](#speed-tests) and [Converting a
|
||||
hundred million integers to strings per
|
||||
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html)
|
||||
- Small code size both in terms of source code with the minimum
|
||||
configuration consisting of just three files, `core.h`, `format.h`
|
||||
and `format-inl.h`, and compiled code; see [Compile time and code
|
||||
bloat](#compile-time-and-code-bloat)
|
||||
- Reliability: the library has an extensive set of
|
||||
[tests](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test) and is
|
||||
[continuously fuzzed](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1)
|
||||
- Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can
|
||||
be reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents
|
||||
buffer overflow errors
|
||||
- Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external
|
||||
dependencies, permissive MIT
|
||||
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst)
|
||||
- [Portability](https://fmt.dev/latest/index.html#portability) with
|
||||
consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers
|
||||
- Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as
|
||||
`-Wall -Wextra -pedantic`
|
||||
- Locale independence by default
|
||||
- Optional header-only configuration enabled with the
|
||||
`FMT_HEADER_ONLY` macro
|
||||
|
||||
See the [documentation](https://fmt.dev) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
# Examples
|
||||
|
||||
**Print to stdout** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Tevcjh))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print("Hello, world!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Format a string** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/oK8h33))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
|
||||
// s == "The answer is 42."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Format a string using positional arguments**
|
||||
([run](https://godbolt.org/z/Yn7Txe))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("I'd rather be {1} than {0}.", "right", "happy");
|
||||
// s == "I'd rather be happy than right."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Print dates and times** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/c31ExdY3W))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/chrono.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
|
||||
fmt::print("Date and time: {}\n", now);
|
||||
fmt::print("Time: {:%H:%M}\n", now);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
Date and time: 2023-12-26 19:10:31.557195597
|
||||
Time: 19:10
|
||||
|
||||
**Print a container** ([run](https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7))
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3};
|
||||
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
[1, 2, 3]
|
||||
|
||||
**Check a format string at compile time**
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because `d` is an invalid
|
||||
format specifier for a string.
|
||||
|
||||
**Write a file from a single thread**
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/os.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
|
||||
out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This can be [5 to 9 times faster than
|
||||
fprintf](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html).
|
||||
|
||||
**Print with colors and text styles**
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
#include <fmt/color.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold,
|
||||
"Hello, {}!\n", "world");
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) |
|
||||
fmt::emphasis::underline, "Olá, {}!\n", "Mundo");
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic,
|
||||
"你好{}!\n", "世界");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Output on a modern terminal with Unicode support:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
## Speed tests
|
||||
|
||||
| Library | Method | Run Time, s |
|
||||
|-------------------|---------------|-------------|
|
||||
| libc | printf | 0.91 |
|
||||
| libc++ | std::ostream | 2.49 |
|
||||
| {fmt} 9.1 | fmt::print | 0.74 |
|
||||
| Boost Format 1.80 | boost::format | 6.26 |
|
||||
| Folly Format | folly::format | 1.87 |
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, \~20% faster than
|
||||
`printf`.
|
||||
|
||||
The above results were generated by building `tinyformat_test.cpp` on
|
||||
macOS 12.6.1 with `clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT`, and
|
||||
taking the best of three runs. In the test, the format string
|
||||
`"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"` or equivalent is filled 2,000,000
|
||||
times with output sent to `/dev/null`; for further details refer to the
|
||||
[source](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc).
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than `std::ostringstream` and `sprintf` on
|
||||
IEEE754 `float` and `double` formatting
|
||||
([dtoa-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark)) and faster
|
||||
than [double-conversion](https://github.com/google/double-conversion)
|
||||
and [ryu](https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu):
|
||||
|
||||
[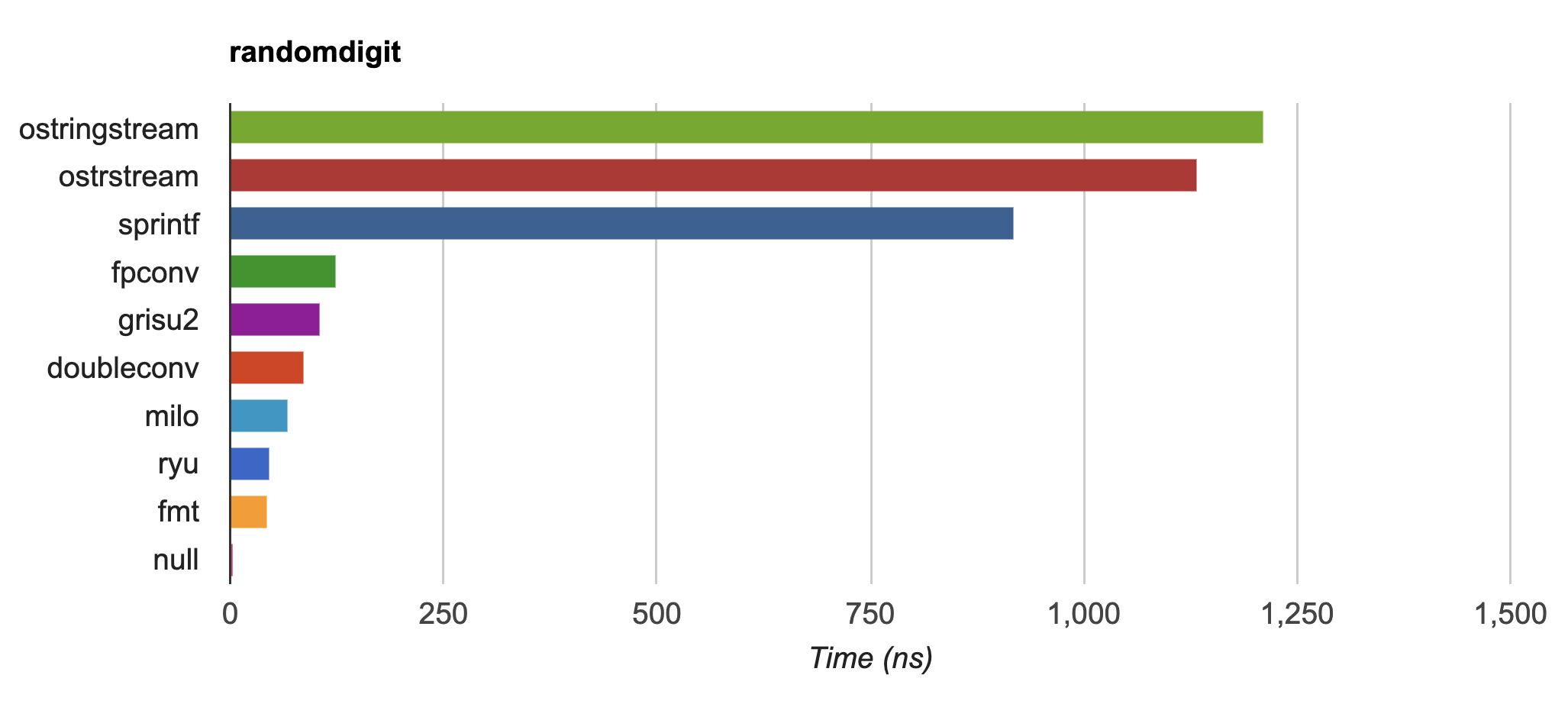](https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang12.0.html)
|
||||
|
||||
## Compile time and code bloat
|
||||
|
||||
The script
|
||||
[bloat-test.py](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/bloat-test.py)
|
||||
from [format-benchmark](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark)
|
||||
tests compile time and code bloat for nontrivial projects. It generates
|
||||
100 translation units and uses `printf()` or its alternative five times
|
||||
in each to simulate a medium-sized project. The resulting executable
|
||||
size and compile time (Apple LLVM version 8.1.0 (clang-802.0.42), macOS
|
||||
Sierra, best of three) is shown in the following tables.
|
||||
|
||||
**Optimized build (-O3)**
|
||||
|
||||
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|
||||
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
|
||||
| printf | 2.6 | 29 | 26 |
|
||||
| printf+string | 16.4 | 29 | 26 |
|
||||
| iostreams | 31.1 | 59 | 55 |
|
||||
| {fmt} | 19.0 | 37 | 34 |
|
||||
| Boost Format | 91.9 | 226 | 203 |
|
||||
| Folly Format | 115.7 | 101 | 88 |
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, {fmt} has 60% less overhead in terms of resulting binary
|
||||
code size compared to iostreams and comes pretty close to `printf`.
|
||||
Boost Format and Folly Format have the largest overheads.
|
||||
|
||||
`printf+string` is the same as `printf` but with an extra `<string>`
|
||||
include to measure the overhead of the latter.
|
||||
|
||||
**Non-optimized build**
|
||||
|
||||
| Method | Compile Time, s | Executable size, KiB | Stripped size, KiB |
|
||||
|---------------|-----------------|----------------------|--------------------|
|
||||
| printf | 2.2 | 33 | 30 |
|
||||
| printf+string | 16.0 | 33 | 30 |
|
||||
| iostreams | 28.3 | 56 | 52 |
|
||||
| {fmt} | 18.2 | 59 | 50 |
|
||||
| Boost Format | 54.1 | 365 | 303 |
|
||||
| Folly Format | 79.9 | 445 | 430 |
|
||||
|
||||
`libc`, `lib(std)c++`, and `libfmt` are all linked as shared libraries
|
||||
to compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a
|
||||
header-only library so it doesn\'t provide any linkage options.
|
||||
|
||||
## Running the tests
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to [Building the
|
||||
library](https://fmt.dev/latest/usage.html#building-the-library) for
|
||||
instructions on how to build the library and run the unit tests.
|
||||
|
||||
Benchmarks reside in a separate repository,
|
||||
[format-benchmarks](https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark), so to
|
||||
run the benchmarks you first need to clone this repository and generate
|
||||
Makefiles with CMake:
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark.git
|
||||
$ cd format-benchmark
|
||||
$ cmake .
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can run the speed test:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make speed-test
|
||||
|
||||
or the bloat test:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make bloat-test
|
||||
|
||||
# Migrating code
|
||||
|
||||
[clang-tidy](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/) v17 (not yet
|
||||
released) provides the
|
||||
[modernize-use-std-print](https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html)
|
||||
check that is capable of converting occurrences of `printf` and
|
||||
`fprintf` to `fmt::print` if configured to do so. (By default it
|
||||
converts to `std::print`.)
|
||||
|
||||
# Notable projects using this library
|
||||
|
||||
- [0 A.D.](https://play0ad.com/): a free, open-source, cross-platform
|
||||
real-time strategy game
|
||||
- [AMPL/MP](https://github.com/ampl/mp): an open-source library for
|
||||
mathematical programming
|
||||
- [Apple's FoundationDB](https://github.com/apple/foundationdb): an open-source,
|
||||
distributed, transactional key-value store
|
||||
- [Aseprite](https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite): animated sprite
|
||||
editor & pixel art tool
|
||||
- [AvioBook](https://www.aviobook.aero/en): a comprehensive aircraft
|
||||
operations suite
|
||||
- [Blizzard Battle.net](https://battle.net/): an online gaming
|
||||
platform
|
||||
- [Celestia](https://celestia.space/): real-time 3D visualization of
|
||||
space
|
||||
- [Ceph](https://ceph.com/): a scalable distributed storage system
|
||||
- [ccache](https://ccache.dev/): a compiler cache
|
||||
- [ClickHouse](https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse): an
|
||||
analytical database management system
|
||||
- [Contour](https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/): a modern
|
||||
terminal emulator
|
||||
- [CUAUV](https://cuauv.org/): Cornell University\'s autonomous
|
||||
underwater vehicle
|
||||
- [Drake](https://drake.mit.edu/): a planning, control, and analysis
|
||||
toolbox for nonlinear dynamical systems (MIT)
|
||||
- [Envoy](https://lyft.github.io/envoy/): C++ L7 proxy and
|
||||
communication bus (Lyft)
|
||||
- [FiveM](https://fivem.net/): a modification framework for GTA V
|
||||
- [fmtlog](https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog): a performant
|
||||
fmtlib-style logging library with latency in nanoseconds
|
||||
- [Folly](https://github.com/facebook/folly): Facebook open-source
|
||||
library
|
||||
- [GemRB](https://gemrb.org/): a portable open-source implementation
|
||||
of Bioware's Infinity Engine
|
||||
- [Grand Mountain
|
||||
Adventure](https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/):
|
||||
a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game
|
||||
- [HarpyWar/pvpgn](https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server): Player vs
|
||||
Player Gaming Network with tweaks
|
||||
- [KBEngine](https://github.com/kbengine/kbengine): an open-source
|
||||
MMOG server engine
|
||||
- [Keypirinha](https://keypirinha.com/): a semantic launcher for
|
||||
Windows
|
||||
- [Kodi](https://kodi.tv/) (formerly xbmc): home theater software
|
||||
- [Knuth](https://kth.cash/): high-performance Bitcoin full-node
|
||||
- [libunicode](https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/): a
|
||||
modern C++17 Unicode library
|
||||
- [MariaDB](https://mariadb.org/): relational database management
|
||||
system
|
||||
- [Microsoft Verona](https://github.com/microsoft/verona): research
|
||||
programming language for concurrent ownership
|
||||
- [MongoDB](https://mongodb.com/): distributed document database
|
||||
- [MongoDB Smasher](https://github.com/duckie/mongo_smasher): a small
|
||||
tool to generate randomized datasets
|
||||
- [OpenSpace](https://openspaceproject.com/): an open-source
|
||||
astrovisualization framework
|
||||
- [PenUltima Online (POL)](https://www.polserver.com/): an MMO server,
|
||||
compatible with most Ultima Online clients
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch): an open-source
|
||||
machine learning library
|
||||
- [quasardb](https://www.quasardb.net/): a distributed,
|
||||
high-performance, associative database
|
||||
- [Quill](https://github.com/odygrd/quill): asynchronous low-latency
|
||||
logging library
|
||||
- [QKW](https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw): generalizing aliasing to
|
||||
simplify navigation, and executing complex multi-line terminal
|
||||
command sequences
|
||||
- [redis-cerberus](https://github.com/HunanTV/redis-cerberus): a Redis
|
||||
cluster proxy
|
||||
- [redpanda](https://vectorized.io/redpanda): a 10x faster Kafka®
|
||||
replacement for mission-critical systems written in C++
|
||||
- [rpclib](http://rpclib.net/): a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and
|
||||
client library
|
||||
- [Salesforce Analytics
|
||||
Cloud](https://www.salesforce.com/analytics-cloud/overview/):
|
||||
business intelligence software
|
||||
- [Scylla](https://www.scylladb.com/): a Cassandra-compatible NoSQL
|
||||
data store that can handle 1 million transactions per second on a
|
||||
single server
|
||||
- [Seastar](http://www.seastar-project.org/): an advanced, open-source
|
||||
C++ framework for high-performance server applications on modern
|
||||
hardware
|
||||
- [spdlog](https://github.com/gabime/spdlog): super fast C++ logging
|
||||
library
|
||||
- [Stellar](https://www.stellar.org/): financial platform
|
||||
- [Touch Surgery](https://www.touchsurgery.com/): surgery simulator
|
||||
- [TrinityCore](https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore):
|
||||
open-source MMORPG framework
|
||||
- [🐙 userver framework](https://userver.tech/): open-source
|
||||
asynchronous framework with a rich set of abstractions and database
|
||||
drivers
|
||||
- [Windows Terminal](https://github.com/microsoft/terminal): the new
|
||||
Windows terminal
|
||||
|
||||
[More\...](https://github.com/search?q=fmtlib&type=Code)
|
||||
|
||||
If you are aware of other projects using this library, please let me
|
||||
know by [email](mailto:victor.zverovich@gmail.com) or by submitting an
|
||||
[issue](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
# Motivation
|
||||
|
||||
So why yet another formatting library?
|
||||
|
||||
There are plenty of methods for doing this task, from standard ones like
|
||||
the printf family of function and iostreams to Boost Format and
|
||||
FastFormat libraries. The reason for creating a new library is that
|
||||
every existing solution that I found either had serious issues or
|
||||
didn\'t provide all the features I needed.
|
||||
|
||||
## printf
|
||||
|
||||
The good thing about `printf` is that it is pretty fast and readily
|
||||
available being a part of the C standard library. The main drawback is
|
||||
that it doesn\'t support user-defined types. `printf` also has safety
|
||||
issues although they are somewhat mitigated with [\_\_attribute\_\_
|
||||
((format (printf,
|
||||
\...))](https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html) in
|
||||
GCC. There is a POSIX extension that adds positional arguments required
|
||||
for
|
||||
[i18n](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internationalization_and_localization)
|
||||
to `printf` but it is not a part of C99 and may not be available on some
|
||||
platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
## iostreams
|
||||
|
||||
The main issue with iostreams is best illustrated with an example:
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
std::cout << std::setprecision(2) << std::fixed << 1.23456 << "\n";
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is a lot of typing compared to printf:
|
||||
|
||||
``` c++
|
||||
printf("%.2f\n", 1.23456);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Matthew Wilson, the author of FastFormat, called this \"chevron hell\".
|
||||
iostreams don\'t support positional arguments by design.
|
||||
|
||||
The good part is that iostreams support user-defined types and are safe
|
||||
although error handling is awkward.
|
||||
|
||||
## Boost Format
|
||||
|
||||
This is a very powerful library that supports both `printf`-like format
|
||||
strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance.
|
||||
According to various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods
|
||||
considered here. Boost Format also has excessive build times and severe
|
||||
code bloat issues (see [Benchmarks](#benchmarks)).
|
||||
|
||||
## FastFormat
|
||||
|
||||
This is an interesting library that is fast, safe, and has positional
|
||||
arguments. However, it has significant limitations, citing its author:
|
||||
|
||||
> Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the
|
||||
> current design are:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - Leading zeros (or any other non-space padding)
|
||||
> - Octal/hexadecimal encoding
|
||||
> - Runtime width/alignment specification
|
||||
|
||||
It is also quite big and has a heavy dependency, STLSoft, which might be
|
||||
too restrictive for using it in some projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## Boost Spirit.Karma
|
||||
|
||||
This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for
|
||||
completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing
|
||||
verbatim text with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on
|
||||
integer formatting than `fmt::format_to` with format string compilation
|
||||
on Karma\'s own benchmark, see [Converting a hundred million integers to
|
||||
strings per
|
||||
second](http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html).
|
||||
|
||||
# License
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is distributed under the MIT
|
||||
[license](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE).
|
||||
|
||||
# Documentation License
|
||||
|
||||
The [Format String Syntax](https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html) section
|
||||
in the documentation is based on the one from Python [string module
|
||||
documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string).
|
||||
For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python
|
||||
Software Foundation license available in
|
||||
[doc/python-license.txt](https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt).
|
||||
It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}.
|
||||
|
||||
# Maintainers
|
||||
|
||||
The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich
|
||||
([vitaut](https://github.com/vitaut)) with contributions from many other
|
||||
people. See
|
||||
[Contributors](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors) and
|
||||
[Releases](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases) for some of the
|
||||
names. Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned
|
||||
incorrectly and we\'ll make it right.
|
||||
|
||||
# Security Policy
|
||||
|
||||
To report a security issue, please disclose it at [security
|
||||
advisory](https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/security/advisories/new).
|
||||
|
||||
This project is maintained by a team of volunteers on a
|
||||
reasonable-effort basis. As such, please give us at least 90 days to
|
||||
work on a fix before public exposure.
|
||||
545
README.rst
545
README.rst
@ -1,545 +0,0 @@
|
||||
.. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/
|
||||
576385/156254208-f5b743a9-88cf-439d-b0c0-923d53e8d551.png
|
||||
:width: 25%
|
||||
:alt: {fmt}
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/workflows/linux/badge.svg
|
||||
:target: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Alinux
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/workflows/macos/badge.svg
|
||||
:target: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Amacos
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/workflows/windows/badge.svg
|
||||
:target: https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/actions?query=workflow%3Awindows
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://oss-fuzz-build-logs.storage.googleapis.com/badges/fmt.svg
|
||||
:alt: fmt is continuously fuzzed at oss-fuzz
|
||||
:target: https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?\
|
||||
colspec=ID%20Type%20Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20\
|
||||
Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/stackoverflow-fmt-blue.svg
|
||||
:alt: Ask questions at StackOverflow with the tag fmt
|
||||
:target: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://api.securityscorecards.dev/projects/github.com/fmtlib/fmt/badge
|
||||
:target: https://securityscorecards.dev/viewer/?uri=github.com/fmtlib/fmt
|
||||
|
||||
**{fmt}** is an open-source formatting library providing a fast and safe
|
||||
alternative to C stdio and C++ iostreams.
|
||||
|
||||
If you like this project, please consider donating to one of the funds that
|
||||
help victims of the war in Ukraine: https://www.stopputin.net/.
|
||||
|
||||
`Documentation <https://fmt.dev>`__
|
||||
|
||||
`Cheat Sheets <https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/libs/fmt.html>`__
|
||||
|
||||
Q&A: ask questions on `StackOverflow with the tag fmt
|
||||
<https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fmt>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
Try {fmt} in `Compiler Explorer <https://godbolt.org/z/Eq5763>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
Features
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
* Simple `format API <https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html>`_ with positional arguments
|
||||
for localization
|
||||
* Implementation of `C++20 std::format
|
||||
<https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/format>`__
|
||||
* `Format string syntax <https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html>`_ similar to Python's
|
||||
`format <https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#str.format>`_
|
||||
* Fast IEEE 754 floating-point formatter with correct rounding, shortness and
|
||||
round-trip guarantees using the `Dragonbox <https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox>`_
|
||||
algorithm
|
||||
* Portable Unicode support
|
||||
* Safe `printf implementation
|
||||
<https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#printf-formatting>`_ including the POSIX
|
||||
extension for positional arguments
|
||||
* Extensibility: `support for user-defined types
|
||||
<https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#formatting-user-defined-types>`_
|
||||
* High performance: faster than common standard library implementations of
|
||||
``(s)printf``, iostreams, ``to_string`` and ``to_chars``, see `Speed tests`_
|
||||
and `Converting a hundred million integers to strings per second
|
||||
<http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html>`_
|
||||
* Small code size both in terms of source code with the minimum configuration
|
||||
consisting of just three files, ``core.h``, ``format.h`` and ``format-inl.h``,
|
||||
and compiled code; see `Compile time and code bloat`_
|
||||
* Reliability: the library has an extensive set of `tests
|
||||
<https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/tree/master/test>`_ and is `continuously fuzzed
|
||||
<https://bugs.chromium.org/p/oss-fuzz/issues/list?colspec=ID%20Type%20
|
||||
Component%20Status%20Proj%20Reported%20Owner%20Summary&q=proj%3Dfmt&can=1>`_
|
||||
* Safety: the library is fully type-safe, errors in format strings can be
|
||||
reported at compile time, automatic memory management prevents buffer overflow
|
||||
errors
|
||||
* Ease of use: small self-contained code base, no external dependencies,
|
||||
permissive MIT `license
|
||||
<https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst>`_
|
||||
* `Portability <https://fmt.dev/latest/index.html#portability>`_ with
|
||||
consistent output across platforms and support for older compilers
|
||||
* Clean warning-free codebase even on high warning levels such as
|
||||
``-Wall -Wextra -pedantic``
|
||||
* Locale independence by default
|
||||
* Optional header-only configuration enabled with the ``FMT_HEADER_ONLY`` macro
|
||||
|
||||
See the `documentation <https://fmt.dev>`_ for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
**Print to stdout** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/Tevcjh>`_)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print("Hello, world!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
**Format a string** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/oK8h33>`_)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("The answer is {}.", 42);
|
||||
// s == "The answer is 42."
|
||||
|
||||
**Format a string using positional arguments** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/Yn7Txe>`_)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("I'd rather be {1} than {0}.", "right", "happy");
|
||||
// s == "I'd rather be happy than right."
|
||||
|
||||
**Print chrono durations** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/K8s4Mc>`_)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/chrono.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals;
|
||||
fmt::print("Default format: {} {}\n", 42s, 100ms);
|
||||
fmt::print("strftime-like format: {:%H:%M:%S}\n", 3h + 15min + 30s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Output::
|
||||
|
||||
Default format: 42s 100ms
|
||||
strftime-like format: 03:15:30
|
||||
|
||||
**Print a container** (`run <https://godbolt.org/z/MxM1YqjE7>`_)
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3};
|
||||
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Output::
|
||||
|
||||
[1, 2, 3]
|
||||
|
||||
**Check a format string at compile time**
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("{:d}", "I am not a number");
|
||||
|
||||
This gives a compile-time error in C++20 because ``d`` is an invalid format
|
||||
specifier for a string.
|
||||
|
||||
**Write a file from a single thread**
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/os.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
auto out = fmt::output_file("guide.txt");
|
||||
out.print("Don't {}", "Panic");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
This can be `5 to 9 times faster than fprintf
|
||||
<http://www.zverovich.net/2020/08/04/optimal-file-buffer-size.html>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
**Print with colors and text styles**
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/color.h>
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::crimson) | fmt::emphasis::bold,
|
||||
"Hello, {}!\n", "world");
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::floral_white) | bg(fmt::color::slate_gray) |
|
||||
fmt::emphasis::underline, "Hello, {}!\n", "мир");
|
||||
fmt::print(fg(fmt::color::steel_blue) | fmt::emphasis::italic,
|
||||
"Hello, {}!\n", "世界");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Output on a modern terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/
|
||||
576385/88485597-d312f600-cf2b-11ea-9cbe-61f535a86e28.png
|
||||
|
||||
Benchmarks
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Speed tests
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
================= ============= ===========
|
||||
Library Method Run Time, s
|
||||
================= ============= ===========
|
||||
libc printf 0.91
|
||||
libc++ std::ostream 2.49
|
||||
{fmt} 9.1 fmt::print 0.74
|
||||
Boost Format 1.80 boost::format 6.26
|
||||
Folly Format folly::format 1.87
|
||||
================= ============= ===========
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is the fastest of the benchmarked methods, ~20% faster than ``printf``.
|
||||
|
||||
The above results were generated by building ``tinyformat_test.cpp`` on macOS
|
||||
12.6.1 with ``clang++ -O3 -DNDEBUG -DSPEED_TEST -DHAVE_FORMAT``, and taking the
|
||||
best of three runs. In the test, the format string ``"%0.10f:%04d:%+g:%s:%p:%c:%%\n"``
|
||||
or equivalent is filled 2,000,000 times with output sent to ``/dev/null``; for
|
||||
further details refer to the `source
|
||||
<https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/src/tinyformat-test.cc>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is up to 20-30x faster than ``std::ostringstream`` and ``sprintf`` on
|
||||
IEEE754 ``float`` and ``double`` formatting (`dtoa-benchmark <https://github.com/fmtlib/dtoa-benchmark>`_)
|
||||
and faster than `double-conversion <https://github.com/google/double-conversion>`_ and
|
||||
`ryu <https://github.com/ulfjack/ryu>`_:
|
||||
|
||||
.. image:: https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/576385/
|
||||
95684665-11719600-0ba8-11eb-8e5b-972ff4e49428.png
|
||||
:target: https://fmt.dev/unknown_mac64_clang12.0.html
|
||||
|
||||
Compile time and code bloat
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
The script `bloat-test.py
|
||||
<https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark/blob/master/bloat-test.py>`_
|
||||
from `format-benchmark <https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark>`_
|
||||
tests compile time and code bloat for nontrivial projects.
|
||||
It generates 100 translation units and uses ``printf()`` or its alternative
|
||||
five times in each to simulate a medium-sized project. The resulting
|
||||
executable size and compile time (Apple LLVM version 8.1.0 (clang-802.0.42),
|
||||
macOS Sierra, best of three) is shown in the following tables.
|
||||
|
||||
**Optimized build (-O3)**
|
||||
|
||||
============= =============== ==================== ==================
|
||||
Method Compile Time, s Executable size, KiB Stripped size, KiB
|
||||
============= =============== ==================== ==================
|
||||
printf 2.6 29 26
|
||||
printf+string 16.4 29 26
|
||||
iostreams 31.1 59 55
|
||||
{fmt} 19.0 37 34
|
||||
Boost Format 91.9 226 203
|
||||
Folly Format 115.7 101 88
|
||||
============= =============== ==================== ==================
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, {fmt} has 60% less overhead in terms of resulting binary code
|
||||
size compared to iostreams and comes pretty close to ``printf``. Boost Format
|
||||
and Folly Format have the largest overheads.
|
||||
|
||||
``printf+string`` is the same as ``printf`` but with an extra ``<string>``
|
||||
include to measure the overhead of the latter.
|
||||
|
||||
**Non-optimized build**
|
||||
|
||||
============= =============== ==================== ==================
|
||||
Method Compile Time, s Executable size, KiB Stripped size, KiB
|
||||
============= =============== ==================== ==================
|
||||
printf 2.2 33 30
|
||||
printf+string 16.0 33 30
|
||||
iostreams 28.3 56 52
|
||||
{fmt} 18.2 59 50
|
||||
Boost Format 54.1 365 303
|
||||
Folly Format 79.9 445 430
|
||||
============= =============== ==================== ==================
|
||||
|
||||
``libc``, ``lib(std)c++``, and ``libfmt`` are all linked as shared libraries to
|
||||
compare formatting function overhead only. Boost Format is a
|
||||
header-only library so it doesn't provide any linkage options.
|
||||
|
||||
Running the tests
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to `Building the library`__ for instructions on how to build
|
||||
the library and run the unit tests.
|
||||
|
||||
__ https://fmt.dev/latest/usage.html#building-the-library
|
||||
|
||||
Benchmarks reside in a separate repository,
|
||||
`format-benchmarks <https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark>`_,
|
||||
so to run the benchmarks you first need to clone this repository and
|
||||
generate Makefiles with CMake::
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/fmtlib/format-benchmark.git
|
||||
$ cd format-benchmark
|
||||
$ cmake .
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can run the speed test::
|
||||
|
||||
$ make speed-test
|
||||
|
||||
or the bloat test::
|
||||
|
||||
$ make bloat-test
|
||||
|
||||
Migrating code
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
`clang-tidy <https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/>`_ v17 (not yet
|
||||
released) provides the `modernize-use-std-print
|
||||
<https://clang.llvm.org/extra/clang-tidy/checks/modernize/use-std-print.html>`_
|
||||
check that is capable of converting occurrences of ``printf`` and
|
||||
``fprintf`` to ``fmt::print`` if configured to do so. (By default it
|
||||
converts to ``std::print``.)
|
||||
|
||||
Projects using this library
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
* `0 A.D. <https://play0ad.com/>`_: a free, open-source, cross-platform
|
||||
real-time strategy game
|
||||
|
||||
* `AMPL/MP <https://github.com/ampl/mp>`_:
|
||||
an open-source library for mathematical programming
|
||||
|
||||
* `Aseprite <https://github.com/aseprite/aseprite>`_:
|
||||
animated sprite editor & pixel art tool
|
||||
|
||||
* `AvioBook <https://www.aviobook.aero/en>`_: a comprehensive aircraft
|
||||
operations suite
|
||||
|
||||
* `Blizzard Battle.net <https://battle.net/>`_: an online gaming platform
|
||||
|
||||
* `Celestia <https://celestia.space/>`_: real-time 3D visualization of space
|
||||
|
||||
* `Ceph <https://ceph.com/>`_: a scalable distributed storage system
|
||||
|
||||
* `ccache <https://ccache.dev/>`_: a compiler cache
|
||||
|
||||
* `ClickHouse <https://github.com/ClickHouse/ClickHouse>`_: an analytical database
|
||||
management system
|
||||
|
||||
* `Contour <https://github.com/contour-terminal/contour/>`_: a modern terminal emulator
|
||||
|
||||
* `CUAUV <https://cuauv.org/>`_: Cornell University's autonomous underwater
|
||||
vehicle
|
||||
|
||||
* `Drake <https://drake.mit.edu/>`_: a planning, control, and analysis toolbox
|
||||
for nonlinear dynamical systems (MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
* `Envoy <https://lyft.github.io/envoy/>`_: C++ L7 proxy and communication bus
|
||||
(Lyft)
|
||||
|
||||
* `FiveM <https://fivem.net/>`_: a modification framework for GTA V
|
||||
|
||||
* `fmtlog <https://github.com/MengRao/fmtlog>`_: a performant fmtlib-style
|
||||
logging library with latency in nanoseconds
|
||||
|
||||
* `Folly <https://github.com/facebook/folly>`_: Facebook open-source library
|
||||
|
||||
* `GemRB <https://gemrb.org/>`_: a portable open-source implementation of
|
||||
Bioware’s Infinity Engine
|
||||
|
||||
* `Grand Mountain Adventure
|
||||
<https://store.steampowered.com/app/1247360/Grand_Mountain_Adventure/>`_:
|
||||
a beautiful open-world ski & snowboarding game
|
||||
|
||||
* `HarpyWar/pvpgn <https://github.com/pvpgn/pvpgn-server>`_:
|
||||
Player vs Player Gaming Network with tweaks
|
||||
|
||||
* `KBEngine <https://github.com/kbengine/kbengine>`_: an open-source MMOG server
|
||||
engine
|
||||
|
||||
* `Keypirinha <https://keypirinha.com/>`_: a semantic launcher for Windows
|
||||
|
||||
* `Kodi <https://kodi.tv/>`_ (formerly xbmc): home theater software
|
||||
|
||||
* `Knuth <https://kth.cash/>`_: high-performance Bitcoin full-node
|
||||
|
||||
* `libunicode <https://github.com/contour-terminal/libunicode/>`_: a modern C++17 Unicode library
|
||||
|
||||
* `MariaDB <https://mariadb.org/>`_: relational database management system
|
||||
|
||||
* `Microsoft Verona <https://github.com/microsoft/verona>`_:
|
||||
research programming language for concurrent ownership
|
||||
|
||||
* `MongoDB <https://mongodb.com/>`_: distributed document database
|
||||
|
||||
* `MongoDB Smasher <https://github.com/duckie/mongo_smasher>`_: a small tool to
|
||||
generate randomized datasets
|
||||
|
||||
* `OpenSpace <https://openspaceproject.com/>`_: an open-source
|
||||
astrovisualization framework
|
||||
|
||||
* `PenUltima Online (POL) <https://www.polserver.com/>`_:
|
||||
an MMO server, compatible with most Ultima Online clients
|
||||
|
||||
* `PyTorch <https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch>`_: an open-source machine
|
||||
learning library
|
||||
|
||||
* `quasardb <https://www.quasardb.net/>`_: a distributed, high-performance,
|
||||
associative database
|
||||
|
||||
* `Quill <https://github.com/odygrd/quill>`_: asynchronous low-latency logging library
|
||||
|
||||
* `QKW <https://github.com/ravijanjam/qkw>`_: generalizing aliasing to simplify
|
||||
navigation, and executing complex multi-line terminal command sequences
|
||||
|
||||
* `redis-cerberus <https://github.com/HunanTV/redis-cerberus>`_: a Redis cluster
|
||||
proxy
|
||||
|
||||
* `redpanda <https://vectorized.io/redpanda>`_: a 10x faster Kafka® replacement
|
||||
for mission-critical systems written in C++
|
||||
|
||||
* `rpclib <http://rpclib.net/>`_: a modern C++ msgpack-RPC server and client
|
||||
library
|
||||
|
||||
* `Salesforce Analytics Cloud
|
||||
<https://www.salesforce.com/analytics-cloud/overview/>`_:
|
||||
business intelligence software
|
||||
|
||||
* `Scylla <https://www.scylladb.com/>`_: a Cassandra-compatible NoSQL data store
|
||||
that can handle 1 million transactions per second on a single server
|
||||
|
||||
* `Seastar <http://www.seastar-project.org/>`_: an advanced, open-source C++
|
||||
framework for high-performance server applications on modern hardware
|
||||
|
||||
* `spdlog <https://github.com/gabime/spdlog>`_: super fast C++ logging library
|
||||
|
||||
* `Stellar <https://www.stellar.org/>`_: financial platform
|
||||
|
||||
* `Touch Surgery <https://www.touchsurgery.com/>`_: surgery simulator
|
||||
|
||||
* `TrinityCore <https://github.com/TrinityCore/TrinityCore>`_: open-source
|
||||
MMORPG framework
|
||||
|
||||
* `🐙 userver framework <https://userver.tech/>`_: open-source asynchronous
|
||||
framework with a rich set of abstractions and database drivers
|
||||
|
||||
* `Windows Terminal <https://github.com/microsoft/terminal>`_: the new Windows
|
||||
terminal
|
||||
|
||||
`More... <https://github.com/search?q=fmtlib&type=Code>`_
|
||||
|
||||
If you are aware of other projects using this library, please let me know
|
||||
by `email <mailto:victor.zverovich@gmail.com>`_ or by submitting an
|
||||
`issue <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
Motivation
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
So why yet another formatting library?
|
||||
|
||||
There are plenty of methods for doing this task, from standard ones like
|
||||
the printf family of function and iostreams to Boost Format and FastFormat
|
||||
libraries. The reason for creating a new library is that every existing
|
||||
solution that I found either had serious issues or didn't provide
|
||||
all the features I needed.
|
||||
|
||||
printf
|
||||
~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
The good thing about ``printf`` is that it is pretty fast and readily available
|
||||
being a part of the C standard library. The main drawback is that it
|
||||
doesn't support user-defined types. ``printf`` also has safety issues although
|
||||
they are somewhat mitigated with `__attribute__ ((format (printf, ...))
|
||||
<https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html>`_ in GCC.
|
||||
There is a POSIX extension that adds positional arguments required for
|
||||
`i18n <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internationalization_and_localization>`_
|
||||
to ``printf`` but it is not a part of C99 and may not be available on some
|
||||
platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
iostreams
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
The main issue with iostreams is best illustrated with an example:
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout << std::setprecision(2) << std::fixed << 1.23456 << "\n";
|
||||
|
||||
which is a lot of typing compared to printf:
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
printf("%.2f\n", 1.23456);
|
||||
|
||||
Matthew Wilson, the author of FastFormat, called this "chevron hell". iostreams
|
||||
don't support positional arguments by design.
|
||||
|
||||
The good part is that iostreams support user-defined types and are safe although
|
||||
error handling is awkward.
|
||||
|
||||
Boost Format
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This is a very powerful library that supports both ``printf``-like format
|
||||
strings and positional arguments. Its main drawback is performance. According to
|
||||
various benchmarks, it is much slower than other methods considered here. Boost
|
||||
Format also has excessive build times and severe code bloat issues (see
|
||||
`Benchmarks`_).
|
||||
|
||||
FastFormat
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This is an interesting library that is fast, safe, and has positional arguments.
|
||||
However, it has significant limitations, citing its author:
|
||||
|
||||
Three features that have no hope of being accommodated within the
|
||||
current design are:
|
||||
|
||||
* Leading zeros (or any other non-space padding)
|
||||
* Octal/hexadecimal encoding
|
||||
* Runtime width/alignment specification
|
||||
|
||||
It is also quite big and has a heavy dependency, STLSoft, which might be too
|
||||
restrictive for using it in some projects.
|
||||
|
||||
Boost Spirit.Karma
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This is not a formatting library but I decided to include it here for
|
||||
completeness. As iostreams, it suffers from the problem of mixing verbatim text
|
||||
with arguments. The library is pretty fast, but slower on integer formatting
|
||||
than ``fmt::format_to`` with format string compilation on Karma's own benchmark,
|
||||
see `Converting a hundred million integers to strings per second
|
||||
<http://www.zverovich.net/2020/06/13/fast-int-to-string-revisited.html>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
License
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
{fmt} is distributed under the MIT `license
|
||||
<https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/blob/master/LICENSE.rst>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation License
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The `Format String Syntax <https://fmt.dev/latest/syntax.html>`_
|
||||
section in the documentation is based on the one from Python `string module
|
||||
documentation <https://docs.python.org/3/library/string.html#module-string>`_.
|
||||
For this reason, the documentation is distributed under the Python Software
|
||||
Foundation license available in `doc/python-license.txt
|
||||
<https://raw.github.com/fmtlib/fmt/master/doc/python-license.txt>`_.
|
||||
It only applies if you distribute the documentation of {fmt}.
|
||||
|
||||
Maintainers
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
The {fmt} library is maintained by Victor Zverovich (`vitaut
|
||||
<https://github.com/vitaut>`_) with contributions from many other people.
|
||||
See `Contributors <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/graphs/contributors>`_ and
|
||||
`Releases <https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/releases>`_ for some of the names.
|
||||
Let us know if your contribution is not listed or mentioned incorrectly and
|
||||
we'll make it right.
|
||||
12
doc/_static/bootstrap.min.js
vendored
12
doc/_static/bootstrap.min.js
vendored
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
137
doc/api.rst
137
doc/api.rst
@ -49,6 +49,10 @@ checked at compile time in C++20. To pass a runtime format string wrap it in
|
||||
|
||||
*args* is an argument list representing objects to be formatted.
|
||||
|
||||
I/O errors are reported as `std::system_error
|
||||
<https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/error/system_error>`_ exceptions unless
|
||||
specified otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _format:
|
||||
|
||||
.. doxygenfunction:: format(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) -> std::string
|
||||
@ -104,7 +108,7 @@ with the same format specifiers. The ``format_as`` function should take an
|
||||
object of your type and return an object of a formattable type. It should be
|
||||
defined in the same namespace as your type.
|
||||
|
||||
Example (https://godbolt.org/z/r7vvGE1v7)::
|
||||
Example (https://godbolt.org/z/nvME4arz8)::
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -119,67 +123,13 @@ Example (https://godbolt.org/z/r7vvGE1v7)::
|
||||
fmt::print("{}\n", kevin_namespacy::film::se7en); // prints "7"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Using the specialization API is more complex but gives you full control over
|
||||
parsing and formatting. To use this method specialize the ``formatter`` struct
|
||||
template for your type and implement ``parse`` and ``format`` methods.
|
||||
For example::
|
||||
Using specialization is more complex but gives you full control over parsing and
|
||||
formatting. To use this method specialize the ``formatter`` struct template for
|
||||
your type and implement ``parse`` and ``format`` methods.
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
|
||||
struct point {
|
||||
double x, y;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct fmt::formatter<point> {
|
||||
// Presentation format: 'f' - fixed, 'e' - exponential.
|
||||
char presentation = 'f';
|
||||
|
||||
// Parses format specifications of the form ['f' | 'e'].
|
||||
constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> format_parse_context::iterator {
|
||||
// [ctx.begin(), ctx.end()) is a character range that contains a part of
|
||||
// the format string starting from the format specifications to be parsed,
|
||||
// e.g. in
|
||||
//
|
||||
// fmt::format("{:f} - point of interest", point{1, 2});
|
||||
//
|
||||
// the range will contain "f} - point of interest". The formatter should
|
||||
// parse specifiers until '}' or the end of the range. In this example
|
||||
// the formatter should parse the 'f' specifier and return an iterator
|
||||
// pointing to '}'.
|
||||
|
||||
// Please also note that this character range may be empty, in case of
|
||||
// the "{}" format string, so therefore you should check ctx.begin()
|
||||
// for equality with ctx.end().
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse the presentation format and store it in the formatter:
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it != end && (*it == 'f' || *it == 'e')) presentation = *it++;
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if reached the end of the range:
|
||||
if (it != end && *it != '}') throw_format_error("invalid format");
|
||||
|
||||
// Return an iterator past the end of the parsed range:
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Formats the point p using the parsed format specification (presentation)
|
||||
// stored in this formatter.
|
||||
auto format(const point& p, format_context& ctx) const -> format_context::iterator {
|
||||
// ctx.out() is an output iterator to write to.
|
||||
return presentation == 'f'
|
||||
? fmt::format_to(ctx.out(), "({:.1f}, {:.1f})", p.x, p.y)
|
||||
: fmt::format_to(ctx.out(), "({:.1e}, {:.1e})", p.x, p.y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can pass objects of type ``point`` to any formatting function::
|
||||
|
||||
point p = {1, 2};
|
||||
std::string s = fmt::format("{:f}", p);
|
||||
// s == "(1.0, 2.0)"
|
||||
|
||||
You can also reuse existing formatters via inheritance or composition, for
|
||||
example::
|
||||
The recommended way of defining a formatter is by reusing an existing one via
|
||||
inheritance or composition. This way you can support standard format specifiers
|
||||
without implementing them yourself. For example::
|
||||
|
||||
// color.h:
|
||||
#include <fmt/core.h>
|
||||
@ -207,9 +157,9 @@ example::
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Note that ``formatter<string_view>::format`` is defined in ``fmt/format.h`` so
|
||||
it has to be included in the source file.
|
||||
Since ``parse`` is inherited from ``formatter<string_view>`` it will recognize
|
||||
all string format specifications, for example
|
||||
it has to be included in the source file. Since ``parse`` is inherited from
|
||||
``formatter<string_view>`` it will recognize all string format specifications,
|
||||
for example
|
||||
|
||||
.. code-block:: c++
|
||||
|
||||
@ -217,6 +167,64 @@ all string format specifications, for example
|
||||
|
||||
will return ``" blue"``.
|
||||
|
||||
The experimental ``nested_formatter`` provides an easy way of applying a
|
||||
formatter to one or more subobjects.
|
||||
|
||||
For example::
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fmt/format.h>
|
||||
|
||||
struct point {
|
||||
double x, y;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
struct fmt::formatter<point> : nested_formatter<double> {
|
||||
auto format(point p, format_context& ctx) const {
|
||||
return write_padded(ctx, [=](auto out) {
|
||||
return format_to(out, "({}, {})", nested(p.x), nested(p.y));
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
int main() {
|
||||
fmt::print("[{:>20.2f}]", point{1, 2});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
prints::
|
||||
|
||||
[ (1.00, 2.00)]
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that fill, align and width are applied to the whole object which is the
|
||||
recommended behavior while the remaining specifiers apply to elements.
|
||||
|
||||
In general the formatter has the following form::
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct fmt::formatter<T> {
|
||||
// Parses format specifiers and stores them in the formatter.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// [ctx.begin(), ctx.end()) is a, possibly empty, character range that
|
||||
// contains a part of the format string starting from the format
|
||||
// specifications to be parsed, e.g. in
|
||||
//
|
||||
// fmt::format("{:f} continued", ...);
|
||||
//
|
||||
// the range will contain "f} continued". The formatter should parse
|
||||
// specifiers until '}' or the end of the range. In this example the
|
||||
// formatter should parse the 'f' specifier and return an iterator
|
||||
// pointing to '}'.
|
||||
constexpr auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx)
|
||||
-> format_parse_context::iterator;
|
||||
|
||||
// Formats value using the parsed format specification stored in this
|
||||
// formatter and writes the output to ctx.out().
|
||||
auto format(const T& value, format_context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> format_context::iterator;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to at least support fill, align and width that apply to the
|
||||
whole object and have the same semantics as in standard formatters.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also write a formatter for a hierarchy of classes::
|
||||
|
||||
// demo.h:
|
||||
@ -592,7 +600,6 @@ System APIs
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
.. doxygenfunction:: fmt::windows_error
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
.. _ostream-api:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
11
doc/build.py
11
doc/build.py
@ -4,7 +4,12 @@
|
||||
import errno, os, re, sys
|
||||
from subprocess import check_call, CalledProcessError, Popen, PIPE, STDOUT
|
||||
|
||||
versions = ['1.0.0', '1.1.0', '2.0.0', '3.0.2', '4.0.0', '4.1.0', '5.0.0', '5.1.0', '5.2.0', '5.2.1', '5.3.0', '6.0.0', '6.1.0', '6.1.1', '6.1.2', '6.2.0', '6.2.1', '7.0.0', '7.0.1', '7.0.2', '7.0.3', '7.1.0', '7.1.1', '7.1.2', '7.1.3', '8.0.0', '8.0.1', '8.1.0', '8.1.1', '9.0.0', '9.1.0', '10.0.0', '10.1.0', '10.1.1']
|
||||
versions = [
|
||||
'1.0.0', '1.1.0', '2.0.0', '3.0.2', '4.0.0', '4.1.0', '5.0.0', '5.1.0',
|
||||
'5.2.0', '5.2.1', '5.3.0', '6.0.0', '6.1.0', '6.1.1', '6.1.2', '6.2.0',
|
||||
'6.2.1', '7.0.0', '7.0.1', '7.0.2', '7.0.3', '7.1.0', '7.1.1', '7.1.2',
|
||||
'7.1.3', '8.0.0', '8.0.1', '8.1.0', '8.1.1', '9.0.0', '9.1.0']
|
||||
versions += ['10.0.0', '10.1.0', '10.1.1', '10.1.1', '10.2.0', '10.2.1']
|
||||
|
||||
class Pip:
|
||||
def __init__(self, venv_dir):
|
||||
@ -31,7 +36,7 @@ def create_build_env(venv_dir='virtualenv'):
|
||||
# Jinja2 >= 3.1 incompatible with sphinx 3.3.0
|
||||
# See: https://github.com/sphinx-doc/sphinx/issues/10291
|
||||
pip.install('Jinja2<3.1')
|
||||
pip.install('sphinx-doc/sphinx', 'v3.3.0')
|
||||
pip.install('sphinx==3.3.0')
|
||||
pip.install('michaeljones/breathe', 'v4.25.0')
|
||||
|
||||
def build_docs(version='dev', **kwargs):
|
||||
@ -50,7 +55,7 @@ def build_docs(version='dev', **kwargs):
|
||||
GENERATE_RTF = NO
|
||||
CASE_SENSE_NAMES = NO
|
||||
INPUT = {0}/args.h {0}/chrono.h {0}/color.h {0}/core.h \
|
||||
{0}/compile.h {0}/format.h {0}/os.h {0}/ostream.h \
|
||||
{0}/compile.h {0}/format.h {0}/os.h {0}/ostream.h \
|
||||
{0}/printf.h {0}/xchar.h
|
||||
QUIET = YES
|
||||
JAVADOC_AUTOBRIEF = YES
|
||||
|
||||
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ The general form of a *standard format specifier* is:
|
||||
width: `integer` | "{" [`arg_id`] "}"
|
||||
precision: `integer` | "{" [`arg_id`] "}"
|
||||
type: "a" | "A" | "b" | "B" | "c" | "d" | "e" | "E" | "f" | "F" | "g" | "G" |
|
||||
: "o" | "p" | "s" | "x" | "X"
|
||||
: "o" | "p" | "s" | "x" | "X" | "?"
|
||||
|
||||
The *fill* character can be any Unicode code point other than ``'{'`` or
|
||||
``'}'``. The presence of a fill character is signaled by the character following
|
||||
@ -177,6 +177,9 @@ The available string presentation types are:
|
||||
| ``'s'`` | String format. This is the default type for strings and |
|
||||
| | may be omitted. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| ``'?'`` | Debug format. The string is quoted and special |
|
||||
| | characters escaped. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| none | The same as ``'s'``. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
@ -188,6 +191,9 @@ The available character presentation types are:
|
||||
| ``'c'`` | Character format. This is the default type for |
|
||||
| | characters and may be omitted. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| ``'?'`` | Debug format. The character is quoted and special |
|
||||
| | characters escaped. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| none | The same as ``'c'``. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
@ -223,9 +229,10 @@ The available integer presentation types are:
|
||||
| none | The same as ``'d'``. |
|
||||
+---------+----------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
Integer presentation types can also be used with character and Boolean values.
|
||||
Boolean values are formatted using textual representation, either ``true`` or
|
||||
``false``, if the presentation type is not specified.
|
||||
Integer presentation types can also be used with character and Boolean values
|
||||
with the only exception that ``'c'`` cannot be used with `bool`. Boolean values
|
||||
are formatted using textual representation, either ``true`` or ``false``, if the
|
||||
presentation type is not specified.
|
||||
|
||||
The available presentation types for floating-point values are:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -134,6 +134,44 @@ For ``build2`` newcomers or to get more details and use cases, you can read the
|
||||
``build2``
|
||||
`toolchain introduction <https://build2.org/build2-toolchain/doc/build2-toolchain-intro.xhtml>`_.
|
||||
|
||||
Usage with Meson
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
`Meson's WrapDB <https://mesonbuild.com/Wrapdb-projects.html>` includes a ``fmt``
|
||||
package, which repackages fmt to be built by Meson as a subproject.
|
||||
|
||||
**Usage:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Install the ``fmt`` subproject from the WrapDB by running::
|
||||
|
||||
meson wrap install fmt
|
||||
|
||||
from the root of your project.
|
||||
|
||||
- In your project's ``meson.build`` file, add an entry for the new subproject::
|
||||
|
||||
fmt = subproject('fmt')
|
||||
fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_dep')
|
||||
|
||||
- Include the new dependency object to link with fmt::
|
||||
|
||||
my_build_target = executable('name', 'src/main.cc', dependencies: [fmt_dep])
|
||||
|
||||
**Options:**
|
||||
|
||||
If desired, ``fmt`` may be built as a static library, or as a header-only
|
||||
library.
|
||||
|
||||
For a static build, use the following subproject definition::
|
||||
|
||||
fmt = subproject('fmt', default_options: 'default_library=static')
|
||||
fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_dep')
|
||||
|
||||
For the header-only version, use::
|
||||
|
||||
fmt = subproject('fmt')
|
||||
fmt_dep = fmt.get_variable('fmt_header_only_dep')
|
||||
|
||||
Building the Documentation
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,8 +22,9 @@ template <typename T> struct is_reference_wrapper : std::false_type {};
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
struct is_reference_wrapper<std::reference_wrapper<T>> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> const T& unwrap(const T& v) { return v; }
|
||||
template <typename T> const T& unwrap(const std::reference_wrapper<T>& v) {
|
||||
template <typename T> auto unwrap(const T& v) -> const T& { return v; }
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto unwrap(const std::reference_wrapper<T>& v) -> const T& {
|
||||
return static_cast<const T&>(v);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +51,7 @@ class dynamic_arg_list {
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<node<>> head_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Arg> const T& push(const Arg& arg) {
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Arg> auto push(const Arg& arg) -> const T& {
|
||||
auto new_node = std::unique_ptr<typed_node<T>>(new typed_node<T>(arg));
|
||||
auto& value = new_node->value;
|
||||
new_node->next = std::move(head_);
|
||||
@ -110,14 +111,14 @@ class dynamic_format_arg_store
|
||||
|
||||
friend class basic_format_args<Context>;
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned long long get_types() const {
|
||||
auto get_types() const -> unsigned long long {
|
||||
return detail::is_unpacked_bit | data_.size() |
|
||||
(named_info_.empty()
|
||||
? 0ULL
|
||||
: static_cast<unsigned long long>(detail::has_named_args_bit));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const basic_format_arg<Context>* data() const {
|
||||
auto data() const -> const basic_format_arg<Context>* {
|
||||
return named_info_.empty() ? data_.data() : data_.data() + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
|
||||
#include <ostream>
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
#include "ostream.h" // formatbuf
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,7 +72,8 @@ template <typename To, typename From,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<From, To>::value &&
|
||||
std::numeric_limits<From>::is_signed ==
|
||||
std::numeric_limits<To>::is_signed)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec)
|
||||
-> To {
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
using F = std::numeric_limits<From>;
|
||||
using T = std::numeric_limits<To>;
|
||||
@ -101,7 +102,8 @@ template <typename To, typename From,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<From, To>::value &&
|
||||
std::numeric_limits<From>::is_signed !=
|
||||
std::numeric_limits<To>::is_signed)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec)
|
||||
-> To {
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
using F = std::numeric_limits<From>;
|
||||
using T = std::numeric_limits<To>;
|
||||
@ -133,7 +135,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename To, typename From,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<From, To>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec)
|
||||
-> To {
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
return from;
|
||||
} // function
|
||||
@ -154,7 +157,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR To lossless_integral_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
// clang-format on
|
||||
template <typename To, typename From,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_same<From, To>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR To safe_float_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto safe_float_conversion(const From from, int& ec) -> To {
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
using T = std::numeric_limits<To>;
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_floating_point<From>::value, "From must be floating");
|
||||
@ -176,7 +179,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR To safe_float_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename To, typename From,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_same<From, To>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR To safe_float_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto safe_float_conversion(const From from, int& ec) -> To {
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_floating_point<From>::value, "From must be floating");
|
||||
return from;
|
||||
@ -188,8 +191,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR To safe_float_conversion(const From from, int& ec) {
|
||||
template <typename To, typename FromRep, typename FromPeriod,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<FromRep>::value),
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<typename To::rep>::value)>
|
||||
To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from,
|
||||
int& ec) {
|
||||
auto safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from,
|
||||
int& ec) -> To {
|
||||
using From = std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod>;
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
// the basic idea is that we need to convert from count() in the from type
|
||||
@ -240,8 +243,8 @@ To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from,
|
||||
template <typename To, typename FromRep, typename FromPeriod,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<FromRep>::value),
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<typename To::rep>::value)>
|
||||
To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from,
|
||||
int& ec) {
|
||||
auto safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from,
|
||||
int& ec) -> To {
|
||||
using From = std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod>;
|
||||
ec = 0;
|
||||
if (std::isnan(from.count())) {
|
||||
@ -321,12 +324,12 @@ To safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from,
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
template <typename T = void> struct null {};
|
||||
inline null<> localtime_r FMT_NOMACRO(...) { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline null<> localtime_s(...) { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline null<> gmtime_r(...) { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline null<> gmtime_s(...) { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline auto localtime_r FMT_NOMACRO(...) -> null<> { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline auto localtime_s(...) -> null<> { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline auto gmtime_r(...) -> null<> { return null<>(); }
|
||||
inline auto gmtime_s(...) -> null<> { return null<>(); }
|
||||
|
||||
inline const std::locale& get_classic_locale() {
|
||||
inline auto get_classic_locale() -> const std::locale& {
|
||||
static const auto& locale = std::locale::classic();
|
||||
return locale;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -336,8 +339,6 @@ template <typename CodeUnit> struct codecvt_result {
|
||||
CodeUnit buf[max_size];
|
||||
CodeUnit* end;
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <typename CodeUnit>
|
||||
constexpr const size_t codecvt_result<CodeUnit>::max_size;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename CodeUnit>
|
||||
void write_codecvt(codecvt_result<CodeUnit>& out, string_view in_buf,
|
||||
@ -408,8 +409,7 @@ inline void do_write(buffer<Char>& buf, const std::tm& time,
|
||||
auto&& format_buf = formatbuf<std::basic_streambuf<Char>>(buf);
|
||||
auto&& os = std::basic_ostream<Char>(&format_buf);
|
||||
os.imbue(loc);
|
||||
using iterator = std::ostreambuf_iterator<Char>;
|
||||
const auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<Char, iterator>>(loc);
|
||||
const auto& facet = std::use_facet<std::time_put<Char>>(loc);
|
||||
auto end = facet.put(os, os, Char(' '), &time, format, modifier);
|
||||
if (end.failed()) FMT_THROW(format_error("failed to format time"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -432,6 +432,51 @@ auto write(OutputIt out, const std::tm& time, const std::locale& loc,
|
||||
return write_encoded_tm_str(out, string_view(buf.data(), buf.size()), loc);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Rep1, typename Rep2>
|
||||
struct is_same_arithmetic_type
|
||||
: public std::integral_constant<bool,
|
||||
(std::is_integral<Rep1>::value &&
|
||||
std::is_integral<Rep2>::value) ||
|
||||
(std::is_floating_point<Rep1>::value &&
|
||||
std::is_floating_point<Rep2>::value)> {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <
|
||||
typename To, typename FromRep, typename FromPeriod,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_same_arithmetic_type<FromRep, typename To::rep>::value)>
|
||||
auto fmt_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from) -> To {
|
||||
#if FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST
|
||||
// Throwing version of safe_duration_cast is only available for
|
||||
// integer to integer or float to float casts.
|
||||
int ec;
|
||||
To to = safe_duration_cast::safe_duration_cast<To>(from, ec);
|
||||
if (ec) FMT_THROW(format_error("cannot format duration"));
|
||||
return to;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
// Standard duration cast, may overflow.
|
||||
return std::chrono::duration_cast<To>(from);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <
|
||||
typename To, typename FromRep, typename FromPeriod,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_same_arithmetic_type<FromRep, typename To::rep>::value)>
|
||||
auto fmt_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from) -> To {
|
||||
// Mixed integer <-> float cast is not supported by safe_duration_cast.
|
||||
return std::chrono::duration_cast<To>(from);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Duration>
|
||||
auto to_time_t(
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration> time_point)
|
||||
-> std::time_t {
|
||||
// Cannot use std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t since this would first
|
||||
// require a cast to std::chrono::system_clock::time_point, which could
|
||||
// overflow.
|
||||
return fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<std::time_t>>(
|
||||
time_point.time_since_epoch())
|
||||
.count();
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
@ -441,29 +486,29 @@ FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
expressed in local time. Unlike ``std::localtime``, this function is
|
||||
thread-safe on most platforms.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
inline std::tm localtime(std::time_t time) {
|
||||
inline auto localtime(std::time_t time) -> std::tm {
|
||||
struct dispatcher {
|
||||
std::time_t time_;
|
||||
std::tm tm_;
|
||||
|
||||
dispatcher(std::time_t t) : time_(t) {}
|
||||
|
||||
bool run() {
|
||||
auto run() -> bool {
|
||||
using namespace fmt::detail;
|
||||
return handle(localtime_r(&time_, &tm_));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool handle(std::tm* tm) { return tm != nullptr; }
|
||||
auto handle(std::tm* tm) -> bool { return tm != nullptr; }
|
||||
|
||||
bool handle(detail::null<>) {
|
||||
auto handle(detail::null<>) -> bool {
|
||||
using namespace fmt::detail;
|
||||
return fallback(localtime_s(&tm_, &time_));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool fallback(int res) { return res == 0; }
|
||||
auto fallback(int res) -> bool { return res == 0; }
|
||||
|
||||
#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION
|
||||
bool fallback(detail::null<>) {
|
||||
auto fallback(detail::null<>) -> bool {
|
||||
using namespace fmt::detail;
|
||||
std::tm* tm = std::localtime(&time_);
|
||||
if (tm) tm_ = *tm;
|
||||
@ -480,8 +525,8 @@ inline std::tm localtime(std::time_t time) {
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_LOCAL_TIME
|
||||
template <typename Duration>
|
||||
inline auto localtime(std::chrono::local_time<Duration> time) -> std::tm {
|
||||
return localtime(std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(
|
||||
std::chrono::current_zone()->to_sys(time)));
|
||||
return localtime(
|
||||
detail::to_time_t(std::chrono::current_zone()->to_sys(time)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -490,29 +535,29 @@ inline auto localtime(std::chrono::local_time<Duration> time) -> std::tm {
|
||||
expressed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Unlike ``std::gmtime``, this
|
||||
function is thread-safe on most platforms.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
inline std::tm gmtime(std::time_t time) {
|
||||
inline auto gmtime(std::time_t time) -> std::tm {
|
||||
struct dispatcher {
|
||||
std::time_t time_;
|
||||
std::tm tm_;
|
||||
|
||||
dispatcher(std::time_t t) : time_(t) {}
|
||||
|
||||
bool run() {
|
||||
auto run() -> bool {
|
||||
using namespace fmt::detail;
|
||||
return handle(gmtime_r(&time_, &tm_));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool handle(std::tm* tm) { return tm != nullptr; }
|
||||
auto handle(std::tm* tm) -> bool { return tm != nullptr; }
|
||||
|
||||
bool handle(detail::null<>) {
|
||||
auto handle(detail::null<>) -> bool {
|
||||
using namespace fmt::detail;
|
||||
return fallback(gmtime_s(&tm_, &time_));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool fallback(int res) { return res == 0; }
|
||||
auto fallback(int res) -> bool { return res == 0; }
|
||||
|
||||
#if !FMT_MSC_VERSION
|
||||
bool fallback(detail::null<>) {
|
||||
auto fallback(detail::null<>) -> bool {
|
||||
std::tm* tm = std::gmtime(&time_);
|
||||
if (tm) tm_ = *tm;
|
||||
return tm != nullptr;
|
||||
@ -525,9 +570,11 @@ inline std::tm gmtime(std::time_t time) {
|
||||
return gt.tm_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::tm gmtime(
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock> time_point) {
|
||||
return gmtime(std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(time_point));
|
||||
template <typename Duration>
|
||||
inline auto gmtime(
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration> time_point)
|
||||
-> std::tm {
|
||||
return gmtime(detail::to_time_t(time_point));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
@ -566,7 +613,8 @@ inline void write_digit2_separated(char* buf, unsigned a, unsigned b,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Period> FMT_CONSTEXPR inline const char* get_units() {
|
||||
template <typename Period>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto get_units() -> const char* {
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::atto>::value) return "as";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::femto>::value) return "fs";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::pico>::value) return "ps";
|
||||
@ -584,8 +632,9 @@ template <typename Period> FMT_CONSTEXPR inline const char* get_units() {
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::tera>::value) return "Ts";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::peta>::value) return "Ps";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::exa>::value) return "Es";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<60>>::value) return "m";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<60>>::value) return "min";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<3600>>::value) return "h";
|
||||
if (std::is_same<Period, std::ratio<86400>>::value) return "d";
|
||||
return nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -621,9 +670,8 @@ auto write_padding(OutputIt out, pad_type pad) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
|
||||
// Parses a put_time-like format string and invokes handler actions.
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Handler>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin,
|
||||
const Char* end,
|
||||
Handler&& handler) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_chrono_format(const Char* begin, const Char* end,
|
||||
Handler&& handler) -> const Char* {
|
||||
if (begin == end || *begin == '}') return begin;
|
||||
if (*begin != '%') FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid format"));
|
||||
auto ptr = begin;
|
||||
@ -954,25 +1002,25 @@ struct tm_format_checker : null_chrono_spec_handler<tm_format_checker> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_tz_name() {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
inline const char* tm_wday_full_name(int wday) {
|
||||
inline auto tm_wday_full_name(int wday) -> const char* {
|
||||
static constexpr const char* full_name_list[] = {
|
||||
"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday",
|
||||
"Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"};
|
||||
return wday >= 0 && wday <= 6 ? full_name_list[wday] : "?";
|
||||
}
|
||||
inline const char* tm_wday_short_name(int wday) {
|
||||
inline auto tm_wday_short_name(int wday) -> const char* {
|
||||
static constexpr const char* short_name_list[] = {"Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed",
|
||||
"Thu", "Fri", "Sat"};
|
||||
return wday >= 0 && wday <= 6 ? short_name_list[wday] : "???";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline const char* tm_mon_full_name(int mon) {
|
||||
inline auto tm_mon_full_name(int mon) -> const char* {
|
||||
static constexpr const char* full_name_list[] = {
|
||||
"January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June",
|
||||
"July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"};
|
||||
return mon >= 0 && mon <= 11 ? full_name_list[mon] : "?";
|
||||
}
|
||||
inline const char* tm_mon_short_name(int mon) {
|
||||
inline auto tm_mon_short_name(int mon) -> const char* {
|
||||
static constexpr const char* short_name_list[] = {
|
||||
"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun",
|
||||
"Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec",
|
||||
@ -1004,21 +1052,21 @@ inline void tzset_once() {
|
||||
|
||||
// Converts value to Int and checks that it's in the range [0, upper).
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Int, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
inline Int to_nonnegative_int(T value, Int upper) {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(std::is_unsigned<Int>::value ||
|
||||
(value >= 0 && to_unsigned(value) <= to_unsigned(upper)),
|
||||
"invalid value");
|
||||
(void)upper;
|
||||
inline auto to_nonnegative_int(T value, Int upper) -> Int {
|
||||
if (!std::is_unsigned<Int>::value &&
|
||||
(value < 0 || to_unsigned(value) > to_unsigned(upper))) {
|
||||
FMT_THROW(fmt::format_error("chrono value is out of range"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
return static_cast<Int>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Int, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
inline Int to_nonnegative_int(T value, Int upper) {
|
||||
inline auto to_nonnegative_int(T value, Int upper) -> Int {
|
||||
if (value < 0 || value > static_cast<T>(upper))
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("invalid value"));
|
||||
return static_cast<Int>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr long long pow10(std::uint32_t n) {
|
||||
constexpr auto pow10(std::uint32_t n) -> long long {
|
||||
return n == 0 ? 1 : 10 * pow10(n - 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1052,13 +1100,12 @@ void write_fractional_seconds(OutputIt& out, Duration d, int precision = -1) {
|
||||
std::chrono::seconds::rep>::type,
|
||||
std::ratio<1, detail::pow10(num_fractional_digits)>>;
|
||||
|
||||
const auto fractional =
|
||||
d - std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d);
|
||||
const auto fractional = d - fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d);
|
||||
const auto subseconds =
|
||||
std::chrono::treat_as_floating_point<
|
||||
typename subsecond_precision::rep>::value
|
||||
? fractional.count()
|
||||
: std::chrono::duration_cast<subsecond_precision>(fractional).count();
|
||||
: fmt_duration_cast<subsecond_precision>(fractional).count();
|
||||
auto n = static_cast<uint32_or_64_or_128_t<long long>>(subseconds);
|
||||
const int num_digits = detail::count_digits(n);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1109,11 +1156,11 @@ void write_floating_seconds(memory_buffer& buf, Duration duration,
|
||||
num_fractional_digits = 6;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), FMT_STRING("{:.{}f}"),
|
||||
std::fmod(val * static_cast<rep>(Duration::period::num) /
|
||||
static_cast<rep>(Duration::period::den),
|
||||
static_cast<rep>(60)),
|
||||
num_fractional_digits);
|
||||
fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), FMT_STRING("{:.{}f}"),
|
||||
std::fmod(val * static_cast<rep>(Duration::period::num) /
|
||||
static_cast<rep>(Duration::period::den),
|
||||
static_cast<rep>(60)),
|
||||
num_fractional_digits);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename Char,
|
||||
@ -1174,8 +1221,7 @@ class tm_writer {
|
||||
return static_cast<int>(l);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Algorithm:
|
||||
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_week_date#Calculating_the_week_number_from_a_month_and_day_of_the_month_or_ordinal_date
|
||||
// Algorithm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_week_date.
|
||||
auto iso_year_weeks(long long curr_year) const noexcept -> int {
|
||||
const auto prev_year = curr_year - 1;
|
||||
const auto curr_p =
|
||||
@ -1315,7 +1361,7 @@ class tm_writer {
|
||||
subsecs_(subsecs),
|
||||
tm_(tm) {}
|
||||
|
||||
OutputIt out() const { return out_; }
|
||||
auto out() const -> OutputIt { return out_; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char* begin, const Char* end) {
|
||||
out_ = copy_str<Char>(begin, end, out_);
|
||||
@ -1579,6 +1625,7 @@ struct chrono_format_checker : null_chrono_spec_handler<chrono_format_checker> {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_text(const Char*, const Char*) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_day_of_year() {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_24_hour(numeric_system, pad_type) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_12_hour(numeric_system, pad_type) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void on_minute(numeric_system, pad_type) {}
|
||||
@ -1597,16 +1644,16 @@ struct chrono_format_checker : null_chrono_spec_handler<chrono_format_checker> {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value&& has_isfinite<T>::value)>
|
||||
inline bool isfinite(T) {
|
||||
inline auto isfinite(T) -> bool {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
inline T mod(T x, int y) {
|
||||
inline auto mod(T x, int y) -> T {
|
||||
return x % static_cast<T>(y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value)>
|
||||
inline T mod(T x, int y) {
|
||||
inline auto mod(T x, int y) -> T {
|
||||
return std::fmod(x, static_cast<T>(y));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1621,49 +1668,38 @@ template <typename T> struct make_unsigned_or_unchanged<T, true> {
|
||||
using type = typename std::make_unsigned<T>::type;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST
|
||||
// throwing version of safe_duration_cast
|
||||
template <typename To, typename FromRep, typename FromPeriod>
|
||||
To fmt_safe_duration_cast(std::chrono::duration<FromRep, FromPeriod> from) {
|
||||
int ec;
|
||||
To to = safe_duration_cast::safe_duration_cast<To>(from, ec);
|
||||
if (ec) FMT_THROW(format_error("cannot format duration"));
|
||||
return to;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Rep, typename Period,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<Rep>::value)>
|
||||
inline std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli> get_milliseconds(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period> d) {
|
||||
inline auto get_milliseconds(std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period> d)
|
||||
-> std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli> {
|
||||
// this may overflow and/or the result may not fit in the
|
||||
// target type.
|
||||
#if FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST
|
||||
using CommonSecondsType =
|
||||
typename std::common_type<decltype(d), std::chrono::seconds>::type;
|
||||
const auto d_as_common = fmt_safe_duration_cast<CommonSecondsType>(d);
|
||||
const auto d_as_common = fmt_duration_cast<CommonSecondsType>(d);
|
||||
const auto d_as_whole_seconds =
|
||||
fmt_safe_duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d_as_common);
|
||||
fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d_as_common);
|
||||
// this conversion should be nonproblematic
|
||||
const auto diff = d_as_common - d_as_whole_seconds;
|
||||
const auto ms =
|
||||
fmt_safe_duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli>>(diff);
|
||||
fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<Rep, std::milli>>(diff);
|
||||
return ms;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
auto s = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d);
|
||||
return std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(d - s);
|
||||
auto s = fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d);
|
||||
return fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(d - s);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Rep, typename OutputIt,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<Rep>::value)>
|
||||
OutputIt format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int) {
|
||||
auto format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
return write<Char>(out, val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Rep, typename OutputIt,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<Rep>::value)>
|
||||
OutputIt format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int precision) {
|
||||
auto format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int precision) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
auto specs = format_specs<Char>();
|
||||
specs.precision = precision;
|
||||
specs.type = precision >= 0 ? presentation_type::fixed_lower
|
||||
@ -1672,12 +1708,12 @@ OutputIt format_duration_value(OutputIt out, Rep val, int precision) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
OutputIt copy_unit(string_view unit, OutputIt out, Char) {
|
||||
auto copy_unit(string_view unit, OutputIt out, Char) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
return std::copy(unit.begin(), unit.end(), out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt>
|
||||
OutputIt copy_unit(string_view unit, OutputIt out, wchar_t) {
|
||||
auto copy_unit(string_view unit, OutputIt out, wchar_t) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
// This works when wchar_t is UTF-32 because units only contain characters
|
||||
// that have the same representation in UTF-16 and UTF-32.
|
||||
utf8_to_utf16 u(unit);
|
||||
@ -1685,7 +1721,7 @@ OutputIt copy_unit(string_view unit, OutputIt out, wchar_t) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Period, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
OutputIt format_duration_unit(OutputIt out) {
|
||||
auto format_duration_unit(OutputIt out) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
if (const char* unit = get_units<Period>())
|
||||
return copy_unit(string_view(unit), out, Char());
|
||||
*out++ = '[';
|
||||
@ -1752,18 +1788,12 @@ struct chrono_formatter {
|
||||
|
||||
// this may overflow and/or the result may not fit in the
|
||||
// target type.
|
||||
#if FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST
|
||||
// might need checked conversion (rep!=Rep)
|
||||
auto tmpval = std::chrono::duration<rep, Period>(val);
|
||||
s = fmt_safe_duration_cast<seconds>(tmpval);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
s = std::chrono::duration_cast<seconds>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<rep, Period>(val));
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
s = fmt_duration_cast<seconds>(std::chrono::duration<rep, Period>(val));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// returns true if nan or inf, writes to out.
|
||||
bool handle_nan_inf() {
|
||||
auto handle_nan_inf() -> bool {
|
||||
if (isfinite(val)) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1780,17 +1810,22 @@ struct chrono_formatter {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Rep hour() const { return static_cast<Rep>(mod((s.count() / 3600), 24)); }
|
||||
auto days() const -> Rep { return static_cast<Rep>(s.count() / 86400); }
|
||||
auto hour() const -> Rep {
|
||||
return static_cast<Rep>(mod((s.count() / 3600), 24));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Rep hour12() const {
|
||||
auto hour12() const -> Rep {
|
||||
Rep hour = static_cast<Rep>(mod((s.count() / 3600), 12));
|
||||
return hour <= 0 ? 12 : hour;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Rep minute() const { return static_cast<Rep>(mod((s.count() / 60), 60)); }
|
||||
Rep second() const { return static_cast<Rep>(mod(s.count(), 60)); }
|
||||
auto minute() const -> Rep {
|
||||
return static_cast<Rep>(mod((s.count() / 60), 60));
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto second() const -> Rep { return static_cast<Rep>(mod(s.count(), 60)); }
|
||||
|
||||
std::tm time() const {
|
||||
auto time() const -> std::tm {
|
||||
auto time = std::tm();
|
||||
time.tm_hour = to_nonnegative_int(hour(), 24);
|
||||
time.tm_min = to_nonnegative_int(minute(), 60);
|
||||
@ -1858,10 +1893,14 @@ struct chrono_formatter {
|
||||
void on_dec0_week_of_year(numeric_system) {}
|
||||
void on_dec1_week_of_year(numeric_system) {}
|
||||
void on_iso_week_of_year(numeric_system) {}
|
||||
void on_day_of_year() {}
|
||||
void on_day_of_month(numeric_system) {}
|
||||
void on_day_of_month_space(numeric_system) {}
|
||||
|
||||
void on_day_of_year() {
|
||||
if (handle_nan_inf()) return;
|
||||
write(days(), 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void on_24_hour(numeric_system ns, pad_type pad) {
|
||||
if (handle_nan_inf()) return;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1968,7 +2007,7 @@ class weekday {
|
||||
weekday() = default;
|
||||
explicit constexpr weekday(unsigned wd) noexcept
|
||||
: value(static_cast<unsigned char>(wd != 7 ? wd : 0)) {}
|
||||
constexpr unsigned c_encoding() const noexcept { return value; }
|
||||
constexpr auto c_encoding() const noexcept -> unsigned { return value; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class year_month_day {};
|
||||
@ -2083,25 +2122,22 @@ struct formatter<std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration>,
|
||||
period::num != 1 || period::den != 1 ||
|
||||
std::is_floating_point<typename Duration::rep>::value)) {
|
||||
const auto epoch = val.time_since_epoch();
|
||||
auto subsecs = std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>(
|
||||
epoch - std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(epoch));
|
||||
auto subsecs = detail::fmt_duration_cast<Duration>(
|
||||
epoch - detail::fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(epoch));
|
||||
|
||||
if (subsecs.count() < 0) {
|
||||
auto second =
|
||||
std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>(std::chrono::seconds(1));
|
||||
detail::fmt_duration_cast<Duration>(std::chrono::seconds(1));
|
||||
if (epoch.count() < ((Duration::min)() + second).count())
|
||||
FMT_THROW(format_error("duration is too small"));
|
||||
subsecs += second;
|
||||
val -= second;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::do_format(
|
||||
gmtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)), ctx,
|
||||
&subsecs);
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::do_format(gmtime(val), ctx, &subsecs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format(
|
||||
gmtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)), ctx);
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format(gmtime(val), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2120,17 +2156,13 @@ struct formatter<std::chrono::local_time<Duration>, Char>
|
||||
if (period::num != 1 || period::den != 1 ||
|
||||
std::is_floating_point<typename Duration::rep>::value) {
|
||||
const auto epoch = val.time_since_epoch();
|
||||
const auto subsecs = std::chrono::duration_cast<Duration>(
|
||||
epoch - std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(epoch));
|
||||
const auto subsecs = detail::fmt_duration_cast<Duration>(
|
||||
epoch - detail::fmt_duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(epoch));
|
||||
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::do_format(
|
||||
localtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)),
|
||||
ctx, &subsecs);
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::do_format(localtime(val), ctx, &subsecs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format(
|
||||
localtime(std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(val)),
|
||||
ctx);
|
||||
return formatter<std::tm, Char>::format(localtime(val), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ class text_style {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style(emphasis em = emphasis()) noexcept
|
||||
: set_foreground_color(), set_background_color(), ems(em) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style& operator|=(const text_style& rhs) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator|=(const text_style& rhs) -> text_style& {
|
||||
if (!set_foreground_color) {
|
||||
set_foreground_color = rhs.set_foreground_color;
|
||||
foreground_color = rhs.foreground_color;
|
||||
@ -257,29 +257,29 @@ class text_style {
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style operator|(text_style lhs,
|
||||
const text_style& rhs) {
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator|(text_style lhs, const text_style& rhs)
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return lhs |= rhs;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_foreground() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_foreground() const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return set_foreground_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_background() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_background() const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return set_background_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_emphasis() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_emphasis() const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return static_cast<uint8_t>(ems) != 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::color_type get_foreground() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_foreground() const noexcept -> detail::color_type {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(has_foreground(), "no foreground specified for this style");
|
||||
return foreground_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR detail::color_type get_background() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_background() const noexcept -> detail::color_type {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(has_background(), "no background specified for this style");
|
||||
return background_color;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR emphasis get_emphasis() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_emphasis() const noexcept -> emphasis {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(has_emphasis(), "no emphasis specified for this style");
|
||||
return ems;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -297,9 +297,11 @@ class text_style {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept;
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style;
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR text_style bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept;
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR auto bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style;
|
||||
|
||||
detail::color_type foreground_color;
|
||||
detail::color_type background_color;
|
||||
@ -309,16 +311,19 @@ class text_style {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/** Creates a text style from the foreground (text) color. */
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline text_style fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto fg(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return text_style(true, foreground);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/** Creates a text style from the background color. */
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline text_style bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto bg(detail::color_type background) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return text_style(false, background);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline text_style operator|(emphasis lhs, emphasis rhs) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto operator|(emphasis lhs, emphasis rhs) noexcept
|
||||
-> text_style {
|
||||
return text_style(lhs) | rhs;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -384,8 +389,8 @@ template <typename Char> struct ansi_color_escape {
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR operator const Char*() const noexcept { return buffer; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR const Char* begin() const noexcept { return buffer; }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS const Char* end() const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto begin() const noexcept -> const Char* { return buffer; }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS auto end() const noexcept -> const Char* {
|
||||
return buffer + std::char_traits<Char>::length(buffer);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -400,25 +405,27 @@ template <typename Char> struct ansi_color_escape {
|
||||
out[2] = static_cast<Char>('0' + c % 10);
|
||||
out[3] = static_cast<Char>(delimiter);
|
||||
}
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR bool has_emphasis(emphasis em, emphasis mask) noexcept {
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR auto has_emphasis(emphasis em, emphasis mask) noexcept
|
||||
-> bool {
|
||||
return static_cast<uint8_t>(em) & static_cast<uint8_t>(mask);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_foreground_color(
|
||||
detail::color_type foreground) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_foreground_color(detail::color_type foreground) noexcept
|
||||
-> ansi_color_escape<Char> {
|
||||
return ansi_color_escape<Char>(foreground, "\x1b[38;2;");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_background_color(
|
||||
detail::color_type background) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_background_color(detail::color_type background) noexcept
|
||||
-> ansi_color_escape<Char> {
|
||||
return ansi_color_escape<Char>(background, "\x1b[48;2;");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR ansi_color_escape<Char> make_emphasis(emphasis em) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto make_emphasis(emphasis em) noexcept
|
||||
-> ansi_color_escape<Char> {
|
||||
return ansi_color_escape<Char>(em);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -427,9 +434,10 @@ template <typename Char> inline void reset_color(buffer<Char>& buffer) {
|
||||
buffer.append(reset_color.begin(), reset_color.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct styled_arg {
|
||||
template <typename T> struct styled_arg : detail::view {
|
||||
const T& value;
|
||||
text_style style;
|
||||
styled_arg(const T& v, text_style s) : value(v), style(s) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
@ -510,9 +518,10 @@ void print(const text_style& ts, const S& format_str, const Args&... args) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename Char = char_t<S>>
|
||||
inline std::basic_string<Char> vformat(
|
||||
inline auto vformat(
|
||||
const text_style& ts, const S& format_str,
|
||||
basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) {
|
||||
basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args)
|
||||
-> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
basic_memory_buffer<Char> buf;
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, detail::to_string_view(format_str), args);
|
||||
return fmt::to_string(buf);
|
||||
@ -531,8 +540,8 @@ inline std::basic_string<Char> vformat(
|
||||
\endrst
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args, typename Char = char_t<S>>
|
||||
inline std::basic_string<Char> format(const text_style& ts, const S& format_str,
|
||||
const Args&... args) {
|
||||
inline auto format(const text_style& ts, const S& format_str,
|
||||
const Args&... args) -> std::basic_string<Char> {
|
||||
return fmt::vformat(ts, detail::to_string_view(format_str),
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args<buffer_context<Char>>(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -542,9 +551,10 @@ inline std::basic_string<Char> format(const text_style& ts, const S& format_str,
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename Char,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value)>
|
||||
OutputIt vformat_to(
|
||||
OutputIt out, const text_style& ts, basic_string_view<Char> format_str,
|
||||
basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args) {
|
||||
auto vformat_to(OutputIt out, const text_style& ts,
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> format_str,
|
||||
basic_format_args<buffer_context<type_identity_t<Char>>> args)
|
||||
-> OutputIt {
|
||||
auto&& buf = detail::get_buffer<Char>(out);
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buf, ts, format_str, args);
|
||||
return detail::get_iterator(buf, out);
|
||||
@ -562,9 +572,10 @@ OutputIt vformat_to(
|
||||
fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), "{}", 42);
|
||||
\endrst
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char_t<S>>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_string<S>::value>
|
||||
template <
|
||||
typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, char_t<S>>::value &&
|
||||
detail::is_string<S>::value>
|
||||
inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const text_style& ts, const S& format_str,
|
||||
Args&&... args) ->
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename InputIt>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline counting_iterator copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end,
|
||||
counting_iterator it) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto copy_str(InputIt begin, InputIt end,
|
||||
counting_iterator it) -> counting_iterator {
|
||||
return it + (end - begin);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ struct udl_compiled_string : compiled_string {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename... Tail>
|
||||
const T& first(const T& value, const Tail&...) {
|
||||
auto first(const T& value, const Tail&...) -> const T& {
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -488,18 +488,19 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR OutputIt format_to(OutputIt out, const S&, Args&&... args) {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
format_to_n_result<OutputIt> format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n,
|
||||
const S& format_str, Args&&... args) {
|
||||
auto format_to_n(OutputIt out, size_t n, const S& format_str, Args&&... args)
|
||||
-> format_to_n_result<OutputIt> {
|
||||
using traits = detail::fixed_buffer_traits;
|
||||
auto buf = detail::iterator_buffer<OutputIt, char, traits>(out, n);
|
||||
format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str, std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), format_str,
|
||||
std::forward<Args>(args)...);
|
||||
return {buf.out(), buf.count()};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename S, typename... Args,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(detail::is_compiled_string<S>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 size_t formatted_size(const S& format_str,
|
||||
const Args&... args) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto formatted_size(const S& format_str, const Args&... args)
|
||||
-> size_t {
|
||||
return fmt::format_to(detail::counting_iterator(), format_str, args...)
|
||||
.count();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
|
||||
#include <type_traits>
|
||||
|
||||
// The fmt library version in the form major * 10000 + minor * 100 + patch.
|
||||
#define FMT_VERSION 100100
|
||||
#define FMT_VERSION 100201
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__clang__) && !defined(__ibmxl__)
|
||||
# define FMT_CLANG_VERSION (__clang_major__ * 100 + __clang_minor__)
|
||||
@ -105,9 +105,12 @@
|
||||
# define FMT_CONSTEXPR
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if ((FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) && \
|
||||
(!defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) || _GLIBCXX_RELEASE > 9)) || \
|
||||
(FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L && FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1002)
|
||||
#if (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L || \
|
||||
(FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L && FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1002)) && \
|
||||
((!defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) || _GLIBCXX_RELEASE >= 10) && \
|
||||
(!defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION) || _LIBCPP_VERSION >= 10000) && \
|
||||
(!FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1928)) && \
|
||||
defined(__cpp_lib_is_constant_evaluated)
|
||||
# define FMT_CONSTEXPR20 constexpr
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_CONSTEXPR20
|
||||
@ -185,18 +188,20 @@
|
||||
# define FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_CLANG_VERSION
|
||||
# define FMT_VISIBILITY(value) __attribute__((visibility(value)))
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_VISIBILITY(value)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if !defined(FMT_HEADER_ONLY) && defined(_WIN32)
|
||||
# ifdef FMT_LIB_EXPORT
|
||||
# if defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT)
|
||||
# define FMT_API __declspec(dllexport)
|
||||
# elif defined(FMT_SHARED)
|
||||
# define FMT_API __declspec(dllimport)
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# if defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT) || defined(FMT_SHARED)
|
||||
# if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)
|
||||
# define FMT_API __attribute__((visibility("default")))
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#elif defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT) || defined(FMT_SHARED)
|
||||
# define FMT_API FMT_VISIBILITY("default")
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_API
|
||||
# define FMT_API
|
||||
@ -222,8 +227,9 @@
|
||||
__apple_build_version__ >= 14000029L) && \
|
||||
FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) || \
|
||||
(defined(__cpp_consteval) && \
|
||||
(!FMT_MSC_VERSION || _MSC_FULL_VER >= 193030704))
|
||||
// consteval is broken in MSVC before VS2022 and Apple clang before 14.
|
||||
(!FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1929))
|
||||
// consteval is broken in MSVC before VS2019 version 16.10 and Apple clang
|
||||
// before 14.
|
||||
# define FMT_CONSTEVAL consteval
|
||||
# define FMT_HAS_CONSTEVAL
|
||||
# else
|
||||
@ -242,6 +248,15 @@
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// GCC < 5 requires this-> in decltype
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_DECLTYPE_THIS
|
||||
# if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 500
|
||||
# define FMT_DECLTYPE_THIS this->
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_DECLTYPE_THIS
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Enable minimal optimizations for more compact code in debug mode.
|
||||
FMT_GCC_PRAGMA("GCC push_options")
|
||||
#if !defined(__OPTIMIZE__) && !defined(__NVCOMPILER) && !defined(__LCC__) && \
|
||||
@ -263,7 +278,9 @@ template <typename T>
|
||||
using remove_const_t = typename std::remove_const<T>::type;
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using remove_cvref_t = typename std::remove_cv<remove_reference_t<T>>::type;
|
||||
template <typename T> struct type_identity { using type = T; };
|
||||
template <typename T> struct type_identity {
|
||||
using type = T;
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <typename T> using type_identity_t = typename type_identity<T>::type;
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using underlying_t = typename std::underlying_type<T>::type;
|
||||
@ -454,15 +471,15 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_string_view {
|
||||
size_ -= n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS bool starts_with(
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> sv) const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS auto starts_with(
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char> sv) const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return size_ >= sv.size_ &&
|
||||
std::char_traits<Char>::compare(data_, sv.data_, sv.size_) == 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS bool starts_with(Char c) const noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS auto starts_with(Char c) const noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
return size_ >= 1 && std::char_traits<Char>::eq(*data_, c);
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS bool starts_with(const Char* s) const {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR_CHAR_TRAITS auto starts_with(const Char* s) const -> bool {
|
||||
return starts_with(basic_string_view<Char>(s));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -600,10 +617,10 @@ FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(const Char*, cstring_type);
|
||||
FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(basic_string_view<Char>, string_type);
|
||||
FMT_TYPE_CONSTANT(const void*, pointer_type);
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr bool is_integral_type(type t) {
|
||||
constexpr auto is_integral_type(type t) -> bool {
|
||||
return t > type::none_type && t <= type::last_integer_type;
|
||||
}
|
||||
constexpr bool is_arithmetic_type(type t) {
|
||||
constexpr auto is_arithmetic_type(type t) -> bool {
|
||||
return t > type::none_type && t <= type::last_numeric_type;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -627,6 +644,7 @@ enum {
|
||||
pointer_set = set(type::pointer_type)
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// DEPRECATED!
|
||||
FMT_NORETURN FMT_API void throw_format_error(const char* message);
|
||||
|
||||
struct error_handler {
|
||||
@ -804,7 +822,7 @@ template <typename T> class buffer {
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
// Don't initialize ptr_ since it is not accessed to save a few cycles.
|
||||
FMT_MSC_WARNING(suppress : 26495)
|
||||
buffer(size_t sz) noexcept : size_(sz), capacity_(sz) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR buffer(size_t sz) noexcept : size_(sz), capacity_(sz) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 buffer(T* p = nullptr, size_t sz = 0, size_t cap = 0) noexcept
|
||||
: ptr_(p), size_(sz), capacity_(cap) {}
|
||||
@ -819,6 +837,7 @@ template <typename T> class buffer {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/** Increases the buffer capacity to hold at least *capacity* elements. */
|
||||
// DEPRECATED!
|
||||
virtual FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void grow(size_t capacity) = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
@ -1305,6 +1324,7 @@ template <typename Context> class value {
|
||||
parse_ctx.advance_to(f.parse(parse_ctx));
|
||||
using qualified_type =
|
||||
conditional_t<has_const_formatter<T, Context>(), const T, T>;
|
||||
// Calling format through a mutable reference is deprecated.
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(f.format(*static_cast<qualified_type*>(arg), ctx));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -1318,7 +1338,7 @@ using ulong_type = conditional_t<long_short, unsigned, unsigned long long>;
|
||||
template <typename T> struct format_as_result {
|
||||
template <typename U,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_enum<U>::value || std::is_class<U>::value)>
|
||||
static auto map(U*) -> decltype(format_as(std::declval<U>()));
|
||||
static auto map(U*) -> remove_cvref_t<decltype(format_as(std::declval<U>()))>;
|
||||
static auto map(...) -> void;
|
||||
|
||||
using type = decltype(map(static_cast<T*>(nullptr)));
|
||||
@ -1435,7 +1455,8 @@ template <typename Context> struct arg_mapper {
|
||||
// Only map owning types because mapping views can be unsafe.
|
||||
template <typename T, typename U = format_as_t<T>,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_arithmetic<U>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T& val) -> decltype(this->map(U())) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T& val)
|
||||
-> decltype(FMT_DECLTYPE_THIS map(U())) {
|
||||
return map(format_as(val));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1459,13 +1480,14 @@ template <typename Context> struct arg_mapper {
|
||||
!is_string<U>::value && !is_char<U>::value &&
|
||||
!is_named_arg<U>::value &&
|
||||
!std::is_arithmetic<format_as_t<U>>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(T& val) -> decltype(this->do_map(val)) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(T& val)
|
||||
-> decltype(FMT_DECLTYPE_THIS do_map(val)) {
|
||||
return do_map(val);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_named_arg<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto map(const T& named_arg)
|
||||
-> decltype(this->map(named_arg.value)) {
|
||||
-> decltype(FMT_DECLTYPE_THIS map(named_arg.value)) {
|
||||
return map(named_arg.value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1504,7 +1526,9 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR auto copy_str(R&& rng, OutputIt out) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_GCC_VERSION && FMT_GCC_VERSION < 500
|
||||
// A workaround for gcc 4.8 to make void_t work in a SFINAE context.
|
||||
template <typename...> struct void_t_impl { using type = void; };
|
||||
template <typename...> struct void_t_impl {
|
||||
using type = void;
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <typename... T> using void_t = typename void_t_impl<T...>::type;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
template <typename...> using void_t = void;
|
||||
@ -1598,8 +1622,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto make_arg(T& val) -> basic_format_arg<Context> {
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
// A formatting argument. It is a trivially copyable/constructible type to
|
||||
// allow storage in basic_memory_buffer.
|
||||
// A formatting argument. Context is a template parameter for the compiled API
|
||||
// where output can be unbuffered.
|
||||
template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
detail::value<Context> value_;
|
||||
@ -1651,6 +1675,15 @@ template <typename Context> class basic_format_arg {
|
||||
auto is_arithmetic() const -> bool {
|
||||
return detail::is_arithmetic_type(type_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_INLINE auto format_custom(const char_type* parse_begin,
|
||||
typename Context::parse_context_type& parse_ctx,
|
||||
Context& ctx) -> bool {
|
||||
if (type_ != detail::type::custom_type) return false;
|
||||
parse_ctx.advance_to(parse_begin);
|
||||
value_.custom.format(value_.custom.value, parse_ctx, ctx);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
@ -1739,6 +1772,7 @@ template <typename OutputIt, typename Char> class basic_format_context {
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto args() const -> const format_args& { return args_; }
|
||||
|
||||
// DEPRECATED!
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto error_handler() -> detail::error_handler { return {}; }
|
||||
void on_error(const char* message) { error_handler().on_error(message); }
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2300,9 +2334,12 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_format_specs(
|
||||
dynamic_format_specs<Char>& specs;
|
||||
type arg_type;
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(pres type, int set) -> const Char* {
|
||||
if (!in(arg_type, set)) throw_format_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
specs.type = type;
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(pres pres_type, int set) -> const Char* {
|
||||
if (!in(arg_type, set)) {
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin;
|
||||
throw_format_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
}
|
||||
specs.type = pres_type;
|
||||
return begin + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} parse_presentation_type{begin, specs, arg_type};
|
||||
@ -2319,6 +2356,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_format_specs(
|
||||
case '+':
|
||||
case '-':
|
||||
case ' ':
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin;
|
||||
enter_state(state::sign, in(arg_type, sint_set | float_set));
|
||||
switch (c) {
|
||||
case '+':
|
||||
@ -2334,14 +2372,17 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_format_specs(
|
||||
++begin;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case '#':
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin;
|
||||
enter_state(state::hash, is_arithmetic_type(arg_type));
|
||||
specs.alt = true;
|
||||
++begin;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case '0':
|
||||
enter_state(state::zero);
|
||||
if (!is_arithmetic_type(arg_type))
|
||||
if (!is_arithmetic_type(arg_type)) {
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin;
|
||||
throw_format_error("format specifier requires numeric argument");
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (specs.align == align::none) {
|
||||
// Ignore 0 if align is specified for compatibility with std::format.
|
||||
specs.align = align::numeric;
|
||||
@ -2363,12 +2404,14 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_format_specs(
|
||||
begin = parse_dynamic_spec(begin, end, specs.width, specs.width_ref, ctx);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case '.':
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin;
|
||||
enter_state(state::precision,
|
||||
in(arg_type, float_set | string_set | cstring_set));
|
||||
begin = parse_precision(begin, end, specs.precision, specs.precision_ref,
|
||||
ctx);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'L':
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::none_type) return begin;
|
||||
enter_state(state::locale, is_arithmetic_type(arg_type));
|
||||
specs.localized = true;
|
||||
++begin;
|
||||
@ -2402,6 +2445,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR FMT_INLINE auto parse_format_specs(
|
||||
case 'G':
|
||||
return parse_presentation_type(pres::general_upper, float_set);
|
||||
case 'c':
|
||||
if (arg_type == type::bool_type)
|
||||
throw_format_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
return parse_presentation_type(pres::chr, integral_set);
|
||||
case 's':
|
||||
return parse_presentation_type(pres::string,
|
||||
@ -2541,8 +2586,8 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_format_specs(ParseContext& ctx)
|
||||
decltype(arg_mapper<context>().map(std::declval<const T&>())),
|
||||
typename strip_named_arg<T>::type>;
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_if_constexpr)
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_default_constructible_v<
|
||||
formatter<mapped_type, char_type>>) {
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_default_constructible<
|
||||
formatter<mapped_type, char_type>>::value) {
|
||||
return formatter<mapped_type, char_type>().parse(ctx);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
type_is_unformattable_for<T, char_type> _;
|
||||
@ -2667,7 +2712,9 @@ template <typename Char = char> struct vformat_args {
|
||||
using type = basic_format_args<
|
||||
basic_format_context<std::back_insert_iterator<buffer<Char>>, Char>>;
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <> struct vformat_args<char> { using type = format_args; };
|
||||
template <> struct vformat_args<char> {
|
||||
using type = format_args;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Use vformat_args and avoid type_identity to keep symbols short.
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@
|
||||
# include <locale>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(FMT_WINDOWS_NO_WCHAR)
|
||||
# include <io.h> // _isatty
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,8 +58,8 @@ FMT_FUNC void format_error_code(detail::buffer<char>& out, int error_code,
|
||||
error_code_size += detail::to_unsigned(detail::count_digits(abs_value));
|
||||
auto it = buffer_appender<char>(out);
|
||||
if (message.size() <= inline_buffer_size - error_code_size)
|
||||
format_to(it, FMT_STRING("{}{}"), message, SEP);
|
||||
format_to(it, FMT_STRING("{}{}"), ERROR_STR, error_code);
|
||||
fmt::format_to(it, FMT_STRING("{}{}"), message, SEP);
|
||||
fmt::format_to(it, FMT_STRING("{}{}"), ERROR_STR, error_code);
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(out.size() <= inline_buffer_size, "");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,9 +73,8 @@ FMT_FUNC void report_error(format_func func, int error_code,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A wrapper around fwrite that throws on error.
|
||||
inline void fwrite_fully(const void* ptr, size_t size, size_t count,
|
||||
FILE* stream) {
|
||||
size_t written = std::fwrite(ptr, size, count, stream);
|
||||
inline void fwrite_fully(const void* ptr, size_t count, FILE* stream) {
|
||||
size_t written = std::fwrite(ptr, 1, count, stream);
|
||||
if (written < count)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot write to file")));
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -86,7 +85,7 @@ locale_ref::locale_ref(const Locale& loc) : locale_(&loc) {
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<Locale, std::locale>::value, "");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Locale> Locale locale_ref::get() const {
|
||||
template <typename Locale> auto locale_ref::get() const -> Locale {
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<Locale, std::locale>::value, "");
|
||||
return locale_ ? *static_cast<const std::locale*>(locale_) : std::locale();
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -98,7 +97,8 @@ FMT_FUNC auto thousands_sep_impl(locale_ref loc) -> thousands_sep_result<Char> {
|
||||
auto thousands_sep = grouping.empty() ? Char() : facet.thousands_sep();
|
||||
return {std::move(grouping), thousands_sep};
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename Char> FMT_FUNC Char decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc) {
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto decimal_point_impl(locale_ref loc) -> Char {
|
||||
return std::use_facet<std::numpunct<Char>>(loc.get<std::locale>())
|
||||
.decimal_point();
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -144,24 +144,25 @@ FMT_API FMT_FUNC auto format_facet<std::locale>::do_put(
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_FUNC std::system_error vsystem_error(int error_code, string_view fmt,
|
||||
format_args args) {
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto vsystem_error(int error_code, string_view fmt, format_args args)
|
||||
-> std::system_error {
|
||||
auto ec = std::error_code(error_code, std::generic_category());
|
||||
return std::system_error(ec, vformat(fmt, args));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename F> inline bool operator==(basic_fp<F> x, basic_fp<F> y) {
|
||||
template <typename F>
|
||||
inline auto operator==(basic_fp<F> x, basic_fp<F> y) -> bool {
|
||||
return x.f == y.f && x.e == y.e;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compilers should be able to optimize this into the ror instruction.
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint32_t rotr(uint32_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto rotr(uint32_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept -> uint32_t {
|
||||
r &= 31;
|
||||
return (n >> r) | (n << (32 - r));
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint64_t rotr(uint64_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto rotr(uint64_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept -> uint64_t {
|
||||
r &= 63;
|
||||
return (n >> r) | (n << (64 - r));
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -170,14 +171,14 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint64_t rotr(uint64_t n, uint32_t r) noexcept {
|
||||
namespace dragonbox {
|
||||
// Computes upper 64 bits of multiplication of a 32-bit unsigned integer and a
|
||||
// 64-bit unsigned integer.
|
||||
inline uint64_t umul96_upper64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto umul96_upper64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept -> uint64_t {
|
||||
return umul128_upper64(static_cast<uint64_t>(x) << 32, y);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes lower 128 bits of multiplication of a 64-bit unsigned integer and a
|
||||
// 128-bit unsigned integer.
|
||||
inline uint128_fallback umul192_lower128(uint64_t x,
|
||||
uint128_fallback y) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto umul192_lower128(uint64_t x, uint128_fallback y) noexcept
|
||||
-> uint128_fallback {
|
||||
uint64_t high = x * y.high();
|
||||
uint128_fallback high_low = umul128(x, y.low());
|
||||
return {high + high_low.high(), high_low.low()};
|
||||
@ -185,12 +186,12 @@ inline uint128_fallback umul192_lower128(uint64_t x,
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes lower 64 bits of multiplication of a 32-bit unsigned integer and a
|
||||
// 64-bit unsigned integer.
|
||||
inline uint64_t umul96_lower64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto umul96_lower64(uint32_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept -> uint64_t {
|
||||
return x * y;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Various fast log computations.
|
||||
inline int floor_log10_pow2_minus_log10_4_over_3(int e) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto floor_log10_pow2_minus_log10_4_over_3(int e) noexcept -> int {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(e <= 2936 && e >= -2985, "too large exponent");
|
||||
return (e * 631305 - 261663) >> 21;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -204,7 +205,7 @@ FMT_INLINE_VARIABLE constexpr struct {
|
||||
// divisible by pow(10, N).
|
||||
// Precondition: n <= pow(10, N + 1).
|
||||
template <int N>
|
||||
bool check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow10(uint32_t& n) noexcept {
|
||||
auto check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow10(uint32_t& n) noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
// The numbers below are chosen such that:
|
||||
// 1. floor(n/d) = floor(nm / 2^k) where d=10 or d=100,
|
||||
// 2. nm mod 2^k < m if and only if n is divisible by d,
|
||||
@ -229,7 +230,7 @@ bool check_divisibility_and_divide_by_pow10(uint32_t& n) noexcept {
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes floor(n / pow(10, N)) for small n and N.
|
||||
// Precondition: n <= pow(10, N + 1).
|
||||
template <int N> uint32_t small_division_by_pow10(uint32_t n) noexcept {
|
||||
template <int N> auto small_division_by_pow10(uint32_t n) noexcept -> uint32_t {
|
||||
constexpr auto info = div_small_pow10_infos[N - 1];
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(n <= info.divisor * 10, "n is too large");
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t magic_number =
|
||||
@ -238,12 +239,12 @@ template <int N> uint32_t small_division_by_pow10(uint32_t n) noexcept {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes floor(n / 10^(kappa + 1)) (float)
|
||||
inline uint32_t divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint32_t n) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint32_t n) noexcept -> uint32_t {
|
||||
// 1374389535 = ceil(2^37/100)
|
||||
return static_cast<uint32_t>((static_cast<uint64_t>(n) * 1374389535) >> 37);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Computes floor(n / 10^(kappa + 1)) (double)
|
||||
inline uint64_t divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint64_t n) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto divide_by_10_to_kappa_plus_1(uint64_t n) noexcept -> uint64_t {
|
||||
// 2361183241434822607 = ceil(2^(64+7)/1000)
|
||||
return umul128_upper64(n, 2361183241434822607ull) >> 7;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -255,7 +256,7 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<float> {
|
||||
using carrier_uint = float_info<float>::carrier_uint;
|
||||
using cache_entry_type = uint64_t;
|
||||
|
||||
static uint64_t get_cached_power(int k) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto get_cached_power(int k) noexcept -> uint64_t {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(k >= float_info<float>::min_k && k <= float_info<float>::max_k,
|
||||
"k is out of range");
|
||||
static constexpr const uint64_t pow10_significands[] = {
|
||||
@ -297,20 +298,23 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<float> {
|
||||
bool is_integer;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
static compute_mul_result compute_mul(
|
||||
carrier_uint u, const cache_entry_type& cache) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_mul(carrier_uint u,
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache) noexcept
|
||||
-> compute_mul_result {
|
||||
auto r = umul96_upper64(u, cache);
|
||||
return {static_cast<carrier_uint>(r >> 32),
|
||||
static_cast<carrier_uint>(r) == 0};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static uint32_t compute_delta(const cache_entry_type& cache,
|
||||
int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_delta(const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept
|
||||
-> uint32_t {
|
||||
return static_cast<uint32_t>(cache >> (64 - 1 - beta));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static compute_mul_parity_result compute_mul_parity(
|
||||
carrier_uint two_f, const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_mul_parity(carrier_uint two_f,
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache,
|
||||
int beta) noexcept
|
||||
-> compute_mul_parity_result {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(beta >= 1, "");
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(beta < 64, "");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -319,22 +323,22 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<float> {
|
||||
static_cast<uint32_t>(r >> (32 - beta)) == 0};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static carrier_uint compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept -> carrier_uint {
|
||||
return static_cast<carrier_uint>(
|
||||
(cache - (cache >> (num_significand_bits<float>() + 2))) >>
|
||||
(64 - num_significand_bits<float>() - 1 - beta));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static carrier_uint compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept -> carrier_uint {
|
||||
return static_cast<carrier_uint>(
|
||||
(cache + (cache >> (num_significand_bits<float>() + 1))) >>
|
||||
(64 - num_significand_bits<float>() - 1 - beta));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static carrier_uint compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept -> carrier_uint {
|
||||
return (static_cast<carrier_uint>(
|
||||
cache >> (64 - num_significand_bits<float>() - 2 - beta)) +
|
||||
1) /
|
||||
@ -346,7 +350,7 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> {
|
||||
using carrier_uint = float_info<double>::carrier_uint;
|
||||
using cache_entry_type = uint128_fallback;
|
||||
|
||||
static uint128_fallback get_cached_power(int k) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto get_cached_power(int k) noexcept -> uint128_fallback {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(k >= float_info<double>::min_k && k <= float_info<double>::max_k,
|
||||
"k is out of range");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -985,8 +989,7 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> {
|
||||
{0xe0accfa875af45a7, 0x93eb1b80a33b8606},
|
||||
{0x8c6c01c9498d8b88, 0xbc72f130660533c4},
|
||||
{0xaf87023b9bf0ee6a, 0xeb8fad7c7f8680b5},
|
||||
{ 0xdb68c2ca82ed2a05,
|
||||
0xa67398db9f6820e2 }
|
||||
{0xdb68c2ca82ed2a05, 0xa67398db9f6820e2},
|
||||
#else
|
||||
{0xff77b1fcbebcdc4f, 0x25e8e89c13bb0f7b},
|
||||
{0xce5d73ff402d98e3, 0xfb0a3d212dc81290},
|
||||
@ -1071,19 +1074,22 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> {
|
||||
bool is_integer;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
static compute_mul_result compute_mul(
|
||||
carrier_uint u, const cache_entry_type& cache) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_mul(carrier_uint u,
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache) noexcept
|
||||
-> compute_mul_result {
|
||||
auto r = umul192_upper128(u, cache);
|
||||
return {r.high(), r.low() == 0};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static uint32_t compute_delta(cache_entry_type const& cache,
|
||||
int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_delta(cache_entry_type const& cache, int beta) noexcept
|
||||
-> uint32_t {
|
||||
return static_cast<uint32_t>(cache.high() >> (64 - 1 - beta));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static compute_mul_parity_result compute_mul_parity(
|
||||
carrier_uint two_f, const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_mul_parity(carrier_uint two_f,
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache,
|
||||
int beta) noexcept
|
||||
-> compute_mul_parity_result {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(beta >= 1, "");
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(beta < 64, "");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1092,35 +1098,35 @@ template <> struct cache_accessor<double> {
|
||||
((r.high() << beta) | (r.low() >> (64 - beta))) == 0};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static carrier_uint compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_left_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept -> carrier_uint {
|
||||
return (cache.high() -
|
||||
(cache.high() >> (num_significand_bits<double>() + 2))) >>
|
||||
(64 - num_significand_bits<double>() - 1 - beta);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static carrier_uint compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_right_endpoint_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept -> carrier_uint {
|
||||
return (cache.high() +
|
||||
(cache.high() >> (num_significand_bits<double>() + 1))) >>
|
||||
(64 - num_significand_bits<double>() - 1 - beta);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static carrier_uint compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept {
|
||||
static auto compute_round_up_for_shorter_interval_case(
|
||||
const cache_entry_type& cache, int beta) noexcept -> carrier_uint {
|
||||
return ((cache.high() >> (64 - num_significand_bits<double>() - 2 - beta)) +
|
||||
1) /
|
||||
2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_FUNC uint128_fallback get_cached_power(int k) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto get_cached_power(int k) noexcept -> uint128_fallback {
|
||||
return cache_accessor<double>::get_cached_power(k);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Various integer checks
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
bool is_left_endpoint_integer_shorter_interval(int exponent) noexcept {
|
||||
auto is_left_endpoint_integer_shorter_interval(int exponent) noexcept -> bool {
|
||||
const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold = 2;
|
||||
const int case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_upper_threshold = 3;
|
||||
return exponent >= case_shorter_interval_left_endpoint_lower_threshold &&
|
||||
@ -1132,7 +1138,7 @@ FMT_INLINE int remove_trailing_zeros(uint32_t& n, int s = 0) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(n != 0, "");
|
||||
// Modular inverse of 5 (mod 2^32): (mod_inv_5 * 5) mod 2^32 = 1.
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t mod_inv_5 = 0xcccccccd;
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t mod_inv_25 = 0xc28f5c29; // = mod_inv_5 * mod_inv_5
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t mod_inv_25 = 0xc28f5c29; // = mod_inv_5 * mod_inv_5
|
||||
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
auto q = rotr(n * mod_inv_25, 2);
|
||||
@ -1168,7 +1174,7 @@ FMT_INLINE int remove_trailing_zeros(uint64_t& n) noexcept {
|
||||
|
||||
// If n is not divisible by 10^8, work with n itself.
|
||||
constexpr uint64_t mod_inv_5 = 0xcccccccccccccccd;
|
||||
constexpr uint64_t mod_inv_25 = 0x8f5c28f5c28f5c29; // = mod_inv_5 * mod_inv_5
|
||||
constexpr uint64_t mod_inv_25 = 0x8f5c28f5c28f5c29; // mod_inv_5 * mod_inv_5
|
||||
|
||||
int s = 0;
|
||||
while (true) {
|
||||
@ -1234,7 +1240,7 @@ FMT_INLINE decimal_fp<T> shorter_interval_case(int exponent) noexcept {
|
||||
return ret_value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> decimal_fp<T> to_decimal(T x) noexcept {
|
||||
template <typename T> auto to_decimal(T x) noexcept -> decimal_fp<T> {
|
||||
// Step 1: integer promotion & Schubfach multiplier calculation.
|
||||
|
||||
using carrier_uint = typename float_info<T>::carrier_uint;
|
||||
@ -1373,15 +1379,15 @@ template <> struct formatter<detail::bigint> {
|
||||
for (auto i = n.bigits_.size(); i > 0; --i) {
|
||||
auto value = n.bigits_[i - 1u];
|
||||
if (first) {
|
||||
out = format_to(out, FMT_STRING("{:x}"), value);
|
||||
out = fmt::format_to(out, FMT_STRING("{:x}"), value);
|
||||
first = false;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
out = format_to(out, FMT_STRING("{:08x}"), value);
|
||||
out = fmt::format_to(out, FMT_STRING("{:08x}"), value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (n.exp_ > 0)
|
||||
out = format_to(out, FMT_STRING("p{}"),
|
||||
n.exp_ * detail::bigint::bigit_bits);
|
||||
out = fmt::format_to(out, FMT_STRING("p{}"),
|
||||
n.exp_ * detail::bigint::bigit_bits);
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -1417,7 +1423,7 @@ FMT_FUNC void report_system_error(int error_code,
|
||||
report_error(format_system_error, error_code, message);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_FUNC std::string vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) {
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) -> std::string {
|
||||
// Don't optimize the "{}" case to keep the binary size small and because it
|
||||
// can be better optimized in fmt::format anyway.
|
||||
auto buffer = memory_buffer();
|
||||
@ -1426,33 +1432,43 @@ FMT_FUNC std::string vformat(string_view fmt, format_args args) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
#ifndef _WIN32
|
||||
FMT_FUNC bool write_console(std::FILE*, string_view) { return false; }
|
||||
#if !defined(_WIN32) || defined(FMT_WINDOWS_NO_WCHAR)
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto write_console(int, string_view) -> bool { return false; }
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto write_console(std::FILE*, string_view) -> bool { return false; }
|
||||
#else
|
||||
using dword = conditional_t<sizeof(long) == 4, unsigned long, unsigned>;
|
||||
extern "C" __declspec(dllimport) int __stdcall WriteConsoleW( //
|
||||
void*, const void*, dword, dword*, void*);
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_FUNC bool write_console(std::FILE* f, string_view text) {
|
||||
auto fd = _fileno(f);
|
||||
if (!_isatty(fd)) return false;
|
||||
FMT_FUNC bool write_console(int fd, string_view text) {
|
||||
auto u16 = utf8_to_utf16(text);
|
||||
auto written = dword();
|
||||
return WriteConsoleW(reinterpret_cast<void*>(_get_osfhandle(fd)), u16.c_str(),
|
||||
static_cast<uint32_t>(u16.size()), &written, nullptr) != 0;
|
||||
static_cast<dword>(u16.size()), nullptr, nullptr) != 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_FUNC auto write_console(std::FILE* f, string_view text) -> bool {
|
||||
return write_console(_fileno(f), text);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
// Print assuming legacy (non-Unicode) encoding.
|
||||
FMT_FUNC void vprint_mojibake(std::FILE* f, string_view fmt, format_args args) {
|
||||
auto buffer = memory_buffer();
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt,
|
||||
basic_format_args<buffer_context<char>>(args));
|
||||
fwrite_fully(buffer.data(), 1, buffer.size(), f);
|
||||
detail::vformat_to(buffer, fmt, args);
|
||||
fwrite_fully(buffer.data(), buffer.size(), f);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_FUNC void print(std::FILE* f, string_view text) {
|
||||
if (!write_console(f, text)) fwrite_fully(text.data(), 1, text.size(), f);
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
int fd = _fileno(f);
|
||||
if (_isatty(fd)) {
|
||||
std::fflush(f);
|
||||
if (write_console(fd, text)) return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
fwrite_fully(text.data(), text.size(), f);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@
|
||||
#include <system_error> // std::system_error
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_bit_cast
|
||||
# include <bit> // std::bitcast
|
||||
# include <bit> // std::bit_cast
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "core.h"
|
||||
@ -93,10 +93,11 @@
|
||||
# define FMT_NO_UNIQUE_ADDRESS
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_GCC_VERSION || defined(__clang__)
|
||||
# define FMT_VISIBILITY(value) __attribute__((visibility(value)))
|
||||
// Visibility when compiled as a shared library/object.
|
||||
#if defined(FMT_LIB_EXPORT) || defined(FMT_SHARED)
|
||||
# define FMT_SO_VISIBILITY(value) FMT_VISIBILITY(value)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_VISIBILITY(value)
|
||||
# define FMT_SO_VISIBILITY(value)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __has_builtin
|
||||
@ -152,7 +153,10 @@ FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS
|
||||
// EDG based compilers (Intel, NVIDIA, Elbrus, etc), GCC and MSVC support UDLs.
|
||||
# if (FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_user_literals) || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 407 || \
|
||||
//
|
||||
// GCC before 4.9 requires a space in `operator"" _a` which is invalid in later
|
||||
// compiler versions.
|
||||
# if (FMT_HAS_FEATURE(cxx_user_literals) || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 409 || \
|
||||
FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1900) && \
|
||||
(!defined(__EDG_VERSION__) || __EDG_VERSION__ >= /* UDL feature */ 480)
|
||||
# define FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS 1
|
||||
@ -273,19 +277,6 @@ FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename...> struct disjunction : std::false_type {};
|
||||
template <typename P> struct disjunction<P> : P {};
|
||||
template <typename P1, typename... Pn>
|
||||
struct disjunction<P1, Pn...>
|
||||
: conditional_t<bool(P1::value), P1, disjunction<Pn...>> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename...> struct conjunction : std::true_type {};
|
||||
template <typename P> struct conjunction<P> : P {};
|
||||
template <typename P1, typename... Pn>
|
||||
struct conjunction<P1, Pn...>
|
||||
: conditional_t<bool(P1::value), conjunction<Pn...>, P1> {};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline void abort_fuzzing_if(bool condition) {
|
||||
@ -307,37 +298,6 @@ template <typename CharT, CharT... C>
|
||||
constexpr CharT string_literal<CharT, C...>::value[sizeof...(C)];
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Streambuf> class formatbuf : public Streambuf {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using char_type = typename Streambuf::char_type;
|
||||
using streamsize = decltype(std::declval<Streambuf>().sputn(nullptr, 0));
|
||||
using int_type = typename Streambuf::int_type;
|
||||
using traits_type = typename Streambuf::traits_type;
|
||||
|
||||
buffer<char_type>& buffer_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit formatbuf(buffer<char_type>& buf) : buffer_(buf) {}
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
// The put area is always empty. This makes the implementation simpler and has
|
||||
// the advantage that the streambuf and the buffer are always in sync and
|
||||
// sputc never writes into uninitialized memory. A disadvantage is that each
|
||||
// call to sputc always results in a (virtual) call to overflow. There is no
|
||||
// disadvantage here for sputn since this always results in a call to xsputn.
|
||||
|
||||
auto overflow(int_type ch) -> int_type override {
|
||||
if (!traits_type::eq_int_type(ch, traits_type::eof()))
|
||||
buffer_.push_back(static_cast<char_type>(ch));
|
||||
return ch;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto xsputn(const char_type* s, streamsize count) -> streamsize override {
|
||||
buffer_.append(s, s + count);
|
||||
return count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Implementation of std::bit_cast for pre-C++20.
|
||||
template <typename To, typename From, FMT_ENABLE_IF(sizeof(To) == sizeof(From))>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto bit_cast(const From& from) -> To {
|
||||
@ -373,8 +333,8 @@ class uint128_fallback {
|
||||
constexpr uint128_fallback(uint64_t hi, uint64_t lo) : lo_(lo), hi_(hi) {}
|
||||
constexpr uint128_fallback(uint64_t value = 0) : lo_(value), hi_(0) {}
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr uint64_t high() const noexcept { return hi_; }
|
||||
constexpr uint64_t low() const noexcept { return lo_; }
|
||||
constexpr auto high() const noexcept -> uint64_t { return hi_; }
|
||||
constexpr auto low() const noexcept -> uint64_t { return lo_; }
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_integral<T>::value)>
|
||||
constexpr explicit operator T() const {
|
||||
@ -450,7 +410,7 @@ class uint128_fallback {
|
||||
hi_ &= n.hi_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 uint128_fallback& operator+=(uint64_t n) noexcept {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto operator+=(uint64_t n) noexcept -> uint128_fallback& {
|
||||
if (is_constant_evaluated()) {
|
||||
lo_ += n;
|
||||
hi_ += (lo_ < n ? 1 : 0);
|
||||
@ -740,7 +700,7 @@ inline auto compute_width(basic_string_view<Char> s) -> size_t {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes approximate display width of a UTF-8 string.
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline size_t compute_width(string_view s) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto compute_width(string_view s) -> size_t {
|
||||
size_t num_code_points = 0;
|
||||
// It is not a lambda for compatibility with C++14.
|
||||
struct count_code_points {
|
||||
@ -787,12 +747,17 @@ inline auto code_point_index(basic_string_view<Char> s, size_t n) -> size_t {
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculates the index of the nth code point in a UTF-8 string.
|
||||
inline auto code_point_index(string_view s, size_t n) -> size_t {
|
||||
const char* data = s.data();
|
||||
size_t num_code_points = 0;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0, size = s.size(); i != size; ++i) {
|
||||
if ((data[i] & 0xc0) != 0x80 && ++num_code_points > n) return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.size();
|
||||
size_t result = s.size();
|
||||
const char* begin = s.begin();
|
||||
for_each_codepoint(s, [begin, &n, &result](uint32_t, string_view sv) {
|
||||
if (n != 0) {
|
||||
--n;
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
result = to_unsigned(sv.begin() - begin);
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
});
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto code_point_index(basic_string_view<char8_type> s, size_t n)
|
||||
@ -902,7 +867,7 @@ enum { inline_buffer_size = 500 };
|
||||
**Example**::
|
||||
|
||||
auto out = fmt::memory_buffer();
|
||||
format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "The answer is {}.", 42);
|
||||
fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), "The answer is {}.", 42);
|
||||
|
||||
This will append the following output to the ``out`` object:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1018,7 +983,6 @@ class basic_memory_buffer final : public detail::buffer<T> {
|
||||
/** Increases the buffer capacity to *new_capacity*. */
|
||||
void reserve(size_t new_capacity) { this->try_reserve(new_capacity); }
|
||||
|
||||
// Directly append data into the buffer
|
||||
using detail::buffer<T>::append;
|
||||
template <typename ContiguousRange>
|
||||
void append(const ContiguousRange& range) {
|
||||
@ -1034,7 +998,8 @@ struct is_contiguous<basic_memory_buffer<T, SIZE, Allocator>> : std::true_type {
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_EXPORT
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
FMT_API bool write_console(std::FILE* f, string_view text);
|
||||
FMT_API auto write_console(int fd, string_view text) -> bool;
|
||||
FMT_API auto write_console(std::FILE* f, string_view text) -> bool;
|
||||
FMT_API void print(std::FILE*, string_view);
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1046,7 +1011,7 @@ FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/** An error reported from a formatting function. */
|
||||
class FMT_VISIBILITY("default") format_error : public std::runtime_error {
|
||||
class FMT_SO_VISIBILITY("default") format_error : public std::runtime_error {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using std::runtime_error::runtime_error;
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -1153,13 +1118,13 @@ using uint32_or_64_or_128_t =
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
using uint64_or_128_t = conditional_t<num_bits<T>() <= 64, uint64_t, uint128_t>;
|
||||
|
||||
#define FMT_POWERS_OF_10(factor) \
|
||||
factor * 10, (factor)*100, (factor)*1000, (factor)*10000, (factor)*100000, \
|
||||
(factor)*1000000, (factor)*10000000, (factor)*100000000, \
|
||||
(factor)*1000000000
|
||||
#define FMT_POWERS_OF_10(factor) \
|
||||
factor * 10, (factor) * 100, (factor) * 1000, (factor) * 10000, \
|
||||
(factor) * 100000, (factor) * 1000000, (factor) * 10000000, \
|
||||
(factor) * 100000000, (factor) * 1000000000
|
||||
|
||||
// Converts value in the range [0, 100) to a string.
|
||||
constexpr const char* digits2(size_t value) {
|
||||
constexpr auto digits2(size_t value) -> const char* {
|
||||
// GCC generates slightly better code when value is pointer-size.
|
||||
return &"0001020304050607080910111213141516171819"
|
||||
"2021222324252627282930313233343536373839"
|
||||
@ -1169,7 +1134,7 @@ constexpr const char* digits2(size_t value) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Sign is a template parameter to workaround a bug in gcc 4.8.
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Sign> constexpr Char sign(Sign s) {
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename Sign> constexpr auto sign(Sign s) -> Char {
|
||||
#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 604
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<Sign, sign_t>::value, "");
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1394,7 +1359,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto format_uint(It out, UInt value, int num_digits,
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Buffer should be large enough to hold all digits (digits / BASE_BITS + 1).
|
||||
char buffer[num_bits<UInt>() / BASE_BITS + 1];
|
||||
char buffer[num_bits<UInt>() / BASE_BITS + 1] = {};
|
||||
format_uint<BASE_BITS>(buffer, value, num_digits, upper);
|
||||
return detail::copy_str_noinline<Char>(buffer, buffer + num_digits, out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1430,22 +1395,23 @@ template <typename WChar, typename Buffer = memory_buffer> class to_utf8 {
|
||||
: "invalid utf32"));
|
||||
}
|
||||
operator string_view() const { return string_view(&buffer_[0], size()); }
|
||||
size_t size() const { return buffer_.size() - 1; }
|
||||
const char* c_str() const { return &buffer_[0]; }
|
||||
std::string str() const { return std::string(&buffer_[0], size()); }
|
||||
auto size() const -> size_t { return buffer_.size() - 1; }
|
||||
auto c_str() const -> const char* { return &buffer_[0]; }
|
||||
auto str() const -> std::string { return std::string(&buffer_[0], size()); }
|
||||
|
||||
// Performs conversion returning a bool instead of throwing exception on
|
||||
// conversion error. This method may still throw in case of memory allocation
|
||||
// error.
|
||||
bool convert(basic_string_view<WChar> s,
|
||||
to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort) {
|
||||
auto convert(basic_string_view<WChar> s,
|
||||
to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort)
|
||||
-> bool {
|
||||
if (!convert(buffer_, s, policy)) return false;
|
||||
buffer_.push_back(0);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static bool convert(
|
||||
Buffer& buf, basic_string_view<WChar> s,
|
||||
to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort) {
|
||||
static auto convert(Buffer& buf, basic_string_view<WChar> s,
|
||||
to_utf8_error_policy policy = to_utf8_error_policy::abort)
|
||||
-> bool {
|
||||
for (auto p = s.begin(); p != s.end(); ++p) {
|
||||
uint32_t c = static_cast<uint32_t>(*p);
|
||||
if (sizeof(WChar) == 2 && c >= 0xd800 && c <= 0xdfff) {
|
||||
@ -1481,7 +1447,7 @@ template <typename WChar, typename Buffer = memory_buffer> class to_utf8 {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes 128-bit result of multiplication of two 64-bit unsigned integers.
|
||||
inline uint128_fallback umul128(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto umul128(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept -> uint128_fallback {
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_INT128
|
||||
auto p = static_cast<uint128_opt>(x) * static_cast<uint128_opt>(y);
|
||||
return {static_cast<uint64_t>(p >> 64), static_cast<uint64_t>(p)};
|
||||
@ -1512,19 +1478,19 @@ inline uint128_fallback umul128(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept {
|
||||
namespace dragonbox {
|
||||
// Computes floor(log10(pow(2, e))) for e in [-2620, 2620] using the method from
|
||||
// https://fmt.dev/papers/Dragonbox.pdf#page=28, section 6.1.
|
||||
inline int floor_log10_pow2(int e) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto floor_log10_pow2(int e) noexcept -> int {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(e <= 2620 && e >= -2620, "too large exponent");
|
||||
static_assert((-1 >> 1) == -1, "right shift is not arithmetic");
|
||||
return (e * 315653) >> 20;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline int floor_log2_pow10(int e) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto floor_log2_pow10(int e) noexcept -> int {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(e <= 1233 && e >= -1233, "too large exponent");
|
||||
return (e * 1741647) >> 19;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes upper 64 bits of multiplication of two 64-bit unsigned integers.
|
||||
inline uint64_t umul128_upper64(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto umul128_upper64(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept -> uint64_t {
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_INT128
|
||||
auto p = static_cast<uint128_opt>(x) * static_cast<uint128_opt>(y);
|
||||
return static_cast<uint64_t>(p >> 64);
|
||||
@ -1537,14 +1503,14 @@ inline uint64_t umul128_upper64(uint64_t x, uint64_t y) noexcept {
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes upper 128 bits of multiplication of a 64-bit unsigned integer and a
|
||||
// 128-bit unsigned integer.
|
||||
inline uint128_fallback umul192_upper128(uint64_t x,
|
||||
uint128_fallback y) noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto umul192_upper128(uint64_t x, uint128_fallback y) noexcept
|
||||
-> uint128_fallback {
|
||||
uint128_fallback r = umul128(x, y.high());
|
||||
r += umul128_upper64(x, y.low());
|
||||
return r;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_API uint128_fallback get_cached_power(int k) noexcept;
|
||||
FMT_API auto get_cached_power(int k) noexcept -> uint128_fallback;
|
||||
|
||||
// Type-specific information that Dragonbox uses.
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Enable = void> struct float_info;
|
||||
@ -1598,14 +1564,14 @@ template <typename T> FMT_API auto to_decimal(T x) noexcept -> decimal_fp<T>;
|
||||
} // namespace dragonbox
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns true iff Float has the implicit bit which is not stored.
|
||||
template <typename Float> constexpr bool has_implicit_bit() {
|
||||
template <typename Float> constexpr auto has_implicit_bit() -> bool {
|
||||
// An 80-bit FP number has a 64-bit significand an no implicit bit.
|
||||
return std::numeric_limits<Float>::digits != 64;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the number of significand bits stored in Float. The implicit bit is
|
||||
// not counted since it is not stored.
|
||||
template <typename Float> constexpr int num_significand_bits() {
|
||||
template <typename Float> constexpr auto num_significand_bits() -> int {
|
||||
// std::numeric_limits may not support __float128.
|
||||
return is_float128<Float>() ? 112
|
||||
: (std::numeric_limits<Float>::digits -
|
||||
@ -1698,7 +1664,7 @@ using fp = basic_fp<unsigned long long>;
|
||||
|
||||
// Normalizes the value converted from double and multiplied by (1 << SHIFT).
|
||||
template <int SHIFT = 0, typename F>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_fp<F> normalize(basic_fp<F> value) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto normalize(basic_fp<F> value) -> basic_fp<F> {
|
||||
// Handle subnormals.
|
||||
const auto implicit_bit = F(1) << num_significand_bits<double>();
|
||||
const auto shifted_implicit_bit = implicit_bit << SHIFT;
|
||||
@ -1715,7 +1681,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_fp<F> normalize(basic_fp<F> value) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes lhs * rhs / pow(2, 64) rounded to nearest with half-up tie breaking.
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint64_t multiply(uint64_t lhs, uint64_t rhs) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto multiply(uint64_t lhs, uint64_t rhs) -> uint64_t {
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_INT128
|
||||
auto product = static_cast<__uint128_t>(lhs) * rhs;
|
||||
auto f = static_cast<uint64_t>(product >> 64);
|
||||
@ -1732,33 +1698,10 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR inline uint64_t multiply(uint64_t lhs, uint64_t rhs) {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline fp operator*(fp x, fp y) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline auto operator*(fp x, fp y) -> fp {
|
||||
return {multiply(x.f, y.f), x.e + y.e + 64};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T = void> struct basic_data {
|
||||
// For checking rounding thresholds.
|
||||
// The kth entry is chosen to be the smallest integer such that the
|
||||
// upper 32-bits of 10^(k+1) times it is strictly bigger than 5 * 10^k.
|
||||
static constexpr uint32_t fractional_part_rounding_thresholds[8] = {
|
||||
2576980378U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^1)
|
||||
2190433321U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^2)
|
||||
2151778616U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^3)
|
||||
2147913145U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^4)
|
||||
2147526598U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^5)
|
||||
2147487943U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^6)
|
||||
2147484078U, // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^7)
|
||||
2147483691U // ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^8)
|
||||
};
|
||||
};
|
||||
// This is a struct rather than an alias to avoid shadowing warnings in gcc.
|
||||
struct data : basic_data<> {};
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS < 201703L
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
constexpr uint32_t basic_data<T>::fractional_part_rounding_thresholds[];
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, bool doublish = num_bits<T>() == num_bits<double>()>
|
||||
using convert_float_result =
|
||||
conditional_t<std::is_same<T, float>::value || doublish, double, T>;
|
||||
@ -1977,11 +1920,13 @@ auto write_escaped_string(OutputIt out, basic_string_view<Char> str)
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
auto write_escaped_char(OutputIt out, Char v) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
Char v_array[1] = {v};
|
||||
*out++ = static_cast<Char>('\'');
|
||||
if ((needs_escape(static_cast<uint32_t>(v)) && v != static_cast<Char>('"')) ||
|
||||
v == static_cast<Char>('\'')) {
|
||||
out = write_escaped_cp(
|
||||
out, find_escape_result<Char>{&v, &v + 1, static_cast<uint32_t>(v)});
|
||||
out = write_escaped_cp(out,
|
||||
find_escape_result<Char>{v_array, v_array + 1,
|
||||
static_cast<uint32_t>(v)});
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*out++ = v;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -2070,10 +2015,10 @@ template <typename Char> class digit_grouping {
|
||||
std::string::const_iterator group;
|
||||
int pos;
|
||||
};
|
||||
next_state initial_state() const { return {grouping_.begin(), 0}; }
|
||||
auto initial_state() const -> next_state { return {grouping_.begin(), 0}; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the next digit group separator position.
|
||||
int next(next_state& state) const {
|
||||
auto next(next_state& state) const -> int {
|
||||
if (thousands_sep_.empty()) return max_value<int>();
|
||||
if (state.group == grouping_.end()) return state.pos += grouping_.back();
|
||||
if (*state.group <= 0 || *state.group == max_value<char>())
|
||||
@ -2092,9 +2037,9 @@ template <typename Char> class digit_grouping {
|
||||
digit_grouping(std::string grouping, std::basic_string<Char> sep)
|
||||
: grouping_(std::move(grouping)), thousands_sep_(std::move(sep)) {}
|
||||
|
||||
bool has_separator() const { return !thousands_sep_.empty(); }
|
||||
auto has_separator() const -> bool { return !thousands_sep_.empty(); }
|
||||
|
||||
int count_separators(int num_digits) const {
|
||||
auto count_separators(int num_digits) const -> int {
|
||||
int count = 0;
|
||||
auto state = initial_state();
|
||||
while (num_digits > next(state)) ++count;
|
||||
@ -2103,7 +2048,7 @@ template <typename Char> class digit_grouping {
|
||||
|
||||
// Applies grouping to digits and write the output to out.
|
||||
template <typename Out, typename C>
|
||||
Out apply(Out out, basic_string_view<C> digits) const {
|
||||
auto apply(Out out, basic_string_view<C> digits) const -> Out {
|
||||
auto num_digits = static_cast<int>(digits.size());
|
||||
auto separators = basic_memory_buffer<int>();
|
||||
separators.push_back(0);
|
||||
@ -2126,24 +2071,66 @@ template <typename Char> class digit_grouping {
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline void prefix_append(unsigned& prefix, unsigned value) {
|
||||
prefix |= prefix != 0 ? value << 8 : value;
|
||||
prefix += (1u + (value > 0xff ? 1 : 0)) << 24;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Writes a decimal integer with digit grouping.
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename UInt, typename Char>
|
||||
auto write_int(OutputIt out, UInt value, unsigned prefix,
|
||||
const format_specs<Char>& specs,
|
||||
const digit_grouping<Char>& grouping) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<uint64_or_128_t<UInt>, UInt>::value, "");
|
||||
int num_digits = count_digits(value);
|
||||
char digits[40];
|
||||
format_decimal(digits, value, num_digits);
|
||||
unsigned size = to_unsigned((prefix != 0 ? 1 : 0) + num_digits +
|
||||
grouping.count_separators(num_digits));
|
||||
int num_digits = 0;
|
||||
auto buffer = memory_buffer();
|
||||
switch (specs.type) {
|
||||
case presentation_type::none:
|
||||
case presentation_type::dec: {
|
||||
num_digits = count_digits(value);
|
||||
format_decimal<char>(appender(buffer), value, num_digits);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case presentation_type::hex_lower:
|
||||
case presentation_type::hex_upper: {
|
||||
bool upper = specs.type == presentation_type::hex_upper;
|
||||
if (specs.alt)
|
||||
prefix_append(prefix, unsigned(upper ? 'X' : 'x') << 8 | '0');
|
||||
num_digits = count_digits<4>(value);
|
||||
format_uint<4, char>(appender(buffer), value, num_digits, upper);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case presentation_type::bin_lower:
|
||||
case presentation_type::bin_upper: {
|
||||
bool upper = specs.type == presentation_type::bin_upper;
|
||||
if (specs.alt)
|
||||
prefix_append(prefix, unsigned(upper ? 'B' : 'b') << 8 | '0');
|
||||
num_digits = count_digits<1>(value);
|
||||
format_uint<1, char>(appender(buffer), value, num_digits);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case presentation_type::oct: {
|
||||
num_digits = count_digits<3>(value);
|
||||
// Octal prefix '0' is counted as a digit, so only add it if precision
|
||||
// is not greater than the number of digits.
|
||||
if (specs.alt && specs.precision <= num_digits && value != 0)
|
||||
prefix_append(prefix, '0');
|
||||
format_uint<3, char>(appender(buffer), value, num_digits);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case presentation_type::chr:
|
||||
return write_char(out, static_cast<Char>(value), specs);
|
||||
default:
|
||||
throw_format_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned size = (prefix != 0 ? prefix >> 24 : 0) + to_unsigned(num_digits) +
|
||||
to_unsigned(grouping.count_separators(num_digits));
|
||||
return write_padded<align::right>(
|
||||
out, specs, size, size, [&](reserve_iterator<OutputIt> it) {
|
||||
if (prefix != 0) {
|
||||
char sign = static_cast<char>(prefix);
|
||||
*it++ = static_cast<Char>(sign);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return grouping.apply(it, string_view(digits, to_unsigned(num_digits)));
|
||||
for (unsigned p = prefix & 0xffffff; p != 0; p >>= 8)
|
||||
*it++ = static_cast<Char>(p & 0xff);
|
||||
return grouping.apply(it, string_view(buffer.data(), buffer.size()));
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2156,11 +2143,6 @@ inline auto write_loc(OutputIt, loc_value, const format_specs<Char>&,
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR inline void prefix_append(unsigned& prefix, unsigned value) {
|
||||
prefix |= prefix != 0 ? value << 8 : value;
|
||||
prefix += (1u + (value > 0xff ? 1 : 0)) << 24;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename UInt> struct write_int_arg {
|
||||
UInt abs_value;
|
||||
unsigned prefix;
|
||||
@ -2307,25 +2289,25 @@ class counting_iterator {
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR counting_iterator() : count_(0) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR size_t count() const { return count_; }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto count() const -> size_t { return count_; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR counting_iterator& operator++() {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator++() -> counting_iterator& {
|
||||
++count_;
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR counting_iterator operator++(int) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator++(int) -> counting_iterator {
|
||||
auto it = *this;
|
||||
++*this;
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR friend counting_iterator operator+(counting_iterator it,
|
||||
difference_type n) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR friend auto operator+(counting_iterator it, difference_type n)
|
||||
-> counting_iterator {
|
||||
it.count_ += static_cast<size_t>(n);
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR value_type operator*() const { return {}; }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator*() const -> value_type { return {}; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
@ -2360,9 +2342,10 @@ template <typename Char, typename OutputIt>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, const Char* s,
|
||||
const format_specs<Char>& specs, locale_ref)
|
||||
-> OutputIt {
|
||||
return specs.type != presentation_type::pointer
|
||||
? write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(s), specs, {})
|
||||
: write_ptr<Char>(out, bit_cast<uintptr_t>(s), &specs);
|
||||
if (specs.type == presentation_type::pointer)
|
||||
return write_ptr<Char>(out, bit_cast<uintptr_t>(s), &specs);
|
||||
if (!s) throw_format_error("string pointer is null");
|
||||
return write(out, basic_string_view<Char>(s), specs, {});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T,
|
||||
@ -2448,9 +2431,8 @@ struct float_specs {
|
||||
bool showpoint : 1;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename ErrorHandler = error_handler, typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_float_type_spec(const format_specs<Char>& specs,
|
||||
ErrorHandler&& eh = {})
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_float_type_spec(const format_specs<Char>& specs)
|
||||
-> float_specs {
|
||||
auto result = float_specs();
|
||||
result.showpoint = specs.alt;
|
||||
@ -2486,7 +2468,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse_float_type_spec(const format_specs<Char>& specs,
|
||||
result.format = float_format::hex;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
eh.on_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
throw_format_error("invalid format specifier");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
@ -2725,12 +2707,12 @@ template <typename Char> class fallback_digit_grouping {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
constexpr fallback_digit_grouping(locale_ref, bool) {}
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr bool has_separator() const { return false; }
|
||||
constexpr auto has_separator() const -> bool { return false; }
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr int count_separators(int) const { return 0; }
|
||||
constexpr auto count_separators(int) const -> int { return 0; }
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Out, typename C>
|
||||
constexpr Out apply(Out out, basic_string_view<C>) const {
|
||||
constexpr auto apply(Out out, basic_string_view<C>) const -> Out {
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -2749,7 +2731,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto write_float(OutputIt out, const DecimalFP& f,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> constexpr bool isnan(T value) {
|
||||
template <typename T> constexpr auto isnan(T value) -> bool {
|
||||
return !(value >= value); // std::isnan doesn't support __float128.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2762,14 +2744,14 @@ struct has_isfinite<T, enable_if_t<sizeof(std::isfinite(T())) != 0>>
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_floating_point<T>::value&&
|
||||
has_isfinite<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bool isfinite(T value) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto isfinite(T value) -> bool {
|
||||
constexpr T inf = T(std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity());
|
||||
if (is_constant_evaluated())
|
||||
return !detail::isnan(value) && value < inf && value > -inf;
|
||||
return std::isfinite(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!has_isfinite<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR bool isfinite(T value) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto isfinite(T value) -> bool {
|
||||
T inf = T(std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity());
|
||||
// std::isfinite doesn't support __float128.
|
||||
return !detail::isnan(value) && value < inf && value > -inf;
|
||||
@ -2806,10 +2788,10 @@ class bigint {
|
||||
basic_memory_buffer<bigit, bigits_capacity> bigits_;
|
||||
int exp_;
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigit operator[](int index) const {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto operator[](int index) const -> bigit {
|
||||
return bigits_[to_unsigned(index)];
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigit& operator[](int index) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto operator[](int index) -> bigit& {
|
||||
return bigits_[to_unsigned(index)];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2905,11 +2887,11 @@ class bigint {
|
||||
assign(uint64_or_128_t<Int>(n));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int num_bigits() const {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto num_bigits() const -> int {
|
||||
return static_cast<int>(bigits_.size()) + exp_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_NOINLINE FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigint& operator<<=(int shift) {
|
||||
FMT_NOINLINE FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto operator<<=(int shift) -> bigint& {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(shift >= 0, "");
|
||||
exp_ += shift / bigit_bits;
|
||||
shift %= bigit_bits;
|
||||
@ -2924,13 +2906,15 @@ class bigint {
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Int> FMT_CONSTEXPR20 bigint& operator*=(Int value) {
|
||||
template <typename Int>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto operator*=(Int value) -> bigint& {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(value > 0, "");
|
||||
multiply(uint32_or_64_or_128_t<Int>(value));
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int compare(const bigint& lhs, const bigint& rhs) {
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto compare(const bigint& lhs, const bigint& rhs)
|
||||
-> int {
|
||||
int num_lhs_bigits = lhs.num_bigits(), num_rhs_bigits = rhs.num_bigits();
|
||||
if (num_lhs_bigits != num_rhs_bigits)
|
||||
return num_lhs_bigits > num_rhs_bigits ? 1 : -1;
|
||||
@ -2947,8 +2931,9 @@ class bigint {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns compare(lhs1 + lhs2, rhs).
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int add_compare(const bigint& lhs1, const bigint& lhs2,
|
||||
const bigint& rhs) {
|
||||
friend FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto add_compare(const bigint& lhs1,
|
||||
const bigint& lhs2, const bigint& rhs)
|
||||
-> int {
|
||||
auto minimum = [](int a, int b) { return a < b ? a : b; };
|
||||
auto maximum = [](int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; };
|
||||
int max_lhs_bigits = maximum(lhs1.num_bigits(), lhs2.num_bigits());
|
||||
@ -3029,13 +3014,13 @@ class bigint {
|
||||
bigits_.resize(to_unsigned(num_bigits + exp_difference));
|
||||
for (int i = num_bigits - 1, j = i + exp_difference; i >= 0; --i, --j)
|
||||
bigits_[j] = bigits_[i];
|
||||
std::uninitialized_fill_n(bigits_.data(), exp_difference, 0);
|
||||
std::uninitialized_fill_n(bigits_.data(), exp_difference, 0u);
|
||||
exp_ -= exp_difference;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Divides this bignum by divisor, assigning the remainder to this and
|
||||
// returning the quotient.
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 int divmod_assign(const bigint& divisor) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto divmod_assign(const bigint& divisor) -> int {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(this != &divisor, "");
|
||||
if (compare(*this, divisor) < 0) return 0;
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(divisor.bigits_[divisor.bigits_.size() - 1u] != 0, "");
|
||||
@ -3178,8 +3163,10 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR20 inline void format_dragon(basic_fp<uint128_t> value,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (buf[0] == overflow) {
|
||||
buf[0] = '1';
|
||||
if ((flags & dragon::fixed) != 0) buf.push_back('0');
|
||||
else ++exp10;
|
||||
if ((flags & dragon::fixed) != 0)
|
||||
buf.push_back('0');
|
||||
else
|
||||
++exp10;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -3276,6 +3263,17 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR20 void format_hexfloat(Float value, int precision,
|
||||
format_hexfloat(static_cast<double>(value), precision, specs, buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr auto fractional_part_rounding_thresholds(int index) -> uint32_t {
|
||||
// For checking rounding thresholds.
|
||||
// The kth entry is chosen to be the smallest integer such that the
|
||||
// upper 32-bits of 10^(k+1) times it is strictly bigger than 5 * 10^k.
|
||||
// It is equal to ceil(2^31 + 2^32/10^(k + 1)).
|
||||
// These are stored in a string literal because we cannot have static arrays
|
||||
// in constexpr functions and non-static ones are poorly optimized.
|
||||
return U"\x9999999a\x828f5c29\x80418938\x80068db9\x8000a7c6\x800010c7"
|
||||
U"\x800001ae\x8000002b"[index];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Float>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto format_float(Float value, int precision, float_specs specs,
|
||||
buffer<char>& buf) -> int {
|
||||
@ -3480,12 +3478,12 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto format_float(Float value, int precision, float_specs specs,
|
||||
// fractional part is strictly larger than 1/2.
|
||||
if (precision < 9) {
|
||||
uint32_t fractional_part = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod);
|
||||
should_round_up = fractional_part >=
|
||||
data::fractional_part_rounding_thresholds
|
||||
[8 - number_of_digits_to_print] ||
|
||||
((fractional_part >> 31) &
|
||||
((digits & 1) | (second_third_subsegments != 0) |
|
||||
has_more_segments)) != 0;
|
||||
should_round_up =
|
||||
fractional_part >= fractional_part_rounding_thresholds(
|
||||
8 - number_of_digits_to_print) ||
|
||||
((fractional_part >> 31) &
|
||||
((digits & 1) | (second_third_subsegments != 0) |
|
||||
has_more_segments)) != 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Rounding at the subsegment boundary.
|
||||
// In this case, the fractional part is at least 1/2 if and only if
|
||||
@ -3520,12 +3518,12 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR20 auto format_float(Float value, int precision, float_specs specs,
|
||||
// of 19 digits, so in this case the third segment should be
|
||||
// consisting of a genuine digit from the input.
|
||||
uint32_t fractional_part = static_cast<uint32_t>(prod);
|
||||
should_round_up = fractional_part >=
|
||||
data::fractional_part_rounding_thresholds
|
||||
[8 - number_of_digits_to_print] ||
|
||||
((fractional_part >> 31) &
|
||||
((digits & 1) | (third_subsegment != 0) |
|
||||
has_more_segments)) != 0;
|
||||
should_round_up =
|
||||
fractional_part >= fractional_part_rounding_thresholds(
|
||||
8 - number_of_digits_to_print) ||
|
||||
((fractional_part >> 31) &
|
||||
((digits & 1) | (third_subsegment != 0) |
|
||||
has_more_segments)) != 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Rounding at the subsegment boundary.
|
||||
else {
|
||||
@ -3757,8 +3755,11 @@ template <typename Char, typename OutputIt, typename T,
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto write(OutputIt out, const T& value)
|
||||
-> enable_if_t<mapped_type_constant<T, Context>::value == type::custom_type,
|
||||
OutputIt> {
|
||||
auto formatter = typename Context::template formatter_type<T>();
|
||||
auto parse_ctx = typename Context::parse_context_type({});
|
||||
formatter.parse(parse_ctx);
|
||||
auto ctx = Context(out, {}, {});
|
||||
return typename Context::template formatter_type<T>().format(value, ctx);
|
||||
return formatter.format(value, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An argument visitor that formats the argument and writes it via the output
|
||||
@ -3801,62 +3802,39 @@ template <typename Char> struct arg_formatter {
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct custom_formatter {
|
||||
basic_format_parse_context<Char>& parse_ctx;
|
||||
buffer_context<Char>& ctx;
|
||||
|
||||
void operator()(
|
||||
typename basic_format_arg<buffer_context<Char>>::handle h) const {
|
||||
h.format(parse_ctx, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename T> void operator()(T) const {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename ErrorHandler> class width_checker {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR width_checker(ErrorHandler& eh) : handler_(eh) {}
|
||||
|
||||
struct width_checker {
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integer<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T value) -> unsigned long long {
|
||||
if (is_negative(value)) handler_.on_error("negative width");
|
||||
if (is_negative(value)) throw_format_error("negative width");
|
||||
return static_cast<unsigned long long>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_integer<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T) -> unsigned long long {
|
||||
handler_.on_error("width is not integer");
|
||||
throw_format_error("width is not integer");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
ErrorHandler& handler_;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename ErrorHandler> class precision_checker {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR precision_checker(ErrorHandler& eh) : handler_(eh) {}
|
||||
|
||||
struct precision_checker {
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(is_integer<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T value) -> unsigned long long {
|
||||
if (is_negative(value)) handler_.on_error("negative precision");
|
||||
if (is_negative(value)) throw_format_error("negative precision");
|
||||
return static_cast<unsigned long long>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(!is_integer<T>::value)>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(T) -> unsigned long long {
|
||||
handler_.on_error("precision is not integer");
|
||||
throw_format_error("precision is not integer");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
ErrorHandler& handler_;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <template <typename> class Handler, typename FormatArg,
|
||||
typename ErrorHandler>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_dynamic_spec(FormatArg arg, ErrorHandler eh) -> int {
|
||||
unsigned long long value = visit_format_arg(Handler<ErrorHandler>(eh), arg);
|
||||
if (value > to_unsigned(max_value<int>())) eh.on_error("number is too big");
|
||||
template <typename Handler, typename FormatArg>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_dynamic_spec(FormatArg arg) -> int {
|
||||
unsigned long long value = visit_format_arg(Handler(), arg);
|
||||
if (value > to_unsigned(max_value<int>()))
|
||||
throw_format_error("number is too big");
|
||||
return static_cast<int>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3867,7 +3845,7 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR auto get_arg(Context& ctx, ID id) -> decltype(ctx.arg(id)) {
|
||||
return arg;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <template <typename> class Handler, typename Context>
|
||||
template <typename Handler, typename Context>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void handle_dynamic_spec(int& value,
|
||||
arg_ref<typename Context::char_type> ref,
|
||||
Context& ctx) {
|
||||
@ -3875,12 +3853,10 @@ FMT_CONSTEXPR void handle_dynamic_spec(int& value,
|
||||
case arg_id_kind::none:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case arg_id_kind::index:
|
||||
value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(get_arg(ctx, ref.val.index),
|
||||
ctx.error_handler());
|
||||
value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(get_arg(ctx, ref.val.index));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case arg_id_kind::name:
|
||||
value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(get_arg(ctx, ref.val.name),
|
||||
ctx.error_handler());
|
||||
value = detail::get_dynamic_spec<Handler>(get_arg(ctx, ref.val.name));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -4052,12 +4028,10 @@ class format_int {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<T, Char, enable_if_t<detail::has_format_as<T>::value>>
|
||||
: private formatter<detail::format_as_t<T>, Char> {
|
||||
using base = formatter<detail::format_as_t<T>, Char>;
|
||||
using base::parse;
|
||||
|
||||
: formatter<detail::format_as_t<T>, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const T& value, FormatContext& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
using base = formatter<detail::format_as_t<T>, Char>;
|
||||
return base::format(format_as(value), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -4198,6 +4172,59 @@ template <typename T> struct formatter<group_digits_view<T>> : formatter<T> {
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct nested_view {
|
||||
const formatter<T>* fmt;
|
||||
const T* value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct formatter<nested_view<T>> {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> const char* {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto format(nested_view<T> view, format_context& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return view.fmt->format(*view.value, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct nested_formatter {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
int width_;
|
||||
detail::fill_t<char> fill_;
|
||||
align_t align_ : 4;
|
||||
formatter<T> formatter_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
constexpr nested_formatter() : width_(0), align_(align_t::none) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(format_parse_context& ctx) -> const char* {
|
||||
auto specs = detail::dynamic_format_specs<char>();
|
||||
auto it = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs, ctx,
|
||||
detail::type::none_type);
|
||||
width_ = specs.width;
|
||||
fill_ = specs.fill;
|
||||
align_ = specs.align;
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(it);
|
||||
return formatter_.parse(ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename F>
|
||||
auto write_padded(format_context& ctx, F write) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
if (width_ == 0) return write(ctx.out());
|
||||
auto buf = memory_buffer();
|
||||
write(std::back_inserter(buf));
|
||||
auto specs = format_specs<>();
|
||||
specs.width = width_;
|
||||
specs.fill = fill_;
|
||||
specs.align = align_;
|
||||
return detail::write(ctx.out(), string_view(buf.data(), buf.size()), specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto nested(const T& value) const -> nested_view<T> {
|
||||
return nested_view<T>{&formatter_, &value};
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// DEPRECATED! join_view will be moved to ranges.h.
|
||||
template <typename It, typename Sentinel, typename Char = char>
|
||||
struct join_view : detail::view {
|
||||
@ -4329,7 +4356,7 @@ void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
auto out = buffer_appender<Char>(buf);
|
||||
if (fmt.size() == 2 && equal2(fmt.data(), "{}")) {
|
||||
auto arg = args.get(0);
|
||||
if (!arg) error_handler().on_error("argument not found");
|
||||
if (!arg) throw_format_error("argument not found");
|
||||
visit_format_arg(default_arg_formatter<Char>{out, args, loc}, arg);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -4356,7 +4383,7 @@ void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(basic_string_view<Char> id) -> int {
|
||||
int arg_id = context.arg_id(id);
|
||||
if (arg_id < 0) on_error("argument not found");
|
||||
if (arg_id < 0) throw_format_error("argument not found");
|
||||
return arg_id;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4371,11 +4398,9 @@ void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
auto on_format_specs(int id, const Char* begin, const Char* end)
|
||||
-> const Char* {
|
||||
auto arg = get_arg(context, id);
|
||||
if (arg.type() == type::custom_type) {
|
||||
parse_context.advance_to(begin);
|
||||
visit_format_arg(custom_formatter<Char>{parse_context, context}, arg);
|
||||
// Not using a visitor for custom types gives better codegen.
|
||||
if (arg.format_custom(begin, parse_context, context))
|
||||
return parse_context.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto specs = detail::dynamic_format_specs<Char>();
|
||||
begin = parse_format_specs(begin, end, specs, parse_context, arg.type());
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(
|
||||
@ -4383,7 +4408,7 @@ void vformat_to(buffer<Char>& buf, basic_string_view<Char> fmt,
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>(
|
||||
specs.precision, specs.precision_ref, context);
|
||||
if (begin == end || *begin != '}')
|
||||
on_error("missing '}' in format string");
|
||||
throw_format_error("missing '}' in format string");
|
||||
auto f = arg_formatter<Char>{context.out(), specs, context.locale()};
|
||||
context.advance_to(visit_format_arg(f, arg));
|
||||
return begin;
|
||||
@ -4426,7 +4451,7 @@ template <detail_exported::fixed_string Str> constexpr auto operator""_a() {
|
||||
return detail::udl_arg<char_t, sizeof(Str.data) / sizeof(char_t), Str>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
# else
|
||||
constexpr auto operator"" _a(const char* s, size_t) -> detail::udl_arg<char> {
|
||||
constexpr auto operator""_a(const char* s, size_t) -> detail::udl_arg<char> {
|
||||
return {s};
|
||||
}
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
@ -4486,16 +4511,16 @@ formatter<T, Char,
|
||||
detail::type::custom_type>>::format(const T& val,
|
||||
FormatContext& ctx)
|
||||
const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
if (specs_.width_ref.kind != detail::arg_id_kind::none ||
|
||||
specs_.precision_ref.kind != detail::arg_id_kind::none) {
|
||||
auto specs = specs_;
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width,
|
||||
specs.width_ref, ctx);
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>(
|
||||
specs.precision, specs.precision_ref, ctx);
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), val, specs, ctx.locale());
|
||||
if (specs_.width_ref.kind == detail::arg_id_kind::none &&
|
||||
specs_.precision_ref.kind == detail::arg_id_kind::none) {
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), val, specs_, ctx.locale());
|
||||
}
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), val, specs_, ctx.locale());
|
||||
auto specs = specs_;
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width,
|
||||
specs.width_ref, ctx);
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::precision_checker>(
|
||||
specs.precision, specs.precision_ref, ctx);
|
||||
return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), val, specs, ctx.locale());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,12 +13,14 @@
|
||||
#include <cstdio>
|
||||
#include <system_error> // std::system_error
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined __APPLE__ || defined(__FreeBSD__)
|
||||
# include <xlocale.h> // for LC_NUMERIC_MASK on OS X
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined __APPLE__ || defined(__FreeBSD__)
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<xlocale.h>)
|
||||
# include <xlocale.h> // for LC_NUMERIC_MASK on OS X
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
// UWP doesn't provide _pipe.
|
||||
# if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE("winapifamily.h")
|
||||
@ -46,6 +48,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
// Calls to system functions are wrapped in FMT_SYSTEM for testability.
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_SYSTEM
|
||||
# define FMT_HAS_SYSTEM
|
||||
# define FMT_POSIX_CALL(call) FMT_SYSTEM(call)
|
||||
#else
|
||||
# define FMT_SYSTEM(call) ::call
|
||||
@ -114,7 +117,7 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_cstring_view {
|
||||
basic_cstring_view(const std::basic_string<Char>& s) : data_(s.c_str()) {}
|
||||
|
||||
/** Returns the pointer to a C string. */
|
||||
const Char* c_str() const { return data_; }
|
||||
auto c_str() const -> const Char* { return data_; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
using cstring_view = basic_cstring_view<char>;
|
||||
@ -169,7 +172,7 @@ std::system_error windows_error(int error_code, string_view message,
|
||||
// Can be used to report errors from destructors.
|
||||
FMT_API void report_windows_error(int error_code, const char* message) noexcept;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
inline const std::error_category& system_category() noexcept {
|
||||
inline auto system_category() noexcept -> const std::error_category& {
|
||||
return std::system_category();
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // _WIN32
|
||||
@ -206,7 +209,7 @@ class buffered_file {
|
||||
other.file_ = nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buffered_file& operator=(buffered_file&& other) {
|
||||
auto operator=(buffered_file&& other) -> buffered_file& {
|
||||
close();
|
||||
file_ = other.file_;
|
||||
other.file_ = nullptr;
|
||||
@ -220,9 +223,9 @@ class buffered_file {
|
||||
FMT_API void close();
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the pointer to a FILE object representing this file.
|
||||
FILE* get() const noexcept { return file_; }
|
||||
auto get() const noexcept -> FILE* { return file_; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_API int descriptor() const;
|
||||
FMT_API auto descriptor() const -> int;
|
||||
|
||||
void vprint(string_view format_str, format_args args) {
|
||||
fmt::vprint(file_, format_str, args);
|
||||
@ -272,7 +275,7 @@ class FMT_API file {
|
||||
file(file&& other) noexcept : fd_(other.fd_) { other.fd_ = -1; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Move assignment is not noexcept because close may throw.
|
||||
file& operator=(file&& other) {
|
||||
auto operator=(file&& other) -> file& {
|
||||
close();
|
||||
fd_ = other.fd_;
|
||||
other.fd_ = -1;
|
||||
@ -283,24 +286,24 @@ class FMT_API file {
|
||||
~file() noexcept;
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the file descriptor.
|
||||
int descriptor() const noexcept { return fd_; }
|
||||
auto descriptor() const noexcept -> int { return fd_; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Closes the file.
|
||||
void close();
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the file size. The size has signed type for consistency with
|
||||
// stat::st_size.
|
||||
long long size() const;
|
||||
auto size() const -> long long;
|
||||
|
||||
// Attempts to read count bytes from the file into the specified buffer.
|
||||
size_t read(void* buffer, size_t count);
|
||||
auto read(void* buffer, size_t count) -> size_t;
|
||||
|
||||
// Attempts to write count bytes from the specified buffer to the file.
|
||||
size_t write(const void* buffer, size_t count);
|
||||
auto write(const void* buffer, size_t count) -> size_t;
|
||||
|
||||
// Duplicates a file descriptor with the dup function and returns
|
||||
// the duplicate as a file object.
|
||||
static file dup(int fd);
|
||||
static auto dup(int fd) -> file;
|
||||
|
||||
// Makes fd be the copy of this file descriptor, closing fd first if
|
||||
// necessary.
|
||||
@ -312,11 +315,12 @@ class FMT_API file {
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates a pipe setting up read_end and write_end file objects for reading
|
||||
// and writing respectively.
|
||||
// DEPRECATED! Taking files as out parameters is deprecated.
|
||||
static void pipe(file& read_end, file& write_end);
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates a buffered_file object associated with this file and detaches
|
||||
// this file object from the file.
|
||||
buffered_file fdopen(const char* mode);
|
||||
auto fdopen(const char* mode) -> buffered_file;
|
||||
|
||||
# if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
// Opens a file and constructs a file object representing this file by
|
||||
@ -326,14 +330,14 @@ class FMT_API file {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the memory page size.
|
||||
long getpagesize();
|
||||
auto getpagesize() -> long;
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
struct buffer_size {
|
||||
buffer_size() = default;
|
||||
size_t value = 0;
|
||||
buffer_size operator=(size_t val) const {
|
||||
auto operator=(size_t val) const -> buffer_size {
|
||||
auto bs = buffer_size();
|
||||
bs.value = val;
|
||||
return bs;
|
||||
@ -410,7 +414,7 @@ class FMT_API ostream {
|
||||
void flush() { buffer_.flush(); }
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
friend ostream output_file(cstring_view path, T... params);
|
||||
friend auto output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) -> ostream;
|
||||
|
||||
void close() { buffer_.close(); }
|
||||
|
||||
@ -419,7 +423,7 @@ class FMT_API ostream {
|
||||
output to the file.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T> void print(format_string<T...> fmt, T&&... args) {
|
||||
vformat_to(detail::buffer_appender<char>(buffer_), fmt,
|
||||
vformat_to(std::back_inserter(buffer_), fmt,
|
||||
fmt::make_format_args(args...));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -440,7 +444,7 @@ class FMT_API ostream {
|
||||
\endrst
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
inline ostream output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) {
|
||||
inline auto output_file(cstring_view path, T... params) -> ostream {
|
||||
return {path, detail::ostream_params(params...)};
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,19 +10,50 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#include <fstream> // std::filebuf
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(_WIN32) && defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h>
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION)
|
||||
# include <__std_stream>
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
# ifdef __GLIBCXX__
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# include <io.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Streambuf> class formatbuf : public Streambuf {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using char_type = typename Streambuf::char_type;
|
||||
using streamsize = decltype(std::declval<Streambuf>().sputn(nullptr, 0));
|
||||
using int_type = typename Streambuf::int_type;
|
||||
using traits_type = typename Streambuf::traits_type;
|
||||
|
||||
buffer<char_type>& buffer_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit formatbuf(buffer<char_type>& buf) : buffer_(buf) {}
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
// The put area is always empty. This makes the implementation simpler and has
|
||||
// the advantage that the streambuf and the buffer are always in sync and
|
||||
// sputc never writes into uninitialized memory. A disadvantage is that each
|
||||
// call to sputc always results in a (virtual) call to overflow. There is no
|
||||
// disadvantage here for sputn since this always results in a call to xsputn.
|
||||
|
||||
auto overflow(int_type ch) -> int_type override {
|
||||
if (!traits_type::eq_int_type(ch, traits_type::eof()))
|
||||
buffer_.push_back(static_cast<char_type>(ch));
|
||||
return ch;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto xsputn(const char_type* s, streamsize count) -> streamsize override {
|
||||
buffer_.append(s, s + count);
|
||||
return count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Generate a unique explicit instantion in every translation unit using a tag
|
||||
// type in an anonymous namespace.
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
@ -37,36 +68,40 @@ class file_access {
|
||||
template class file_access<file_access_tag, std::filebuf,
|
||||
&std::filebuf::_Myfile>;
|
||||
auto get_file(std::filebuf&) -> FILE*;
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION)
|
||||
template class file_access<file_access_tag, std::__stdoutbuf<char>,
|
||||
&std::__stdoutbuf<char>::__file_>;
|
||||
auto get_file(std::__stdoutbuf<char>&) -> FILE*;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
inline bool write_ostream_unicode(std::ostream& os, fmt::string_view data) {
|
||||
inline auto write_ostream_unicode(std::ostream& os, fmt::string_view data)
|
||||
-> bool {
|
||||
FILE* f = nullptr;
|
||||
#if FMT_MSC_VERSION
|
||||
if (auto* buf = dynamic_cast<std::filebuf*>(os.rdbuf()))
|
||||
if (FILE* f = get_file(*buf)) return write_console(f, data);
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
auto* rdbuf = os.rdbuf();
|
||||
FILE* c_file;
|
||||
if (auto* sfbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_sync_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf))
|
||||
c_file = sfbuf->file();
|
||||
else if (auto* fbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf))
|
||||
c_file = fbuf->file();
|
||||
f = get_file(*buf);
|
||||
else
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
auto* rdbuf = os.rdbuf();
|
||||
if (auto* sfbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_sync_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf))
|
||||
f = sfbuf->file();
|
||||
else if (auto* fbuf = dynamic_cast<__gnu_cxx::stdio_filebuf<char>*>(rdbuf))
|
||||
f = fbuf->file();
|
||||
else
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
if (c_file) return write_console(c_file, data);
|
||||
#elif defined(_WIN32) && defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION)
|
||||
if (auto* buf = dynamic_cast<std::__stdoutbuf<char>*>(os.rdbuf()))
|
||||
if (FILE* f = get_file(*buf)) return write_console(f, data);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
ignore_unused(os, data);
|
||||
ignore_unused(os, data, f);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
if (f) {
|
||||
int fd = _fileno(f);
|
||||
if (_isatty(fd)) {
|
||||
os.flush();
|
||||
return write_console(fd, data);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
inline bool write_ostream_unicode(std::wostream&,
|
||||
fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>) {
|
||||
inline auto write_ostream_unicode(std::wostream&,
|
||||
fmt::basic_string_view<wchar_t>) -> bool {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -87,18 +122,19 @@ void write_buffer(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, buffer<Char>& buf) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename T>
|
||||
void format_value(buffer<Char>& buf, const T& value,
|
||||
locale_ref loc = locale_ref()) {
|
||||
void format_value(buffer<Char>& buf, const T& value) {
|
||||
auto&& format_buf = formatbuf<std::basic_streambuf<Char>>(buf);
|
||||
auto&& output = std::basic_ostream<Char>(&format_buf);
|
||||
#if !defined(FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR)
|
||||
if (loc) output.imbue(loc.get<std::locale>());
|
||||
output.imbue(std::locale::classic()); // The default is always unlocalized.
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
output << value;
|
||||
output.exceptions(std::ios_base::failbit | std::ios_base::badbit);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct streamed_view { const T& value; };
|
||||
template <typename T> struct streamed_view {
|
||||
const T& value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
@ -111,7 +147,7 @@ struct basic_ostream_formatter : formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char> {
|
||||
auto format(const T& value, basic_format_context<OutputIt, Char>& ctx) const
|
||||
-> OutputIt {
|
||||
auto buffer = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::format_value(buffer, value, ctx.locale());
|
||||
detail::format_value(buffer, value);
|
||||
return formatter<basic_string_view<Char>, Char>::format(
|
||||
{buffer.data(), buffer.size()}, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -140,7 +176,7 @@ struct formatter<detail::streamed_view<T>, Char>
|
||||
\endrst
|
||||
*/
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
auto streamed(const T& value) -> detail::streamed_view<T> {
|
||||
constexpr auto streamed(const T& value) -> detail::streamed_view<T> {
|
||||
return {value};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,13 +16,19 @@
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_EXPORT
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct printf_formatter { printf_formatter() = delete; };
|
||||
template <typename T> struct printf_formatter {
|
||||
printf_formatter() = delete;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> class basic_printf_context {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
detail::buffer_appender<Char> out_;
|
||||
basic_format_args<basic_printf_context> args_;
|
||||
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<Char, char>::value ||
|
||||
std::is_same<Char, wchar_t>::value,
|
||||
"Unsupported code unit type.");
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using char_type = Char;
|
||||
using parse_context_type = basic_format_parse_context<Char>;
|
||||
@ -102,7 +108,9 @@ struct is_zero_int {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct make_unsigned_or_bool : std::make_unsigned<T> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct make_unsigned_or_bool<bool> { using type = bool; };
|
||||
template <> struct make_unsigned_or_bool<bool> {
|
||||
using type = bool;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Context> class arg_converter {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,9 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - experimental range support
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - range and tuple support
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 - present, Remotion (Igor Schulz)
|
||||
// All Rights Reserved
|
||||
// {fmt} support for ranges, containers and types tuple interface.
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_RANGES_H_
|
||||
#define FMT_RANGES_H_
|
||||
@ -187,7 +183,7 @@ template <size_t N> using make_index_sequence = std::make_index_sequence<N>;
|
||||
template <typename T, T... N> struct integer_sequence {
|
||||
using value_type = T;
|
||||
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR size_t size() { return sizeof...(N); }
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR auto size() -> size_t { return sizeof...(N); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t... N> using index_sequence = integer_sequence<size_t, N...>;
|
||||
@ -211,15 +207,15 @@ class is_tuple_formattable_ {
|
||||
};
|
||||
template <typename T, typename C> class is_tuple_formattable_<T, C, true> {
|
||||
template <std::size_t... Is>
|
||||
static std::true_type check2(index_sequence<Is...>,
|
||||
integer_sequence<bool, (Is == Is)...>);
|
||||
static std::false_type check2(...);
|
||||
static auto check2(index_sequence<Is...>,
|
||||
integer_sequence<bool, (Is == Is)...>) -> std::true_type;
|
||||
static auto check2(...) -> std::false_type;
|
||||
template <std::size_t... Is>
|
||||
static decltype(check2(
|
||||
static auto check(index_sequence<Is...>) -> decltype(check2(
|
||||
index_sequence<Is...>{},
|
||||
integer_sequence<
|
||||
bool, (is_formattable<typename std::tuple_element<Is, T>::type,
|
||||
C>::value)...>{})) check(index_sequence<Is...>);
|
||||
integer_sequence<bool,
|
||||
(is_formattable<typename std::tuple_element<Is, T>::type,
|
||||
C>::value)...>{}));
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static constexpr const bool value =
|
||||
@ -421,6 +417,12 @@ struct is_formattable_delayed
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename...> struct conjunction : std::true_type {};
|
||||
template <typename P> struct conjunction<P> : P {};
|
||||
template <typename P1, typename... Pn>
|
||||
struct conjunction<P1, Pn...>
|
||||
: conditional_t<bool(P1::value), conjunction<Pn...>, P1> {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char, typename Enable = void>
|
||||
struct range_formatter;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -486,7 +488,8 @@ struct range_formatter<
|
||||
for (; it != end; ++it) {
|
||||
if (i > 0) out = detail::copy_str<Char>(separator_, out);
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(out);
|
||||
out = underlying_.format(mapper.map(*it), ctx);
|
||||
auto&& item = *it;
|
||||
out = underlying_.format(mapper.map(item), ctx);
|
||||
++i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
out = detail::copy_str<Char>(closing_bracket_, out);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,10 @@
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_CPLUSPLUS > 201703L && FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<source_location>)
|
||||
# include <source_location>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// GCC 4 does not support FMT_HAS_INCLUDE.
|
||||
#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<cxxabi.h>) || defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
# include <cxxabi.h>
|
||||
@ -59,43 +63,53 @@
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_filesystem
|
||||
// For older Xcode versions, __cpp_lib_xxx flags are inaccurately defined.
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM
|
||||
# ifdef __cpp_lib_filesystem
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM __cpp_lib_filesystem
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
# ifdef __cpp_lib_variant
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT __cpp_lib_variant
|
||||
# else
|
||||
# define FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT 0
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> auto get_path_string(const std::filesystem::path& p) {
|
||||
return p.string<Char>();
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename PathChar>
|
||||
auto get_path_string(const std::filesystem::path& p,
|
||||
const std::basic_string<PathChar>& native) {
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, char> && std::is_same_v<PathChar, wchar_t>)
|
||||
return to_utf8<wchar_t>(native, to_utf8_error_policy::replace);
|
||||
else
|
||||
return p.string<Char>();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
template <typename Char, typename PathChar>
|
||||
void write_escaped_path(basic_memory_buffer<Char>& quoted,
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& p) {
|
||||
write_escaped_string<Char>(std::back_inserter(quoted), p.string<Char>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
inline auto get_path_string<char>(const std::filesystem::path& p) {
|
||||
return to_utf8<wchar_t>(p.native(), to_utf8_error_policy::replace);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
inline void write_escaped_path<char>(memory_buffer& quoted,
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& p) {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>();
|
||||
write_escaped_string<wchar_t>(std::back_inserter(buf), p.native());
|
||||
bool valid = to_utf8<wchar_t>::convert(quoted, {buf.data(), buf.size()});
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(valid, "invalid utf16");
|
||||
}
|
||||
# endif // _WIN32
|
||||
|
||||
template <>
|
||||
inline void write_escaped_path<std::filesystem::path::value_type>(
|
||||
basic_memory_buffer<std::filesystem::path::value_type>& quoted,
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& p) {
|
||||
write_escaped_string<std::filesystem::path::value_type>(
|
||||
std::back_inserter(quoted), p.native());
|
||||
const std::filesystem::path& p,
|
||||
const std::basic_string<PathChar>& native) {
|
||||
if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, char> &&
|
||||
std::is_same_v<PathChar, wchar_t>) {
|
||||
auto buf = basic_memory_buffer<wchar_t>();
|
||||
write_escaped_string<wchar_t>(std::back_inserter(buf), native);
|
||||
bool valid = to_utf8<wchar_t>::convert(quoted, {buf.data(), buf.size()});
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(valid, "invalid utf16");
|
||||
} else if constexpr (std::is_same_v<Char, PathChar>) {
|
||||
write_escaped_string<std::filesystem::path::value_type>(
|
||||
std::back_inserter(quoted), native);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
write_escaped_string<Char>(std::back_inserter(quoted), p.string<Char>());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
@ -106,6 +120,7 @@ template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::filesystem::path, Char> {
|
||||
format_specs<Char> specs_;
|
||||
detail::arg_ref<Char> width_ref_;
|
||||
bool debug_ = false;
|
||||
char path_type_ = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR void set_debug_format(bool set = true) { debug_ = set; }
|
||||
@ -122,29 +137,62 @@ template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::filesystem::path, Char> {
|
||||
debug_ = true;
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (it != end && (*it == 'g')) path_type_ = *it++;
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::filesystem::path& p, FormatContext& ctx) const {
|
||||
auto specs = specs_;
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
auto path_string = !path_type_ ? p.native() : p.generic_wstring();
|
||||
# else
|
||||
auto path_string = !path_type_ ? p.native() : p.generic_string();
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
detail::handle_dynamic_spec<detail::width_checker>(specs.width, width_ref_,
|
||||
ctx);
|
||||
if (!debug_) {
|
||||
auto s = detail::get_path_string<Char>(p);
|
||||
auto s = detail::get_path_string<Char>(p, path_string);
|
||||
return detail::write(ctx.out(), basic_string_view<Char>(s), specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto quoted = basic_memory_buffer<Char>();
|
||||
detail::write_escaped_path(quoted, p);
|
||||
detail::write_escaped_path(quoted, p, path_string);
|
||||
return detail::write(ctx.out(),
|
||||
basic_string_view<Char>(quoted.data(), quoted.size()),
|
||||
specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#endif // FMT_CPP_LIB_FILESYSTEM
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <std::size_t N, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::bitset<N>, Char> : nested_formatter<string_view> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
// Functor because C++11 doesn't support generic lambdas.
|
||||
struct writer {
|
||||
const std::bitset<N>& bs;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto operator()(OutputIt out) -> OutputIt {
|
||||
for (auto pos = N; pos > 0; --pos) {
|
||||
out = detail::write<Char>(out, bs[pos - 1] ? Char('1') : Char('0'));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::bitset<N>& bs, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return write_padded(ctx, writer{bs});
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::thread::id, Char> : basic_ostream_formatter<Char> {};
|
||||
@ -180,7 +228,7 @@ struct formatter<std::optional<T>, Char,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(std::optional<T> const& opt, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
auto format(const std::optional<T>& opt, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
if (!opt) return detail::write<Char>(ctx.out(), none);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -194,7 +242,32 @@ struct formatter<std::optional<T>, Char,
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_optional
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_variant
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_source_location
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <> struct formatter<std::source_location> {
|
||||
template <typename ParseContext> FMT_CONSTEXPR auto parse(ParseContext& ctx) {
|
||||
return ctx.begin();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::source_location& loc, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto out = ctx.out();
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, loc.file_name());
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, ':');
|
||||
out = detail::write<char>(out, loc.line());
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, ':');
|
||||
out = detail::write<char>(out, loc.column());
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, ": ");
|
||||
out = detail::write(out, loc.function_name());
|
||||
return out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -285,7 +358,7 @@ struct formatter<
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_variant
|
||||
#endif // FMT_CPP_LIB_VARIANT
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
@ -309,7 +382,7 @@ template <typename Char> struct formatter<std::error_code, Char> {
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<
|
||||
T, Char,
|
||||
T, Char, // DEPRECATED! Mixing code unit types.
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<std::is_base_of<std::exception, T>::value>::type> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
bool with_typename_ = false;
|
||||
@ -340,7 +413,7 @@ struct formatter<
|
||||
# ifdef FMT_HAS_ABI_CXA_DEMANGLE
|
||||
int status = 0;
|
||||
std::size_t size = 0;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<char, decltype(&std::free)> demangled_name_ptr(
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<char, void (*)(void*)> demangled_name_ptr(
|
||||
abi::__cxa_demangle(ti.name(), nullptr, &size, &status), &std::free);
|
||||
|
||||
string_view demangled_name_view;
|
||||
@ -451,15 +524,14 @@ struct formatter<std::atomic<T>, Char,
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
FMT_EXPORT
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
struct formatter<std::atomic_flag, Char>
|
||||
: formatter<bool, Char> {
|
||||
struct formatter<std::atomic_flag, Char> : formatter<bool, Char> {
|
||||
template <typename FormatContext>
|
||||
auto format(const std::atomic_flag& v, FormatContext& ctx) const
|
||||
-> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return formatter<bool, Char>::format(v.test(), ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
#endif // FMT_STD_H_
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,14 +63,15 @@ template <> struct is_char<char16_t> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
template <> struct is_char<char32_t> : std::true_type {};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
constexpr format_arg_store<wformat_context, T...> make_wformat_args(
|
||||
const T&... args) {
|
||||
constexpr auto make_wformat_args(const T&... args)
|
||||
-> format_arg_store<wformat_context, T...> {
|
||||
return {args...};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline namespace literals {
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_USER_DEFINED_LITERALS && !FMT_USE_NONTYPE_TEMPLATE_ARGS
|
||||
constexpr detail::udl_arg<wchar_t> operator"" _a(const wchar_t* s, size_t) {
|
||||
constexpr auto operator""_a(const wchar_t* s, size_t)
|
||||
-> detail::udl_arg<wchar_t> {
|
||||
return {s};
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -172,11 +173,11 @@ inline auto vformat_to(
|
||||
return detail::get_iterator(buf, out);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <
|
||||
typename OutputIt, typename Locale, typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = char_t<S>,
|
||||
bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value&&
|
||||
detail::is_locale<Locale>::value&& detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value>
|
||||
template <typename OutputIt, typename Locale, typename S, typename... T,
|
||||
typename Char = char_t<S>,
|
||||
bool enable = detail::is_output_iterator<OutputIt, Char>::value &&
|
||||
detail::is_locale<Locale>::value &&
|
||||
detail::is_exotic_char<Char>::value>
|
||||
inline auto format_to(OutputIt out, const Locale& loc, const S& format_str,
|
||||
T&&... args) ->
|
||||
typename std::enable_if<enable, OutputIt>::type {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,8 +63,6 @@ module;
|
||||
# if defined(__GLIBCXX__)
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# include <ext/stdio_sync_filebuf.h>
|
||||
# elif defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION)
|
||||
# include <__std_stream>
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
# define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN
|
||||
# include <windows.h>
|
||||
@ -103,7 +101,7 @@ extern "C++" {
|
||||
|
||||
// gcc doesn't yet implement private module fragments
|
||||
#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION
|
||||
module : private;
|
||||
module :private;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "format.cc"
|
||||
|
||||
14
src/os.cc
14
src/os.cc
@ -18,8 +18,8 @@
|
||||
# include <sys/stat.h>
|
||||
# include <sys/types.h>
|
||||
|
||||
# ifdef _WRS_KERNEL // VxWorks7 kernel
|
||||
# include <ioLib.h> // getpagesize
|
||||
# ifdef _WRS_KERNEL // VxWorks7 kernel
|
||||
# include <ioLib.h> // getpagesize
|
||||
# endif
|
||||
|
||||
# ifndef _WIN32
|
||||
@ -182,10 +182,14 @@ void buffered_file::close() {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int buffered_file::descriptor() const {
|
||||
#ifdef fileno // fileno is a macro on OpenBSD so we cannot use FMT_POSIX_CALL.
|
||||
int fd = fileno(file_);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#if !defined(fileno)
|
||||
int fd = FMT_POSIX_CALL(fileno(file_));
|
||||
#elif defined(FMT_HAS_SYSTEM)
|
||||
// fileno is a macro on OpenBSD so we cannot use FMT_POSIX_CALL.
|
||||
# define FMT_DISABLE_MACRO
|
||||
int fd = FMT_SYSTEM(fileno FMT_DISABLE_MACRO(file_));
|
||||
#else
|
||||
int fd = fileno(file_);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (fd == -1)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("cannot get file descriptor")));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1 +1 @@
|
||||
<manifest package="net.fmtlib" />
|
||||
<manifest package="dev.fmt" />
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ obtained from https://github.com/settings/tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import datetime, docopt, errno, fileinput, json, os
|
||||
import re, requests, shutil, sys, tempfile
|
||||
import re, requests, shutil, sys
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from distutils.version import LooseVersion
|
||||
from subprocess import check_call
|
||||
@ -229,12 +229,50 @@ def release(args):
|
||||
if not fmt_repo.update('-b', branch, fmt_repo_url):
|
||||
clean_checkout(fmt_repo, branch)
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert changelog from RST to GitHub-flavored Markdown and get the
|
||||
# version.
|
||||
changelog = 'ChangeLog.rst'
|
||||
# Update the date in the changelog and extract the version and the first
|
||||
# section content.
|
||||
changelog = 'ChangeLog.md'
|
||||
changelog_path = os.path.join(fmt_repo.dir, changelog)
|
||||
import rst2md
|
||||
changes, version = rst2md.convert(changelog_path)
|
||||
is_first_section = True
|
||||
first_section = []
|
||||
for i, line in enumerate(fileinput.input(changelog_path, inplace=True)):
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
version = re.match(r'# (.*) - TBD', line).group(1)
|
||||
line = '# {} - {}\n'.format(
|
||||
version, datetime.date.today().isoformat())
|
||||
elif not is_first_section:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
elif line.startswith('#'):
|
||||
is_first_section = False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
first_section.append(line)
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(line)
|
||||
if first_section[0] == '\n':
|
||||
first_section.pop(0)
|
||||
|
||||
changes = ''
|
||||
code_block = False
|
||||
stripped = False
|
||||
for line in first_section:
|
||||
if re.match(r'^\s*```', line):
|
||||
code_block = not code_block
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
stripped = False
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if code_block:
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if line == '\n':
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
if stripped:
|
||||
changes += line
|
||||
stripped = False
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if stripped:
|
||||
line = ' ' + line.lstrip()
|
||||
changes += line.rstrip()
|
||||
stripped = True
|
||||
|
||||
cmakelists = 'CMakeLists.txt'
|
||||
for line in fileinput.input(os.path.join(fmt_repo.dir, cmakelists),
|
||||
inplace=True):
|
||||
@ -243,23 +281,11 @@ def release(args):
|
||||
line = prefix + version + ')\n'
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(line)
|
||||
|
||||
# Update the version in the changelog.
|
||||
title_len = 0
|
||||
for line in fileinput.input(changelog_path, inplace=True):
|
||||
if line.startswith(version + ' - TBD'):
|
||||
line = version + ' - ' + datetime.date.today().isoformat()
|
||||
title_len = len(line)
|
||||
line += '\n'
|
||||
elif title_len:
|
||||
line = '-' * title_len + '\n'
|
||||
title_len = 0
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(line)
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the version to the build script.
|
||||
script = os.path.join('doc', 'build.py')
|
||||
script_path = os.path.join(fmt_repo.dir, script)
|
||||
for line in fileinput.input(script_path, inplace=True):
|
||||
m = re.match(r'( *versions = )\[(.+)\]', line)
|
||||
m = re.match(r'( *versions \+= )\[(.+)\]', line)
|
||||
if m:
|
||||
line = '{}[{}, \'{}\']\n'.format(m.group(1), m.group(2), version)
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(line)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# reStructuredText (RST) to GitHub-flavored Markdown converter
|
||||
|
||||
import re, sys
|
||||
from docutils import core, nodes, writers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_github_ref(node):
|
||||
return re.match('https://github.com/.*/(issues|pull)/.*', node['refuri'])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Translator(nodes.NodeVisitor):
|
||||
def __init__(self, document):
|
||||
nodes.NodeVisitor.__init__(self, document)
|
||||
self.output = ''
|
||||
self.indent = 0
|
||||
self.preserve_newlines = False
|
||||
|
||||
def write(self, text):
|
||||
self.output += text.replace('\n', '\n' + ' ' * self.indent)
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_document(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_document(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_section(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_section(self, node):
|
||||
# Skip all sections except the first one.
|
||||
raise nodes.StopTraversal
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_title(self, node):
|
||||
self.version = re.match(r'(\d+\.\d+\.\d+).*', node.children[0]).group(1)
|
||||
raise nodes.SkipChildren
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_title_reference(self, node):
|
||||
raise Exception(node)
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_title(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_Text(self, node):
|
||||
if not self.preserve_newlines:
|
||||
node = node.replace('\n', ' ')
|
||||
self.write(node)
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_Text(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_bullet_list(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_bullet_list(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_list_item(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('* ')
|
||||
self.indent += 2
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_list_item(self, node):
|
||||
self.indent -= 2
|
||||
self.write('\n\n')
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_paragraph(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('\n\n')
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_paragraph(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_reference(self, node):
|
||||
if not is_github_ref(node):
|
||||
self.write('[')
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_reference(self, node):
|
||||
if not is_github_ref(node):
|
||||
self.write('](' + node['refuri'] + ')')
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_target(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_target(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_literal(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('`')
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_literal(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('`')
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_literal_block(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('\n\n```')
|
||||
if 'c++' in node['classes']:
|
||||
self.write('c++')
|
||||
self.write('\n')
|
||||
self.preserve_newlines = True
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_literal_block(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('\n```\n')
|
||||
self.preserve_newlines = False
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_inline(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_inline(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_image(self, node):
|
||||
self.write('')
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_image(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def write_row(self, row, widths):
|
||||
for i, entry in enumerate(row):
|
||||
text = entry[0][0] if len(entry) > 0 else ''
|
||||
if i != 0:
|
||||
self.write('|')
|
||||
self.write('{:{}}'.format(text, widths[i]))
|
||||
self.write('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_table(self, node):
|
||||
table = node.children[0]
|
||||
colspecs = table[:-2]
|
||||
thead = table[-2]
|
||||
tbody = table[-1]
|
||||
widths = [int(cs['colwidth']) for cs in colspecs]
|
||||
sep = '|'.join(['-' * w for w in widths]) + '\n'
|
||||
self.write('\n\n')
|
||||
self.write_row(thead[0], widths)
|
||||
self.write(sep)
|
||||
for row in tbody:
|
||||
self.write_row(row, widths)
|
||||
raise nodes.SkipChildren
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_table(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def visit_system_message(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def depart_system_message(self, node):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MDWriter(writers.Writer):
|
||||
"""GitHub-flavored markdown writer"""
|
||||
|
||||
supported = ('md',)
|
||||
"""Formats this writer supports."""
|
||||
|
||||
def translate(self):
|
||||
translator = Translator(self.document)
|
||||
self.document.walkabout(translator)
|
||||
self.output = (translator.output, translator.version)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert(rst_path):
|
||||
"""Converts RST file to Markdown."""
|
||||
return core.publish_file(source_path=rst_path, writer=MDWriter())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
convert(sys.argv[1])
|
||||
@ -175,7 +175,12 @@ if (FMT_PEDANTIC)
|
||||
endif ()
|
||||
|
||||
# These tests are disabled on Windows because they take too long.
|
||||
if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32)
|
||||
# They are disabled on GCC < 4.9 because it can not parse UDLs without
|
||||
# a space after `operator""` but that is an incorrect syntax for any more
|
||||
# modern compiler.
|
||||
if (FMT_PEDANTIC AND NOT WIN32 AND NOT (
|
||||
CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "GNU" AND
|
||||
CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 4.9))
|
||||
# Test if incorrect API usages produce compilation error.
|
||||
add_test(compile-error-test ${CMAKE_CTEST_COMMAND}
|
||||
--build-and-test
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,6 +17,9 @@
|
||||
using fmt::runtime;
|
||||
using testing::Contains;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Duration>
|
||||
using sys_time = std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration>;
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__MINGW32__) && !defined(_UCRT)
|
||||
// Only C89 conversion specifiers when using MSVCRT instead of UCRT
|
||||
# define FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME 0
|
||||
@ -24,6 +27,12 @@ using testing::Contains;
|
||||
# define FMT_HAS_C99_STRFTIME 1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_lib_chrono) && __cpp_lib_chrono >= 201907L
|
||||
using days = std::chrono::days;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
using days = std::chrono::duration<std::chrono::hours::rep, std::ratio<86400>>;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
auto make_tm() -> std::tm {
|
||||
auto time = std::tm();
|
||||
time.tm_mday = 1;
|
||||
@ -260,9 +269,8 @@ TEST(chrono_test, system_clock_time_point) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t1), fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t1), fmt::format("{}", t1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t1), fmt::format("{:}", t1));
|
||||
using time_point =
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::seconds>;
|
||||
auto t2 = time_point(std::chrono::seconds(42));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t2 = sys_time<std::chrono::seconds>(std::chrono::seconds(42));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(strftime_full_utc(t2), fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t2));
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::string> spec_list = {
|
||||
@ -331,14 +339,14 @@ TEST(chrono_test, system_clock_time_point) {
|
||||
auto t = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(t1);
|
||||
auto tm = *std::gmtime(&t);
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("+0000", fmt::format("{:%z}", t1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("+0000", fmt::format("{:%z}", tm));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%z}", t1), "+0000");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%z}", tm), "+0000");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Ez}", t1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Ez}", tm));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Ez}", t1), "+00:00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Ez}", tm), "+00:00");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Oz}", t1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("+00:00", fmt::format("{:%Oz}", tm));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Oz}", t1), "+00:00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Oz}", tm), "+00:00");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -423,119 +431,122 @@ TEST(chrono_test, local_system_clock_time_point) {
|
||||
#ifndef FMT_STATIC_THOUSANDS_SEPARATOR
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_default) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::seconds(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42as",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::atto>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42fs",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::femto>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42ps",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::pico>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42ns", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::nanoseconds(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42µs", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::microseconds(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42ms", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::milliseconds(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42cs",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::centi>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42ds",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::deci>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::seconds(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42das",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::deca>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42hs",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::hecto>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42ks",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::kilo>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42Ms",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::mega>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42Gs",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::giga>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42Ts",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::tera>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42Ps",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::peta>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42Es",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::exa>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42m", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::minutes(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42h", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::hours(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::seconds(42)), "42s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::atto>(42)),
|
||||
"42as");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::femto>(42)),
|
||||
"42fs");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::pico>(42)),
|
||||
"42ps");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::nanoseconds(42)), "42ns");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::microseconds(42)), "42µs");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::milliseconds(42)), "42ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::centi>(42)),
|
||||
"42cs");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::deci>(42)),
|
||||
"42ds");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::seconds(42)), "42s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::deca>(42)),
|
||||
"42das");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::hecto>(42)),
|
||||
"42hs");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::kilo>(42)),
|
||||
"42ks");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::mega>(42)),
|
||||
"42Ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::giga>(42)),
|
||||
"42Gs");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::tera>(42)),
|
||||
"42Ts");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::peta>(42)),
|
||||
"42Ps");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::exa>(42)),
|
||||
"42Es");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::minutes(42)), "42min");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::hours(42)), "42h");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", days(42)), "42d");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(
|
||||
"42[15]s",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 1>>(42)));
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 1>>(42)),
|
||||
"42[15]s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(
|
||||
"42[15/4]s",
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 4>>(42)));
|
||||
fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<15, 4>>(42)),
|
||||
"42[15/4]s");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, duration_align) {
|
||||
auto s = std::chrono::seconds(42);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42s ", fmt::format("{:5}", s));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42s ", fmt::format("{:{}}", s, 5));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 42s", fmt::format("{:>5}", s));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("**42s**", fmt::format("{:*^7}", s));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("03:25:45 ",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:12%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 03:25:45",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:>12%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("~~03:25:45~~",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:~^12%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("03:25:45 ",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:{}%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345), 12));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:5}", s), "42s ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:{}}", s, 5), "42s ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>5}", s), " 42s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^7}", s), "**42s**");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:12%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)),
|
||||
"03:25:45 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>12%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)),
|
||||
" 03:25:45");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:~^12%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)),
|
||||
"~~03:25:45~~");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:{}%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345), 12),
|
||||
"03:25:45 ");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, tm_align) {
|
||||
auto t = make_tm(1975, 12, 29, 12, 14, 16);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16", fmt::format("{:%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:{}%F %T}", t, 30));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:<30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1975-12-29 12:14:16 ", fmt::format("{:^30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1975-12-29 12:14:16", fmt::format("{:>30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%F %T}", t), "1975-12-29 12:14:16");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:30%F %T}", t), "1975-12-29 12:14:16 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:{}%F %T}", t, 30), "1975-12-29 12:14:16 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:<30%F %T}", t), "1975-12-29 12:14:16 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:^30%F %T}", t), " 1975-12-29 12:14:16 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>30%F %T}", t), " 1975-12-29 12:14:16");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1975-12-29 12:14:16***********", fmt::format("{:*<30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("*****1975-12-29 12:14:16******", fmt::format("{:*^30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("***********1975-12-29 12:14:16", fmt::format("{:*>30%F %T}", t));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*<30%F %T}", t), "1975-12-29 12:14:16***********");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^30%F %T}", t), "*****1975-12-29 12:14:16******");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*>30%F %T}", t), "***********1975-12-29 12:14:16");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, tp_align) {
|
||||
auto tp = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(
|
||||
std::chrono::system_clock::from_time_t(0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000", fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:{}%M:%S}", tp, 15));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:<15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 00:00.000000 ", fmt::format("{:^15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 00:00.000000", fmt::format("{:>15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", tp), "00:00.000000");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:15%M:%S}", tp), "00:00.000000 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:{}%M:%S}", tp, 15), "00:00.000000 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:<15%M:%S}", tp), "00:00.000000 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:^15%M:%S}", tp), " 00:00.000000 ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>15%M:%S}", tp), " 00:00.000000");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00:00.000000***", fmt::format("{:*<15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("*00:00.000000**", fmt::format("{:*^15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("***00:00.000000", fmt::format("{:*>15%M:%S}", tp));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*<15%M:%S}", tp), "00:00.000000***");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^15%M:%S}", tp), "*00:00.000000**");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*>15%M:%S}", tp), "***00:00.000000");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_specs) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("%", fmt::format("{:%%}", std::chrono::seconds(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("\n", fmt::format("{:%n}", std::chrono::seconds(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("\t", fmt::format("{:%t}", std::chrono::seconds(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00", fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00", fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(60)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("01.234", fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds(1234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00", fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::minutes(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00", fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::minutes(60)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42", fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::minutes(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("01", fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::seconds(61)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00", fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::hours(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00", fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::hours(24)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("14", fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::hours(14)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("01", fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::minutes(61)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("12", fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("12", fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(12)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("12", fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(24)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("04", fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(4)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("02", fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(14)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("03:25:45",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("03:25", fmt::format("{:%R}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("03:25:45", fmt::format("{:%T}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("12345", fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("s", fmt::format("{:%q}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%%}", std::chrono::seconds(0)), "%");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%n}", std::chrono::seconds(0)), "\n");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%t}", std::chrono::seconds(0)), "\t");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(0)), "00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(60)), "00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(42)), "42");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds(1234)), "01.234");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::minutes(0)), "00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::minutes(60)), "00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::minutes(42)), "42");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M}", std::chrono::seconds(61)), "01");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::hours(0)), "00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::hours(24)), "00");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::hours(14)), "14");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H}", std::chrono::minutes(61)), "01");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(0)), "12");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(12)), "12");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(24)), "12");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(4)), "04");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%I}", std::chrono::hours(14)), "02");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%j}", days(12345)), "12345");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%j}", std::chrono::hours(12345 * 24 + 12)), "12345");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)),
|
||||
"03:25:45");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%R}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)), "03:25");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%T}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)), "03:25:45");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)), "12345");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%q}", std::chrono::seconds(12345)), "s");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, invalid_specs) {
|
||||
@ -616,78 +627,77 @@ TEST(chrono_test, locale) {
|
||||
using dms = std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>;
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_default_fp) {
|
||||
typedef std::chrono::duration<float> fs;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234s", fmt::format("{}", fs(1.234)));
|
||||
typedef std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli> fms;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234ms", fmt::format("{}", fms(1.234)));
|
||||
typedef std::chrono::duration<double> ds;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234s", fmt::format("{}", ds(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234ms", fmt::format("{}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<float>(1.234)), "1.234s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli>(1.234)),
|
||||
"1.234ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1.234)), "1.234s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", dms(1.234)), "1.234ms");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_precision) {
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(
|
||||
(void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.2%Q}"), std::chrono::seconds(42)),
|
||||
fmt::format_error, "precision not allowed for this argument type");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1ms", fmt::format("{:.0}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.2ms", fmt::format("{:.1}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.23ms", fmt::format("{:.{}}", dms(1.234), 2));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.0}", dms(1.234)), "1ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.1}", dms(1.234)), "1.2ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.{}}", dms(1.234), 2), "1.23ms");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("13ms", fmt::format("{:.0}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("12.6ms", fmt::format("{:.1}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("12.56ms", fmt::format("{:.2}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.0}", dms(12.56)), "13ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.1}", dms(12.56)), "12.6ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.2}", dms(12.56)), "12.56ms");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_full_specs) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1ms ", fmt::format("{:6.0}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.2ms ", fmt::format("{:6.1}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}}", dms(1.234), 2));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1.2ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}}", dms(1.234), 7, 1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}}", dms(1.234), 2, 8));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("=1.234ms=", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}}", dms(1.234), 9, 3));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("*1.2340ms*", fmt::format("{:*^10.4}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:6.0}", dms(1.234)), "1ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:6.1}", dms(1.234)), "1.2ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>8.{}}", dms(1.234), 2), " 1.23ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:^{}.{}}", dms(1.234), 7, 1), " 1.2ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}}", dms(1.234), 2, 8), " 1.23ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}}", dms(1.234), 9, 3), "=1.234ms=");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^10.4}", dms(1.234)), "*1.2340ms*");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("13ms ", fmt::format("{:6.0}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 13ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}}", dms(12.56), 0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 13ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}}", dms(12.56), 6, 0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 13ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}}", dms(12.56), 0, 8));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("==13ms===", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}}", dms(12.56), 9, 0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("***13ms***", fmt::format("{:*^10.0}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:6.0}", dms(12.56)), "13ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>8.{}}", dms(12.56), 0), " 13ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:^{}.{}}", dms(12.56), 6, 0), " 13ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}}", dms(12.56), 0, 8), " 13ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}}", dms(12.56), 9, 0), "==13ms===");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^10.0}", dms(12.56)), "***13ms***");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_simple_q) {
|
||||
typedef std::chrono::duration<float> fs;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234 s", fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", fs(1.234)));
|
||||
typedef std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli> fms;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234 ms", fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", fms(1.234)));
|
||||
typedef std::chrono::duration<double> ds;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234 s", fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", ds(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.234 ms", fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", std::chrono::duration<float>(1.234)),
|
||||
"1.234 s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli>(1.234)),
|
||||
"1.234 ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1.234)),
|
||||
"1.234 s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Q %q}", dms(1.234)), "1.234 ms");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_precision_q) {
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(
|
||||
(void)fmt::format(runtime("{:.2%Q %q}"), std::chrono::seconds(42)),
|
||||
fmt::format_error, "precision not allowed for this argument type");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.2 ms", fmt::format("{:.1%Q %q}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.23 ms", fmt::format("{:.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.1%Q %q}", dms(1.234)), "1.2 ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2), "1.23 ms");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, format_full_specs_q) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1 ms ", fmt::format("{:7.0%Q %q}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("1.2 ms ", fmt::format("{:7.1%Q %q}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23 ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1.2 ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 8, 1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 1.23 ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2, 9));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("=1.234 ms=", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 10, 3));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("*1.2340 ms*", fmt::format("{:*^11.4%Q %q}", dms(1.234)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:7.0%Q %q}", dms(1.234)), "1 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:7.1%Q %q}", dms(1.234)), "1.2 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>8.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2), " 1.23 ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 8, 1), " 1.2 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 2, 9), " 1.23 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(1.234), 10, 3), "=1.234 ms=");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^11.4%Q %q}", dms(1.234)), "*1.2340 ms*");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("13 ms ", fmt::format("{:7.0%Q %q}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 13 ms", fmt::format("{:>8.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 13 ms ", fmt::format("{:^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 8, 0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(" 13 ms ", fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 0, 9));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("==13 ms==", fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 9, 0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("***13 ms***", fmt::format("{:*^11.0%Q %q}", dms(12.56)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:7.0%Q %q}", dms(12.56)), "13 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:>8.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 0), " 13 ms");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 8, 0), " 13 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{0:^{2}.{1}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 0, 9), " 13 ms ");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:=^{}.{}%Q %q}", dms(12.56), 9, 0), "==13 ms==");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:*^11.0%Q %q}", dms(12.56)), "***13 ms***");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, invalid_width_id) {
|
||||
@ -701,27 +711,26 @@ TEST(chrono_test, invalid_colons) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, negative_durations) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("-12345", fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("-03:25:45",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("-00:01",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>(-1)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("s", fmt::format("{:%q}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("-00.127",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%S}",
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<signed char, std::milli>{-127}));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345)), "-12345");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%H:%M:%S}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345)),
|
||||
"-03:25:45");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>(-1)),
|
||||
"-00:01");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%q}", std::chrono::seconds(-12345)), "s");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}",
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<signed char, std::milli>(-127)),
|
||||
"-00.127");
|
||||
auto min = std::numeric_limits<int>::min();
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", min),
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%Q}", std::chrono::duration<int>(min)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, special_durations) {
|
||||
auto value = fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1e20));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(value, "40");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", std::chrono::duration<double>(1e20)), "40");
|
||||
auto nan = std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN();
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(
|
||||
"nan nan nan nan nan:nan nan",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%I %H %M %S %R %r}", std::chrono::duration<double>(nan)));
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%I %H %M %S %R %r}", std::chrono::duration<double>(nan)),
|
||||
"nan nan nan nan nan:nan nan");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::exa>(1)),
|
||||
"1Es");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::atto>(1)),
|
||||
@ -730,31 +739,30 @@ TEST(chrono_test, special_durations) {
|
||||
"03:33");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%T}", std::chrono::duration<char, std::mega>{2}),
|
||||
"03:33:20");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("01.234",
|
||||
fmt::format("{:.3%S}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::pico>(
|
||||
1.234e12)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(
|
||||
fmt::format("{:.3%S}", std::chrono::duration<float, std::pico>(1.234e12)),
|
||||
"01.234");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, unsigned_duration) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("42s", fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<unsigned>(42)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::chrono::duration<unsigned>(42)), "42s");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, weekday) {
|
||||
auto loc = get_locale("ru_RU.UTF-8");
|
||||
auto loc = get_locale("es_ES.UTF-8");
|
||||
std::locale::global(loc);
|
||||
auto mon = fmt::weekday(1);
|
||||
auto sat = fmt::weekday(6);
|
||||
|
||||
auto tm = std::tm();
|
||||
tm.tm_wday = static_cast<int>(mon.c_encoding());
|
||||
tm.tm_wday = static_cast<int>(sat.c_encoding());
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", mon), "Mon");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%a}", tm), "Mon");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", sat), "Sat");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%a}", tm), "Sat");
|
||||
|
||||
if (loc != std::locale::classic()) {
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT((std::vector<std::string>{"пн", "Пн", "пнд", "Пнд"}),
|
||||
Contains(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", mon)));
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT((std::vector<std::string>{"пн", "Пн", "пнд", "Пнд"}),
|
||||
Contains(fmt::format(loc, "{:%a}", tm)));
|
||||
auto saturdays = std::vector<std::string>{"sáb", "sá."};
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT(saturdays, Contains(fmt::format(loc, "{:L}", sat)));
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT(saturdays, Contains(fmt::format(loc, "{:%a}", tm)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -850,103 +858,86 @@ TEST(chrono_test, utc_clock) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, timestamps_ratios) {
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::milliseconds>
|
||||
t1(std::chrono::milliseconds(67890));
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, timestamp_ratios) {
|
||||
auto t1 =
|
||||
sys_time<std::chrono::milliseconds>(std::chrono::milliseconds(67890));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t1), "01:07.890");
|
||||
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::minutes>
|
||||
t2(std::chrono::minutes(7));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t2 = sys_time<std::chrono::minutes>(std::chrono::minutes(7));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t2), "07:00");
|
||||
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<9>>>
|
||||
t3(std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<9>>(7));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t3 = sys_time<std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<9>>>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<9>>(7));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t3), "01:03");
|
||||
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<63>>>
|
||||
t4(std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<63>>(1));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t4 = sys_time<std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<63>>>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<int, std::ratio<63>>(1));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%M:%S}", t4), "01:03");
|
||||
|
||||
if (sizeof(time_t) > 4) {
|
||||
auto tp =
|
||||
sys_time<std::chrono::milliseconds>(std::chrono::seconds(32503680000));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d}", tp), "3000-01-01");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (FMT_SAFE_DURATION_CAST) {
|
||||
using years = std::chrono::duration<std::int64_t, std::ratio<31556952>>;
|
||||
auto tp = sys_time<years>(years(std::numeric_limits<std::int64_t>::max()));
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG((void)fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d}", tp), fmt::format_error,
|
||||
"cannot format duration");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, timestamps_sub_seconds) {
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>>
|
||||
t1(std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>(4));
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, timestamp_sub_seconds) {
|
||||
auto t1 = sys_time<std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<long long, std::ratio<1, 3>>(4));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t1), "01.333333");
|
||||
|
||||
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 3>>>
|
||||
t2(std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 3>>(4));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t2 = sys_time<std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 3>>>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 3>>(4));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t2), "01.333333");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::seconds>
|
||||
t3(std::chrono::seconds(2));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t3 = sys_time<std::chrono::seconds>(std::chrono::seconds(2));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t3), "02");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<double>>
|
||||
t4(std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1>>(9.5));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t4 = sys_time<std::chrono::duration<double>>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1>>(9.5));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t4), "09.500000");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<double>>
|
||||
t5(std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1>>(9));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t5 = sys_time<std::chrono::duration<double>>(
|
||||
std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1>>(9));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t5), "09");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::milliseconds>
|
||||
t6(std::chrono::seconds(1) + std::chrono::milliseconds(120));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t6 = sys_time<std::chrono::milliseconds>(std::chrono::seconds(1) +
|
||||
std::chrono::milliseconds(120));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t6), "01.120");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::microseconds>
|
||||
t7(std::chrono::microseconds(1234567));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t7 =
|
||||
sys_time<std::chrono::microseconds>(std::chrono::microseconds(1234567));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t7), "01.234567");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::nanoseconds>
|
||||
t8(std::chrono::nanoseconds(123456789));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t8 =
|
||||
sys_time<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(std::chrono::nanoseconds(123456789));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t8), "00.123456789");
|
||||
|
||||
const auto t9 = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(
|
||||
auto t9 = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(
|
||||
std::chrono::system_clock::now());
|
||||
const auto t9_sec = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(t9);
|
||||
auto t9_sec = std::chrono::time_point_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(t9);
|
||||
auto t9_sub_sec_part = fmt::format("{0:09}", (t9 - t9_sec).count());
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}.{}", strftime_full_utc(t9_sec), t9_sub_sec_part),
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}", t9));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}.{}", strftime_full_utc(t9_sec), t9_sub_sec_part),
|
||||
fmt::format("{:%Y-%m-%d %T}", t9));
|
||||
|
||||
const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::milliseconds>
|
||||
t10(std::chrono::milliseconds(2000));
|
||||
|
||||
auto t10 =
|
||||
sys_time<std::chrono::milliseconds>(std::chrono::milliseconds(2000));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", t10), "02.000");
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
const auto epoch = std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock,
|
||||
std::chrono::milliseconds>();
|
||||
const auto d = std::chrono::milliseconds(250);
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("59.750", fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch - d));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00.000", fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ("00.250", fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch + d));
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto epoch = sys_time<std::chrono::milliseconds>();
|
||||
auto d = std::chrono::milliseconds(250);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch - d), "59.750");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch), "00.000");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%S}", epoch + d), "00.250");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, glibc_extensions) {
|
||||
@ -1001,3 +992,8 @@ TEST(chrono_test, glibc_extensions) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:%-S}", d), "3.140000");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(chrono_test, out_of_range) {
|
||||
auto d = std::chrono::duration<unsigned long, std::giga>(538976288);
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW((void)fmt::format("{:%j}", d), fmt::format_error);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -280,15 +280,18 @@ TEST(compile_test, compile_format_string_literal) {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// MSVS 2019 19.29.30145.0 - Support C++20 and OK.
|
||||
// MSVS 2022 19.32.31332.0 - compile-test.cc(362,3): fatal error C1001: Internal
|
||||
// compiler error.
|
||||
// MSVS 2022 19.32.31332.0, 19.37.32826.1 - compile-test.cc(362,3): fatal error
|
||||
// C1001: Internal compiler error.
|
||||
// (compiler file
|
||||
// 'D:\a\_work\1\s\src\vctools\Compiler\CxxFE\sl\p1\c\constexpr\constexpr.cpp',
|
||||
// line 8635)
|
||||
#if ((FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L) && \
|
||||
(!defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) || _GLIBCXX_RELEASE > 9) && \
|
||||
(!FMT_MSC_VERSION || FMT_MSC_VERSION < 1930)) || \
|
||||
(FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L && FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1002)
|
||||
#if (FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 202002L || \
|
||||
(FMT_CPLUSPLUS >= 201709L && FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 1002)) && \
|
||||
((!defined(_GLIBCXX_RELEASE) || _GLIBCXX_RELEASE >= 10) && \
|
||||
(!defined(_LIBCPP_VERSION) || _LIBCPP_VERSION >= 10000) && \
|
||||
(!FMT_MSC_VERSION || \
|
||||
(FMT_MSC_VERSION >= 1928 && FMT_MSC_VERSION < 1930))) && \
|
||||
defined(__cpp_lib_is_constant_evaluated)
|
||||
template <size_t max_string_length, typename Char = char> struct test_string {
|
||||
template <typename T> constexpr bool operator==(const T& rhs) const noexcept {
|
||||
return fmt::basic_string_view<Char>(rhs).compare(buffer) == 0;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,13 +246,6 @@ TEST(format_impl_test, format_error_code) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(format_impl_test, compute_width) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(4,
|
||||
fmt::detail::compute_width(
|
||||
fmt::basic_string_view<fmt::detail::char8_type>(
|
||||
reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>("ёжик"))));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tests fmt::detail::count_digits for integer type Int.
|
||||
template <typename Int> void test_count_digits() {
|
||||
for (Int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) EXPECT_EQ(1u, fmt::detail::count_digits(i));
|
||||
@ -351,7 +344,7 @@ TEST(format_impl_test, write_dragon_even) {
|
||||
if (!FMT_MSC_VERSION) EXPECT_EQ(s, "33554450");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(FMT_WINDOWS_NO_WCHAR)
|
||||
# include <windows.h>
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(format_impl_test, write_console_signature) {
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -354,7 +354,7 @@ TEST(output_redirect_test, dup_error_in_ctor) {
|
||||
FMT_POSIX(close(fd));
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<output_redirect> redir{nullptr};
|
||||
EXPECT_SYSTEM_ERROR_NOASSERT(
|
||||
redir.reset(new output_redirect(f.get())), EBADF,
|
||||
redir.reset(new output_redirect(f.get(), false)), EBADF,
|
||||
fmt::format("cannot duplicate file descriptor {}", fd));
|
||||
copy.dup2(fd); // "undo" close or dtor will fail
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,8 +11,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
using fmt::file;
|
||||
|
||||
output_redirect::output_redirect(FILE* f) : file_(f) {
|
||||
flush();
|
||||
output_redirect::output_redirect(FILE* f, bool flush) : file_(f) {
|
||||
if (flush) this->flush();
|
||||
int fd = FMT_POSIX(fileno(f));
|
||||
// Create a file object referring to the original file.
|
||||
original_ = file::dup(fd);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ class output_redirect {
|
||||
void restore();
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit output_redirect(FILE* file);
|
||||
explicit output_redirect(FILE* file, bool flush = true);
|
||||
~output_redirect() noexcept;
|
||||
|
||||
output_redirect(const output_redirect&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1912,7 +1912,7 @@ void AssertHelper::operator=(const Message& message) const {
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
// When TEST_P is found without a matching INSTANTIATE_TEST_SUITE_P
|
||||
// to creates test cases for it, a syntetic test case is
|
||||
// to creates test cases for it, a synthetic test case is
|
||||
// inserted to report ether an error or a log message.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This configuration bit will likely be removed at some point.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ struct test {};
|
||||
// included after fmt/format.h.
|
||||
namespace fmt {
|
||||
template <> struct formatter<test> : formatter<int> {
|
||||
auto format(const test&, format_context& ctx) -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
auto format(const test&, format_context& ctx) const -> decltype(ctx.out()) {
|
||||
return formatter<int>::format(42, ctx);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -289,3 +289,20 @@ TEST(ostream_test, closed_ofstream) {
|
||||
std::ofstream ofs;
|
||||
fmt::print(ofs, "discard");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct unlocalized {};
|
||||
|
||||
auto operator<<(std::ostream& os, unlocalized)
|
||||
-> std::ostream& {
|
||||
return os << 12345;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace fmt {
|
||||
template <> struct formatter<unlocalized> : ostream_formatter {};
|
||||
} // namespace fmt
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ostream_test, unlocalized) {
|
||||
auto loc = get_locale("en_US.UTF-8");
|
||||
std::locale::global(loc);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(loc, "{}", unlocalized()), "12345");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,13 +30,13 @@ namespace test {
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _MSC_VER
|
||||
// Size type for read and write.
|
||||
typedef size_t size_t;
|
||||
typedef ssize_t ssize_t;
|
||||
using size_t = size_t;
|
||||
using ssize_t = ssize_t;
|
||||
int open(const char* path, int oflag, int mode);
|
||||
int fstat(int fd, struct stat* buf);
|
||||
#else
|
||||
typedef unsigned size_t;
|
||||
typedef int ssize_t;
|
||||
using size_t = unsigned;
|
||||
using ssize_t = int;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _WIN32
|
||||
|
||||
@ -310,10 +310,10 @@ TEST(printf_test, dynamic_precision) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> struct make_signed { typedef T type; };
|
||||
template <typename T> struct make_signed { using type = T; };
|
||||
|
||||
#define SPECIALIZE_MAKE_SIGNED(T, S) \
|
||||
template <> struct make_signed<T> { typedef S type; }
|
||||
template <> struct make_signed<T> { using type = S; }
|
||||
|
||||
SPECIALIZE_MAKE_SIGNED(char, signed char);
|
||||
SPECIALIZE_MAKE_SIGNED(unsigned char, signed char);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,23 +1,25 @@
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - the core API
|
||||
// Formatting library for C++ - ranges tests
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2012 - present, Victor Zverovich and {fmt} contributors
|
||||
// All rights reserved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For the license information refer to format.h.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Copyright (c) 2018 - present, Remotion (Igor Schulz)
|
||||
// All Rights Reserved
|
||||
// {fmt} support for ranges, containers and types tuple interface.
|
||||
|
||||
#include "fmt/ranges.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
#include <map>
|
||||
#include <numeric>
|
||||
#include <queue>
|
||||
#include <stack>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <utility>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_HAS_INCLUDE(<ranges>)
|
||||
# include <ranges>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "gtest/gtest.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#if !FMT_GCC_VERSION || FMT_GCC_VERSION >= 601
|
||||
@ -63,13 +65,18 @@ TEST(ranges_test, format_vector) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:n:}", vvc), "a, b, c, a, b, c");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, format_vector2) {
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, format_nested_vector) {
|
||||
auto v = std::vector<std::vector<int>>{{1, 2}, {3, 5}, {7, 11}};
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[[1, 2], [3, 5], [7, 11]]");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:::#x}", v), "[[0x1, 0x2], [0x3, 0x5], [0x7, 0xb]]");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:n:n:#x}", v), "0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x5, 0x7, 0xb");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, to_string_vector) {
|
||||
auto v = std::vector<std::string>{"a", "b", "c"};
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::to_string(v), "[\"a\", \"b\", \"c\"]");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, format_map) {
|
||||
auto m = std::map<std::string, int>{{"one", 1}, {"two", 2}};
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", m), "{\"one\": 1, \"two\": 2}");
|
||||
@ -83,7 +90,7 @@ TEST(ranges_test, format_set) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Models std::flat_set close enough to test if no ambiguous lookup of a
|
||||
// formatter happens due to the flat_set type matching is_set and
|
||||
// is_container_adaptor_like
|
||||
// is_container_adaptor_like.
|
||||
template <typename T> class flat_set {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using key_type = T;
|
||||
@ -95,11 +102,11 @@ template <typename T> class flat_set {
|
||||
template <typename... Ts>
|
||||
explicit flat_set(Ts&&... args) : c{std::forward<Ts>(args)...} {}
|
||||
|
||||
iterator begin() { return c.begin(); }
|
||||
const_iterator begin() const { return c.begin(); }
|
||||
auto begin() -> iterator { return c.begin(); }
|
||||
auto end() -> iterator { return c.end(); }
|
||||
|
||||
iterator end() { return c.end(); }
|
||||
const_iterator end() const { return c.end(); }
|
||||
auto begin() const -> const_iterator { return c.begin(); }
|
||||
auto end() const -> const_iterator { return c.end(); }
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
std::vector<T> c;
|
||||
@ -116,7 +123,6 @@ struct box {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
auto begin(const box& b) -> const int* { return &b.value; }
|
||||
|
||||
auto end(const box& b) -> const int* { return &b.value + 1; }
|
||||
} // namespace adl
|
||||
|
||||
@ -173,11 +179,12 @@ struct tuple_like {
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
std::string str;
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t N> fmt::enable_if_t<N == 0, int> get() const noexcept {
|
||||
template <size_t N>
|
||||
auto get() const noexcept -> fmt::enable_if_t<N == 0, int> {
|
||||
return i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <size_t N>
|
||||
fmt::enable_if_t<N == 1, fmt::string_view> get() const noexcept {
|
||||
auto get() const noexcept -> fmt::enable_if_t<N == 1, fmt::string_view> {
|
||||
return str;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -210,8 +217,8 @@ TEST(ranges_test, format_to) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> struct path_like {
|
||||
const path_like* begin() const;
|
||||
const path_like* end() const;
|
||||
auto begin() const -> const path_like*;
|
||||
auto end() const -> const path_like*;
|
||||
|
||||
operator std::basic_string<Char>() const;
|
||||
};
|
||||
@ -241,8 +248,8 @@ template <typename T> class non_const_only_range {
|
||||
explicit non_const_only_range(Args&&... args)
|
||||
: vec(std::forward<Args>(args)...) {}
|
||||
|
||||
const_iterator begin() { return vec.begin(); }
|
||||
const_iterator end() { return vec.end(); }
|
||||
auto begin() -> const_iterator { return vec.begin(); }
|
||||
auto end() -> const_iterator { return vec.end(); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> class noncopyable_range {
|
||||
@ -259,16 +266,16 @@ template <typename T> class noncopyable_range {
|
||||
noncopyable_range(noncopyable_range const&) = delete;
|
||||
noncopyable_range(noncopyable_range&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
iterator begin() { return vec.begin(); }
|
||||
iterator end() { return vec.end(); }
|
||||
auto begin() -> iterator { return vec.begin(); }
|
||||
auto end() -> iterator { return vec.end(); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, range) {
|
||||
noncopyable_range<int> w(3u, 0);
|
||||
auto&& w = noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", w), "[0, 0, 0]");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0)), "[0, 0, 0]");
|
||||
|
||||
non_const_only_range<int> x(3u, 0);
|
||||
auto x = non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", x), "[0, 0, 0]");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0)), "[0, 0, 0]");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -343,8 +350,8 @@ bool operator!=(const char* p, zstring_sentinel) { return *p != '\0'; }
|
||||
|
||||
struct zstring {
|
||||
const char* p;
|
||||
const char* begin() const { return p; }
|
||||
zstring_sentinel end() const { return {}; }
|
||||
auto begin() const -> const char* { return p; }
|
||||
auto end() const -> zstring_sentinel { return {}; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
# ifdef __cpp_lib_ranges
|
||||
@ -358,20 +365,22 @@ struct cpp20_only_range {
|
||||
|
||||
iterator() = default;
|
||||
iterator(int i) : val(i) {}
|
||||
int operator*() const { return val; }
|
||||
iterator& operator++() {
|
||||
auto operator*() const -> int { return val; }
|
||||
auto operator++() -> iterator& {
|
||||
++val;
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
void operator++(int) { ++*this; }
|
||||
bool operator==(const iterator& rhs) const { return val == rhs.val; }
|
||||
auto operator==(const iterator& rhs) const -> bool {
|
||||
return val == rhs.val;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
int lo;
|
||||
int hi;
|
||||
|
||||
iterator begin() const { return iterator(lo); }
|
||||
iterator end() const { return iterator(hi); }
|
||||
auto begin() const -> iterator { return iterator(lo); }
|
||||
auto end() const -> iterator { return iterator(hi); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
static_assert(std::input_iterator<cpp20_only_range::iterator>);
|
||||
@ -385,12 +394,12 @@ TEST(ranges_test, join_sentinel) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, join_range) {
|
||||
noncopyable_range<int> w(3u, 0);
|
||||
auto&& w = noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(w, ",")), "0,0,0");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(noncopyable_range<int>(3u, 0), ",")),
|
||||
"0,0,0");
|
||||
|
||||
non_const_only_range<int> x(3u, 0);
|
||||
auto x = non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(x, ",")), "0,0,0");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", fmt::join(non_const_only_range<int>(3u, 0), ",")),
|
||||
"0,0,0");
|
||||
@ -413,6 +422,17 @@ TEST(ranges_test, join_range) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // FMT_RANGES_TEST_ENABLE_JOIN
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(__cpp_lib_ranges) && __cpp_lib_ranges >= 202302L
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, nested_ranges) {
|
||||
auto l = std::list{1, 2, 3};
|
||||
auto r = std::views::iota(0, 3) | std::views::transform([&l](auto i) {
|
||||
return std::views::take(std::ranges::subrange(l), i);
|
||||
}) |
|
||||
std::views::transform(std::views::reverse);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", r), "[[], [1], [2, 1]]");
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, is_printable) {
|
||||
using fmt::detail::is_printable;
|
||||
EXPECT_TRUE(is_printable(0x0323));
|
||||
@ -456,10 +476,10 @@ template <typename R> struct fmt_ref_view {
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, range_of_range_of_mixed_const) {
|
||||
std::vector<std::vector<int>> v = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5}};
|
||||
auto v = std::vector<std::vector<int>>{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5}};
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", v), "[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]");
|
||||
|
||||
fmt_ref_view<decltype(v)> r{&v};
|
||||
auto r = fmt_ref_view<decltype(v)>{&v};
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", r), "[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]]");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -525,3 +545,16 @@ TEST(ranges_test, container_adaptor) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", m), "[1, 2]");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct tieable {
|
||||
int a = 3;
|
||||
double b = 0.42;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
auto format_as(const tieable& t) -> std::tuple<int, double> {
|
||||
return std::tie(t.a, t.b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(ranges_test, format_as_tie) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", tieable()), "(3, 0.42)");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,23 +10,29 @@
|
||||
#include <time.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <climits>
|
||||
#include <thread>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "fmt/os.h"
|
||||
#include "gmock/gmock.h"
|
||||
#include "gtest-extra.h"
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_text) {
|
||||
auto s = fmt::string_view("foo");
|
||||
fmt::string_view s = "foo";
|
||||
auto end = fmt::scan(s, "foo");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(end, s.end());
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("fob", "foo"), fmt::format_error, "invalid input");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_int) {
|
||||
auto n = int();
|
||||
int n = 0;
|
||||
fmt::scan("42", "{}", n);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n, 42);
|
||||
fmt::scan("-42", "{}", n);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n, -42);
|
||||
fmt::scan("42", "{:}", n);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n, 42);
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan(std::to_string(INT_MAX + 1u), "{}", n),
|
||||
fmt::format_error, "number is too big");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_longlong) {
|
||||
@ -38,7 +44,7 @@ TEST(scan_test, read_longlong) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_uint) {
|
||||
auto n = unsigned();
|
||||
unsigned n = 0;
|
||||
fmt::scan("42", "{}", n);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n, 42);
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("-42", "{}", n), fmt::format_error,
|
||||
@ -53,52 +59,63 @@ TEST(scan_test, read_ulonglong) {
|
||||
"invalid input");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_hex) {
|
||||
unsigned n = 0;
|
||||
fmt::scan("2a", "{:x}", n);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n, 42);
|
||||
auto num_digits = std::numeric_limits<unsigned>::digits / 4;
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan(fmt::format("1{:0{}}", 0, num_digits), "{:x}", n),
|
||||
fmt::format_error, "number is too big");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_string) {
|
||||
auto s = std::string();
|
||||
std::string s;
|
||||
fmt::scan("foo", "{}", s);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(s, "foo");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_string_view) {
|
||||
auto s = fmt::string_view();
|
||||
fmt::string_view s;
|
||||
fmt::scan("foo", "{}", s);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(s, "foo");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef FMT_HAVE_STRPTIME
|
||||
namespace fmt {
|
||||
template <> struct scanner<tm> {
|
||||
std::string format;
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, separator) {
|
||||
int n1 = 0, n2 = 0;
|
||||
fmt::scan("10 20", "{} {}", n1, n2);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n1, 10);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n2, 20);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
scan_parse_context::iterator parse(scan_parse_context& ctx) {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin();
|
||||
if (it != ctx.end() && *it == ':') ++it;
|
||||
auto end = it;
|
||||
while (end != ctx.end() && *end != '}') ++end;
|
||||
format.reserve(detail::to_unsigned(end - it + 1));
|
||||
format.append(it, end);
|
||||
format.push_back('\0');
|
||||
return end;
|
||||
struct num {
|
||||
int value;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace fmt {
|
||||
template <> struct scanner<num> {
|
||||
bool hex = false;
|
||||
|
||||
auto parse(scan_parse_context& ctx) -> scan_parse_context::iterator {
|
||||
auto it = ctx.begin(), end = ctx.end();
|
||||
if (it != end && *it == 'x') hex = true;
|
||||
if (it != end && *it != '}') throw_format_error("invalid format");
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <class ScanContext>
|
||||
typename ScanContext::iterator scan(tm& t, ScanContext& ctx) {
|
||||
auto result = strptime(ctx.begin(), format.c_str(), &t);
|
||||
if (!result) throw format_error("failed to parse time");
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
auto scan(num& n, ScanContext& ctx) const -> typename ScanContext::iterator {
|
||||
// TODO: handle specifier
|
||||
return fmt::scan(ctx, "{}", n.value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace fmt
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, read_custom) {
|
||||
auto input = "Date: 1985-10-25";
|
||||
auto t = tm();
|
||||
fmt::scan(input, "Date: {0:%Y-%m-%d}", t);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(t.tm_year, 85);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(t.tm_mon, 9);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(t.tm_mday, 25);
|
||||
auto input = "42";
|
||||
auto n = num();
|
||||
fmt::scan(input, "{:}", n);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n.value, 42);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, invalid_format) {
|
||||
EXPECT_THROW_MSG(fmt::scan("", "{}"), fmt::format_error,
|
||||
@ -108,9 +125,64 @@ TEST(scan_test, invalid_format) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, example) {
|
||||
auto key = std::string();
|
||||
auto value = int();
|
||||
std::string key;
|
||||
int value = 0;
|
||||
fmt::scan("answer = 42", "{} = {}", key, value);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(key, "answer");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(value, 42);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, end_of_input) {
|
||||
int value = 0;
|
||||
fmt::scan("", "{}", value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#if FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, file) {
|
||||
fmt::file read_end, write_end;
|
||||
fmt::file::pipe(read_end, write_end);
|
||||
|
||||
fmt::string_view input = "10 20";
|
||||
write_end.write(input.data(), input.size());
|
||||
write_end.close();
|
||||
|
||||
int n1 = 0, n2 = 0;
|
||||
fmt::buffered_file f = read_end.fdopen("r");
|
||||
fmt::scan(f.get(), "{} {}", n1, n2);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n1, 10);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(n2, 20);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(scan_test, lock) {
|
||||
fmt::file read_end, write_end;
|
||||
fmt::file::pipe(read_end, write_end);
|
||||
|
||||
std::thread producer([&]() {
|
||||
fmt::string_view input = "42 ";
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) write_end.write(input.data(), input.size());
|
||||
write_end.close();
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
std::atomic<int> count(0);
|
||||
fmt::buffered_file f = read_end.fdopen("r");
|
||||
auto fun = [&]() {
|
||||
int value = 0;
|
||||
while (fmt::scan(f.get(), "{}", value)) {
|
||||
if (value != 42) {
|
||||
read_end.close();
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(value, 42);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
++count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
std::thread consumer1(fun);
|
||||
std::thread consumer2(fun);
|
||||
|
||||
producer.join();
|
||||
consumer1.join();
|
||||
consumer2.join();
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(count, 1000);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // FMT_USE_FCNTL
|
||||
|
||||
718
test/scan.h
718
test/scan.h
@ -12,6 +12,264 @@
|
||||
#include "fmt/format.h"
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
inline auto is_whitespace(char c) -> bool { return c == ' ' || c == '\n'; }
|
||||
|
||||
// If c is a hex digit returns its numeric value, othewise -1.
|
||||
inline auto to_hex_digit(char c) -> int {
|
||||
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') return c - '0';
|
||||
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f') return c - 'a' + 10;
|
||||
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'F') return c - 'A' + 10;
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct maybe_contiguous_range {
|
||||
const char* begin;
|
||||
const char* end;
|
||||
|
||||
explicit operator bool() const { return begin != nullptr; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class scan_buffer {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
const char* ptr_;
|
||||
const char* end_;
|
||||
bool contiguous_;
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
scan_buffer(const char* ptr, const char* end, bool contiguous)
|
||||
: ptr_(ptr), end_(end), contiguous_(contiguous) {}
|
||||
~scan_buffer() = default;
|
||||
|
||||
void set(string_view buf) {
|
||||
ptr_ = buf.begin();
|
||||
end_ = buf.end();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto ptr() const -> const char* { return ptr_; }
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
scan_buffer(const scan_buffer&) = delete;
|
||||
void operator=(const scan_buffer&) = delete;
|
||||
|
||||
// Fills the buffer with more input if available.
|
||||
virtual void consume() = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
class sentinel {};
|
||||
|
||||
class iterator {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
const char** ptr_;
|
||||
scan_buffer* buf_; // This could be merged with ptr_.
|
||||
char value_;
|
||||
|
||||
static auto get_sentinel() -> const char** {
|
||||
static const char* ptr = nullptr;
|
||||
return &ptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend class scan_buffer;
|
||||
|
||||
friend auto operator==(iterator lhs, sentinel) -> bool {
|
||||
return *lhs.ptr_ == nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
friend auto operator!=(iterator lhs, sentinel) -> bool {
|
||||
return *lhs.ptr_ != nullptr;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
iterator(scan_buffer* buf) : buf_(buf) {
|
||||
if (buf->ptr_ == buf->end_) {
|
||||
ptr_ = get_sentinel();
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ptr_ = &buf->ptr_;
|
||||
value_ = *buf->ptr_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
friend scan_buffer& get_buffer(iterator it) { return *it.buf_; }
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
iterator() : ptr_(get_sentinel()), buf_(nullptr) {}
|
||||
|
||||
auto operator++() -> iterator& {
|
||||
if (!buf_->try_consume()) ptr_ = get_sentinel();
|
||||
value_ = *buf_->ptr_;
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto operator++(int) -> iterator {
|
||||
iterator copy = *this;
|
||||
++*this;
|
||||
return copy;
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto operator*() const -> char { return value_; }
|
||||
|
||||
auto base() const -> const char* { return buf_->ptr_; }
|
||||
|
||||
friend auto to_contiguous(iterator it) -> maybe_contiguous_range;
|
||||
friend auto advance(iterator it, size_t n) -> iterator;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
friend auto to_contiguous(iterator it) -> maybe_contiguous_range {
|
||||
if (it.buf_->is_contiguous()) return {it.buf_->ptr_, it.buf_->end_};
|
||||
return {nullptr, nullptr};
|
||||
}
|
||||
friend auto advance(iterator it, size_t n) -> iterator {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(it.buf_->is_contiguous(), "");
|
||||
const char*& ptr = it.buf_->ptr_;
|
||||
ptr += n;
|
||||
it.value_ = *ptr;
|
||||
if (ptr == it.buf_->end_) it.ptr_ = iterator::get_sentinel();
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto begin() -> iterator { return this; }
|
||||
auto end() -> sentinel { return {}; }
|
||||
|
||||
auto is_contiguous() const -> bool { return contiguous_; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Tries consuming a single code unit. Returns true iff there is more input.
|
||||
auto try_consume() -> bool {
|
||||
FMT_ASSERT(ptr_ != end_, "");
|
||||
++ptr_;
|
||||
if (ptr_ != end_) return true;
|
||||
consume();
|
||||
return ptr_ != end_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
using scan_iterator = scan_buffer::iterator;
|
||||
using scan_sentinel = scan_buffer::sentinel;
|
||||
|
||||
class string_scan_buffer : public scan_buffer {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
void consume() override {}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit string_scan_buffer(string_view s)
|
||||
: scan_buffer(s.begin(), s.end(), true) {}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
void flockfile(FILE* f) { _lock_file(f); }
|
||||
void funlockfile(FILE* f) { _unlock_file(f); }
|
||||
int getc_unlocked(FILE* f) { return _fgetc_nolock(f); }
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// A FILE wrapper. F is FILE defined as a template parameter to make
|
||||
// system-specific API detection work.
|
||||
template <typename F> class file_base {
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
F* file_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
file_base(F* file) : file_(file) {}
|
||||
operator F*() const { return file_; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Reads a code unit from the stream.
|
||||
auto get() -> int {
|
||||
int result = getc_unlocked(file_);
|
||||
if (result == EOF && ferror(file_) != 0)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("getc failed")));
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Puts the code unit back into the stream buffer.
|
||||
void unget(char c) {
|
||||
if (ungetc(c, file_) == EOF)
|
||||
FMT_THROW(system_error(errno, FMT_STRING("ungetc failed")));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// A FILE wrapper for glibc.
|
||||
template <typename F> class glibc_file : public file_base<F> {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using file_base<F>::file_base;
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the file's read buffer as a string_view.
|
||||
auto buffer() const -> string_view {
|
||||
return {this->file_->_IO_read_ptr,
|
||||
to_unsigned(this->file_->_IO_read_end - this->file_->_IO_read_ptr)};
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// A FILE wrapper for Apple's libc.
|
||||
template <typename F> class apple_file : public file_base<F> {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using file_base<F>::file_base;
|
||||
|
||||
auto buffer() const -> string_view {
|
||||
return {reinterpret_cast<char*>(this->file_->_p),
|
||||
to_unsigned(this->file_->_r)};
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// A fallback FILE wrapper.
|
||||
template <typename F> class fallback_file : public file_base<F> {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
char next_; // The next unconsumed character in the buffer.
|
||||
bool has_next_ = false;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using file_base<F>::file_base;
|
||||
|
||||
auto buffer() const -> string_view { return {&next_, has_next_ ? 1u : 0u}; }
|
||||
|
||||
auto get() -> int {
|
||||
has_next_ = false;
|
||||
return file_base<F>::get();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void unget(char c) {
|
||||
file_base<F>::unget(c);
|
||||
next_ = c;
|
||||
has_next_ = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class file_scan_buffer : public scan_buffer {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
template <typename F, FMT_ENABLE_IF(sizeof(F::_IO_read_ptr) != 0)>
|
||||
static auto get_file(F* f, int) -> glibc_file<F> {
|
||||
return f;
|
||||
}
|
||||
template <typename F, FMT_ENABLE_IF(sizeof(F::_p) != 0)>
|
||||
static auto get_file(F* f, int) -> apple_file<F> {
|
||||
return f;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static auto get_file(FILE* f, ...) -> fallback_file<FILE> { return f; }
|
||||
|
||||
decltype(get_file(static_cast<FILE*>(nullptr), 0)) file_;
|
||||
|
||||
// Fills the buffer if it is empty.
|
||||
void fill() {
|
||||
string_view buf = file_.buffer();
|
||||
if (buf.size() == 0) {
|
||||
int c = file_.get();
|
||||
// Put the character back since we are only filling the buffer.
|
||||
if (c != EOF) file_.unget(static_cast<char>(c));
|
||||
buf = file_.buffer();
|
||||
}
|
||||
set(buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void consume() override {
|
||||
// Consume the current buffer content.
|
||||
size_t n = to_unsigned(ptr() - file_.buffer().begin());
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i != n; ++i) file_.get();
|
||||
fill();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit file_scan_buffer(FILE* f)
|
||||
: scan_buffer(nullptr, nullptr, false), file_(f) {
|
||||
flockfile(f);
|
||||
fill();
|
||||
}
|
||||
~file_scan_buffer() { funlockfile(file_); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, typename Char = char> struct scanner {
|
||||
// A deleted default constructor indicates a disabled scanner.
|
||||
scanner() = delete;
|
||||
@ -27,31 +285,14 @@ class scan_parse_context {
|
||||
explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_parse_context(string_view format)
|
||||
: format_(format) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR iterator begin() const { return format_.begin(); }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR iterator end() const { return format_.end(); }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto begin() const -> iterator { return format_.begin(); }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto end() const -> iterator { return format_.end(); }
|
||||
|
||||
void advance_to(iterator it) {
|
||||
format_.remove_prefix(detail::to_unsigned(it - begin()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct scan_context {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
string_view input_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using iterator = const char*;
|
||||
|
||||
explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_context(string_view input) : input_(input) {}
|
||||
|
||||
iterator begin() const { return input_.data(); }
|
||||
iterator end() const { return begin() + input_.size(); }
|
||||
|
||||
void advance_to(iterator it) {
|
||||
input_.remove_prefix(detail::to_unsigned(it - begin()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
enum class scan_type {
|
||||
none_type,
|
||||
@ -64,181 +305,362 @@ enum class scan_type {
|
||||
custom_type
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct custom_scan_arg {
|
||||
template <typename Context> struct custom_scan_arg {
|
||||
void* value;
|
||||
void (*scan)(void* arg, scan_parse_context& parse_ctx, scan_context& ctx);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class scan_arg {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
scan_type type;
|
||||
union {
|
||||
int* int_value;
|
||||
unsigned* uint_value;
|
||||
long long* long_long_value;
|
||||
unsigned long long* ulong_long_value;
|
||||
std::string* string;
|
||||
fmt::string_view* string_view;
|
||||
custom_scan_arg custom;
|
||||
// TODO: more types
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg() : type(scan_type::none_type), int_value(nullptr) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(int& value)
|
||||
: type(scan_type::int_type), int_value(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(unsigned& value)
|
||||
: type(scan_type::uint_type), uint_value(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(long long& value)
|
||||
: type(scan_type::long_long_type), long_long_value(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(unsigned long long& value)
|
||||
: type(scan_type::ulong_long_type), ulong_long_value(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(std::string& value)
|
||||
: type(scan_type::string_type), string(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(fmt::string_view& value)
|
||||
: type(scan_type::string_view_type), string_view(&value) {}
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_arg(T& value) : type(scan_type::custom_type) {
|
||||
custom.value = &value;
|
||||
custom.scan = scan_custom_arg<T>;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
static void scan_custom_arg(void* arg, scan_parse_context& parse_ctx,
|
||||
scan_context& ctx) {
|
||||
scanner<T> s;
|
||||
parse_ctx.advance_to(s.parse(parse_ctx));
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(s.scan(*static_cast<T*>(arg), ctx));
|
||||
}
|
||||
void (*scan)(void* arg, scan_parse_context& parse_ctx, Context& ctx);
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
// A scan argument. Context is a template parameter for the compiled API where
|
||||
// output can be unbuffered.
|
||||
template <typename Context> class basic_scan_arg {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
using scan_type = detail::scan_type;
|
||||
scan_type type_;
|
||||
union {
|
||||
int* int_value_;
|
||||
unsigned* uint_value_;
|
||||
long long* long_long_value_;
|
||||
unsigned long long* ulong_long_value_;
|
||||
std::string* string_;
|
||||
string_view* string_view_;
|
||||
detail::custom_scan_arg<Context> custom_;
|
||||
// TODO: more types
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
static void scan_custom_arg(void* arg, scan_parse_context& parse_ctx,
|
||||
Context& ctx) {
|
||||
auto s = scanner<T>();
|
||||
parse_ctx.advance_to(s.parse(parse_ctx));
|
||||
ctx.advance_to(s.scan(*static_cast<T*>(arg), ctx));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg()
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::none_type), int_value_(nullptr) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(int& value)
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::int_type), int_value_(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(unsigned& value)
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::uint_type), uint_value_(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(long long& value)
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::long_long_type), long_long_value_(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(unsigned long long& value)
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::ulong_long_type), ulong_long_value_(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(std::string& value)
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::string_type), string_(&value) {}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(string_view& value)
|
||||
: type_(scan_type::string_view_type), string_view_(&value) {}
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR basic_scan_arg(T& value) : type_(scan_type::custom_type) {
|
||||
custom_.value = &value;
|
||||
custom_.scan = scan_custom_arg<T>;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
constexpr explicit operator bool() const noexcept {
|
||||
return type_ != scan_type::none_type;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto type() const -> detail::scan_type { return type_; }
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Visitor>
|
||||
auto visit(Visitor&& vis) -> decltype(vis(monostate())) {
|
||||
switch (type_) {
|
||||
case scan_type::none_type:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case scan_type::int_type:
|
||||
return vis(*int_value_);
|
||||
case scan_type::uint_type:
|
||||
return vis(*uint_value_);
|
||||
case scan_type::long_long_type:
|
||||
return vis(*long_long_value_);
|
||||
case scan_type::ulong_long_type:
|
||||
return vis(*ulong_long_value_);
|
||||
case scan_type::string_type:
|
||||
return vis(*string_);
|
||||
case scan_type::string_view_type:
|
||||
return vis(*string_view_);
|
||||
case scan_type::custom_type:
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return vis(monostate());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto scan_custom(const char* parse_begin, scan_parse_context& parse_ctx,
|
||||
Context& ctx) const -> bool {
|
||||
if (type_ != scan_type::custom_type) return false;
|
||||
parse_ctx.advance_to(parse_begin);
|
||||
custom_.scan(custom_.value, parse_ctx, ctx);
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class scan_context;
|
||||
using scan_arg = basic_scan_arg<scan_context>;
|
||||
|
||||
struct scan_args {
|
||||
int size;
|
||||
const detail::scan_arg* data;
|
||||
const scan_arg* data;
|
||||
|
||||
template <size_t N>
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_args(const std::array<detail::scan_arg, N>& store)
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_args(const std::array<scan_arg, N>& store)
|
||||
: size(N), data(store.data()) {
|
||||
static_assert(N < INT_MAX, "too many arguments");
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
class scan_context {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
detail::scan_buffer& buf_;
|
||||
scan_args args_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
using iterator = detail::scan_iterator;
|
||||
using sentinel = detail::scan_sentinel;
|
||||
|
||||
explicit FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_context(detail::scan_buffer& buf, scan_args args)
|
||||
: buf_(buf), args_(args) {}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto arg(int id) const -> scan_arg {
|
||||
return id < args_.size ? args_.data[id] : scan_arg();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto begin() const -> iterator { return buf_.begin(); }
|
||||
auto end() const -> sentinel { return {}; }
|
||||
|
||||
void advance_to(iterator) { buf_.consume(); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace detail {
|
||||
|
||||
const char* parse_scan_specs(const char* begin, const char* end,
|
||||
format_specs<>& specs, scan_type) {
|
||||
while (begin != end) {
|
||||
switch (to_ascii(*begin)) {
|
||||
// TODO: parse more scan format specifiers
|
||||
case 'x':
|
||||
specs.type = presentation_type::hex_lower;
|
||||
++begin;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case '}':
|
||||
return begin;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return begin;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_unsigned<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto read(scan_iterator it, T& value)
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
if (it == scan_sentinel()) return it;
|
||||
char c = *it;
|
||||
if (c < '0' || c > '9') throw_format_error("invalid input");
|
||||
|
||||
int num_digits = 0;
|
||||
T n = 0, prev = 0;
|
||||
char prev_digit = c;
|
||||
do {
|
||||
prev = n;
|
||||
n = n * 10 + static_cast<unsigned>(c - '0');
|
||||
prev_digit = c;
|
||||
c = *++it;
|
||||
++num_digits;
|
||||
if (c < '0' || c > '9') break;
|
||||
} while (it != scan_sentinel());
|
||||
|
||||
// Check overflow.
|
||||
if (num_digits <= std::numeric_limits<int>::digits10) {
|
||||
value = n;
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
unsigned max = to_unsigned((std::numeric_limits<int>::max)());
|
||||
if (num_digits == std::numeric_limits<int>::digits10 + 1 &&
|
||||
prev * 10ull + unsigned(prev_digit - '0') <= max) {
|
||||
value = n;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
throw_format_error("number is too big");
|
||||
}
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_unsigned<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto read_hex(scan_iterator it, T& value)
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
if (it == scan_sentinel()) return it;
|
||||
int digit = to_hex_digit(*it);
|
||||
if (digit < 0) throw_format_error("invalid input");
|
||||
|
||||
int num_digits = 0;
|
||||
T n = 0;
|
||||
do {
|
||||
n = (n << 4) + static_cast<unsigned>(digit);
|
||||
++num_digits;
|
||||
digit = to_hex_digit(*++it);
|
||||
if (digit < 0) break;
|
||||
} while (it != scan_sentinel());
|
||||
|
||||
// Check overflow.
|
||||
if (num_digits <= (std::numeric_limits<T>::digits >> 2))
|
||||
value = n;
|
||||
else
|
||||
throw_format_error("number is too big");
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_unsigned<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto read(scan_iterator it, T& value, const format_specs<>& specs)
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
if (specs.type == presentation_type::hex_lower)
|
||||
return read_hex(it, value);
|
||||
return read(it, value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T, FMT_ENABLE_IF(std::is_signed<T>::value)>
|
||||
auto read(scan_iterator it, T& value, const format_specs<>& = {})
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
bool negative = it != scan_sentinel() && *it == '-';
|
||||
if (negative) {
|
||||
++it;
|
||||
if (it == scan_sentinel()) throw_format_error("invalid input");
|
||||
}
|
||||
using unsigned_type = typename std::make_unsigned<T>::type;
|
||||
unsigned_type abs_value = 0;
|
||||
it = read(it, abs_value);
|
||||
auto n = static_cast<T>(abs_value);
|
||||
value = negative ? -n : n;
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto read(scan_iterator it, std::string& value, const format_specs<>& = {})
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
while (it != scan_sentinel() && *it != ' ') value.push_back(*it++);
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto read(scan_iterator it, string_view& value, const format_specs<>& = {})
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
auto range = to_contiguous(it);
|
||||
// This could also be checked at compile time in scan.
|
||||
if (!range) throw_format_error("string_view requires contiguous input");
|
||||
auto p = range.begin;
|
||||
while (p != range.end && *p != ' ') ++p;
|
||||
size_t size = to_unsigned(p - range.begin);
|
||||
value = {range.begin, size};
|
||||
return advance(it, size);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
auto read(scan_iterator it, monostate, const format_specs<>& = {})
|
||||
-> scan_iterator {
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An argument scanner that uses the default format, e.g. decimal for integers.
|
||||
struct default_arg_scanner {
|
||||
scan_iterator it;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> FMT_INLINE auto operator()(T&& value) -> scan_iterator {
|
||||
return read(it, value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// An argument scanner with format specifiers.
|
||||
struct arg_scanner {
|
||||
scan_iterator it;
|
||||
const format_specs<>& specs;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T> auto operator()(T&& value) -> scan_iterator {
|
||||
return read(it, value, specs);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
struct scan_handler : error_handler {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
scan_parse_context parse_ctx_;
|
||||
scan_context scan_ctx_;
|
||||
scan_args args_;
|
||||
int next_arg_id_;
|
||||
scan_arg arg_;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T = unsigned> T read_uint() {
|
||||
T value = 0;
|
||||
auto it = scan_ctx_.begin(), end = scan_ctx_.end();
|
||||
while (it != end) {
|
||||
char c = *it++;
|
||||
if (c < '0' || c > '9') on_error("invalid input");
|
||||
// TODO: check overflow
|
||||
value = value * 10 + static_cast<unsigned>(c - '0');
|
||||
}
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(it);
|
||||
return value;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename T = int> T read_int() {
|
||||
auto it = scan_ctx_.begin(), end = scan_ctx_.end();
|
||||
bool negative = it != end && *it == '-';
|
||||
if (negative) ++it;
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(it);
|
||||
const auto value = read_uint<typename std::make_unsigned<T>::type>();
|
||||
if (negative) return -static_cast<T>(value);
|
||||
return static_cast<T>(value);
|
||||
}
|
||||
using sentinel = scan_buffer::sentinel;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_handler(string_view format, string_view input,
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR scan_handler(string_view format, scan_buffer& buf,
|
||||
scan_args args)
|
||||
: parse_ctx_(format), scan_ctx_(input), args_(args), next_arg_id_(0) {}
|
||||
: parse_ctx_(format), scan_ctx_(buf, args), next_arg_id_(0) {}
|
||||
|
||||
const char* pos() const { return scan_ctx_.begin(); }
|
||||
auto pos() const -> scan_buffer::iterator { return scan_ctx_.begin(); }
|
||||
|
||||
void on_text(const char* begin, const char* end) {
|
||||
auto size = to_unsigned(end - begin);
|
||||
if (begin == end) return;
|
||||
auto it = scan_ctx_.begin();
|
||||
if (it + size > scan_ctx_.end() || !std::equal(begin, end, it))
|
||||
on_error("invalid input");
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(it + size);
|
||||
for (; begin != end; ++begin, ++it) {
|
||||
if (it == sentinel() || *begin != *it) on_error("invalid input");
|
||||
}
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(it);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id() { return on_arg_id(next_arg_id_++); }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(int id) {
|
||||
if (id >= args_.size) on_error("argument index out of range");
|
||||
arg_ = args_.data[id];
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id() -> int { return on_arg_id(next_arg_id_++); }
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(int id) -> int {
|
||||
if (!scan_ctx_.arg(id)) on_error("argument index out of range");
|
||||
return id;
|
||||
}
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR int on_arg_id(string_view id) {
|
||||
FMT_CONSTEXPR auto on_arg_id(string_view id) -> int {
|
||||
if (id.data()) on_error("invalid format");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void on_replacement_field(int, const char*) {
|
||||
auto it = scan_ctx_.begin(), end = scan_ctx_.end();
|
||||
switch (arg_.type) {
|
||||
case scan_type::int_type:
|
||||
*arg_.int_value = read_int();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case scan_type::uint_type:
|
||||
*arg_.uint_value = read_uint();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case scan_type::long_long_type:
|
||||
*arg_.long_long_value = read_int<long long>();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case scan_type::ulong_long_type:
|
||||
*arg_.ulong_long_value = read_uint<unsigned long long>();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case scan_type::string_type:
|
||||
while (it != end && *it != ' ') arg_.string->push_back(*it++);
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(it);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case scan_type::string_view_type: {
|
||||
auto s = it;
|
||||
while (it != end && *it != ' ') ++it;
|
||||
*arg_.string_view = fmt::string_view(s, to_unsigned(it - s));
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(it);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case scan_type::none_type:
|
||||
case scan_type::custom_type:
|
||||
assert(false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
void on_replacement_field(int arg_id, const char*) {
|
||||
scan_arg arg = scan_ctx_.arg(arg_id);
|
||||
auto it = scan_ctx_.begin();
|
||||
while (it != sentinel() && is_whitespace(*it)) ++it;
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(arg.visit(default_arg_scanner{it}));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const char* on_format_specs(int, const char* begin, const char*) {
|
||||
if (arg_.type != scan_type::custom_type) return begin;
|
||||
parse_ctx_.advance_to(begin);
|
||||
arg_.custom.scan(arg_.custom.value, parse_ctx_, scan_ctx_);
|
||||
return parse_ctx_.begin();
|
||||
auto on_format_specs(int arg_id, const char* begin, const char* end) -> const
|
||||
char* {
|
||||
scan_arg arg = scan_ctx_.arg(arg_id);
|
||||
if (arg.scan_custom(begin, parse_ctx_, scan_ctx_))
|
||||
return parse_ctx_.begin();
|
||||
auto specs = format_specs<>();
|
||||
begin = parse_scan_specs(begin, end, specs, arg.type());
|
||||
if (begin == end || *begin != '}') on_error("missing '}' in format string");
|
||||
scan_ctx_.advance_to(arg.visit(arg_scanner{scan_ctx_.begin(), specs}));
|
||||
return begin;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void on_error(const char* message) { error_handler::on_error(message); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace detail
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... Args>
|
||||
std::array<detail::scan_arg, sizeof...(Args)> make_scan_args(Args&... args) {
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
auto make_scan_args(T&... args) -> std::array<scan_arg, sizeof...(T)> {
|
||||
return {{args...}};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
string_view::iterator vscan(string_view input, string_view format_str,
|
||||
scan_args args) {
|
||||
detail::scan_handler h(format_str, input, args);
|
||||
detail::parse_format_string<false>(format_str, h);
|
||||
return input.begin() + (h.pos() - &*input.begin());
|
||||
void vscan(detail::scan_buffer& buf, string_view fmt, scan_args args) {
|
||||
auto h = detail::scan_handler(fmt, buf, args);
|
||||
detail::parse_format_string<false>(fmt, h);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... Args>
|
||||
string_view::iterator scan(string_view input, string_view format_str,
|
||||
Args&... args) {
|
||||
return vscan(input, format_str, make_scan_args(args...));
|
||||
template <typename... T>
|
||||
auto scan(string_view input, string_view fmt, T&... args)
|
||||
-> string_view::iterator {
|
||||
auto&& buf = detail::string_scan_buffer(input);
|
||||
vscan(buf, fmt, make_scan_args(args...));
|
||||
return input.begin() + (buf.begin().base() - input.data());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename InputRange, typename... T,
|
||||
FMT_ENABLE_IF(!std::is_convertible<InputRange, string_view>::value)>
|
||||
auto scan(InputRange&& input, string_view fmt, T&... args)
|
||||
-> decltype(std::begin(input)) {
|
||||
auto it = std::begin(input);
|
||||
vscan(get_buffer(it), fmt, make_scan_args(args...));
|
||||
return it;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename... T> bool scan(std::FILE* f, string_view fmt, T&... args) {
|
||||
auto&& buf = detail::file_scan_buffer(f);
|
||||
vscan(buf, fmt, make_scan_args(args...));
|
||||
return buf.begin() != buf.end();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,10 +26,13 @@ TEST(std_test, path) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path("foo\"bar")), "foo\"bar");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", path("foo\"bar")), "\"foo\\\"bar\"");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:g}", path("/usr/bin")), "/usr/bin");
|
||||
# ifdef _WIN32
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path(
|
||||
L"\x0428\x0447\x0443\x0447\x044B\x043D\x0448"
|
||||
L"\x0447\x044B\x043D\x0430")),
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path("C:\\foo")), "C:\\foo");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:g}", path("C:\\foo")), "C:/foo");
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path(L"\x0428\x0447\x0443\x0447\x044B\x043D\x0448"
|
||||
L"\x0447\x044B\x043D\x0430")),
|
||||
"Шчучыншчына");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", path(L"\xd800")), "<EFBFBD>");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:?}", path(L"\xd800")), "\"\\ud800\"");
|
||||
@ -62,6 +65,15 @@ TEST(std_test, thread_id) {
|
||||
EXPECT_FALSE(fmt::format("{}", std::this_thread::get_id()).empty());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_source_location
|
||||
TEST(std_test, source_location) {
|
||||
std::source_location loc = std::source_location::current();
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", loc),
|
||||
fmt::format("{}:{}:{}: {}", loc.file_name(), loc.line(),
|
||||
loc.column(), loc.function_name()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(std_test, optional) {
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_optional
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional<int>{}), "none");
|
||||
@ -90,6 +102,36 @@ TEST(std_test, optional) {
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
namespace my_nso {
|
||||
enum class my_number {
|
||||
one,
|
||||
two,
|
||||
};
|
||||
auto format_as(my_number number) -> fmt::string_view {
|
||||
return number == my_number::one ? "first" : "second";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
class my_class {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int av;
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
friend auto format_as(const my_class& elm) -> std::string {
|
||||
return fmt::to_string(elm.av);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
} // namespace my_nso
|
||||
TEST(std_test, optional_format_as) {
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_optional
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional<my_nso::my_number>{}), "none");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional{my_nso::my_number::one}),
|
||||
"optional(\"first\")");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional<my_nso::my_class>{}), "none");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", std::optional{my_nso::my_class{7}}),
|
||||
"optional(\"7\")");
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
struct throws_on_move {
|
||||
throws_on_move() = default;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -237,6 +279,13 @@ TEST(std_test, format_const_bit_reference) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{} {}", v[0], v[1]), "true false");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(std_test, format_bitset) {
|
||||
auto bs = std::bitset<6>(42);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", bs), "101010");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:0>8}", bs), "00101010");
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{:-^12}", bs), "---101010---");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(std_test, format_atomic) {
|
||||
std::atomic<bool> b(false);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", b), "false");
|
||||
@ -248,10 +297,10 @@ TEST(std_test, format_atomic) {
|
||||
#ifdef __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
TEST(std_test, format_atomic_flag) {
|
||||
std::atomic_flag f = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
|
||||
(void) f.test_and_set();
|
||||
(void)f.test_and_set();
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", f), "true");
|
||||
|
||||
const std::atomic_flag cf = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format("{}", cf), "false");
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
#endif // __cpp_lib_atomic_flag_test
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,9 +37,13 @@ std::locale do_get_locale(const char* name) {
|
||||
|
||||
std::locale get_locale(const char* name, const char* alt_name) {
|
||||
auto loc = do_get_locale(name);
|
||||
if (loc == std::locale::classic() && alt_name) {
|
||||
if (loc == std::locale::classic() && alt_name)
|
||||
loc = do_get_locale(alt_name);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#ifdef __OpenBSD__
|
||||
// Locales are not working in OpenBSD:
|
||||
// https://github.com/fmtlib/fmt/issues/3670.
|
||||
loc = std::locale::classic();
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
if (loc == std::locale::classic())
|
||||
fmt::print(stderr, "{} locale is missing.\n", name);
|
||||
return loc;
|
||||
|
||||
26
test/util.h
26
test/util.h
@ -29,9 +29,9 @@ void safe_sprintf(char (&buffer)[SIZE], const char* format, ...) {
|
||||
extern const char* const file_content;
|
||||
|
||||
// Opens a buffered file for reading.
|
||||
fmt::buffered_file open_buffered_file(FILE** fp = nullptr);
|
||||
auto open_buffered_file(FILE** fp = nullptr) -> fmt::buffered_file;
|
||||
|
||||
inline FILE* safe_fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode) {
|
||||
inline auto safe_fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode) -> FILE* {
|
||||
#if defined(_WIN32) && !defined(__MINGW32__)
|
||||
// Fix MSVC warning about "unsafe" fopen.
|
||||
FILE* f = nullptr;
|
||||
@ -51,17 +51,17 @@ template <typename Char> class basic_test_string {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit basic_test_string(const Char* value = empty) : value_(value) {}
|
||||
|
||||
const std::basic_string<Char>& value() const { return value_; }
|
||||
auto value() const -> const std::basic_string<Char>& { return value_; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char> const Char basic_test_string<Char>::empty[] = {0};
|
||||
|
||||
typedef basic_test_string<char> test_string;
|
||||
typedef basic_test_string<wchar_t> test_wstring;
|
||||
using test_string = basic_test_string<char>;
|
||||
using test_wstring = basic_test_string<wchar_t>;
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Char>
|
||||
std::basic_ostream<Char>& operator<<(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os,
|
||||
const basic_test_string<Char>& s) {
|
||||
auto operator<<(std::basic_ostream<Char>& os, const basic_test_string<Char>& s)
|
||||
-> std::basic_ostream<Char>& {
|
||||
os << s.value();
|
||||
return os;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -72,10 +72,12 @@ class date {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
date(int year, int month, int day) : year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {}
|
||||
|
||||
int year() const { return year_; }
|
||||
int month() const { return month_; }
|
||||
int day() const { return day_; }
|
||||
auto year() const -> int { return year_; }
|
||||
auto month() const -> int { return month_; }
|
||||
auto day() const -> int { return day_; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns a locale with the given name if available or classic locale otherwise.
|
||||
std::locale get_locale(const char* name, const char* alt_name = nullptr);
|
||||
// Returns a locale with the given name if available or classic locale
|
||||
// otherwise.
|
||||
auto get_locale(const char* name, const char* alt_name = nullptr)
|
||||
-> std::locale;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,11 +102,71 @@ struct custom_char {
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
constexpr custom_char(T val) : value(static_cast<int>(val)) {}
|
||||
|
||||
operator char() const {
|
||||
constexpr operator char() const {
|
||||
return value <= 0xff ? static_cast<char>(value) : '\0';
|
||||
}
|
||||
constexpr bool operator<(custom_char c) const { return value < c.value; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
namespace std {
|
||||
|
||||
template <> struct char_traits<custom_char> {
|
||||
using char_type = custom_char;
|
||||
using int_type = int;
|
||||
using off_type = streamoff;
|
||||
using pos_type = streampos;
|
||||
using state_type = mbstate_t;
|
||||
|
||||
static constexpr void assign(char_type& r, const char_type& a) { r = a; }
|
||||
static constexpr bool eq(char_type a, char_type b) { return a == b; }
|
||||
static constexpr bool lt(char_type a, char_type b) { return a < b; }
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR int compare(const char_type* s1, const char_type* s2,
|
||||
size_t count) {
|
||||
for (; count; count--, s1++, s2++) {
|
||||
if (lt(*s1, *s2)) return -1;
|
||||
if (lt(*s2, *s1)) return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR size_t length(const char_type* s) {
|
||||
size_t count = 0;
|
||||
while (!eq(*s++, custom_char(0))) count++;
|
||||
return count;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static const char_type* find(const char_type*, size_t, const char_type&);
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type* move(char_type* dest, const char_type* src,
|
||||
size_t count) {
|
||||
if (count == 0) return dest;
|
||||
char_type* ret = dest;
|
||||
if (src < dest) {
|
||||
dest += count;
|
||||
src += count;
|
||||
for (; count; count--) assign(*--dest, *--src);
|
||||
} else if (src > dest)
|
||||
copy(dest, src, count);
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type* copy(char_type* dest, const char_type* src,
|
||||
size_t count) {
|
||||
char_type* ret = dest;
|
||||
for (; count; count--) assign(*dest++, *src++);
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static FMT_CONSTEXPR char_type* assign(char_type* dest, std::size_t count,
|
||||
char_type a) {
|
||||
char_type* ret = dest;
|
||||
for (; count; count--) assign(*dest++, a);
|
||||
return ret;
|
||||
}
|
||||
static int_type not_eof(int_type);
|
||||
static char_type to_char_type(int_type);
|
||||
static int_type to_int_type(char_type);
|
||||
static bool eq_int_type(int_type, int_type);
|
||||
static int_type eof();
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace std
|
||||
|
||||
auto to_ascii(custom_char c) -> char { return c; }
|
||||
|
||||
FMT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
|
||||
@ -127,18 +187,6 @@ template <typename S> std::string from_u8str(const S& str) {
|
||||
return std::string(str.begin(), str.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(xchar_test, format_utf8_precision) {
|
||||
using str_type = std::basic_string<fmt::detail::char8_type>;
|
||||
auto format =
|
||||
str_type(reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>(u8"{:.4}"));
|
||||
auto str = str_type(reinterpret_cast<const fmt::detail::char8_type*>(
|
||||
u8"caf\u00e9s")); // cafés
|
||||
auto result = fmt::format(format, str);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::detail::compute_width(result), 4);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(result.size(), 5);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(from_u8str(result), from_u8str(str.substr(0, 5)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(xchar_test, format_to) {
|
||||
auto buf = std::vector<wchar_t>();
|
||||
fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(buf), L"{}{}", 42, L'\0');
|
||||
@ -521,7 +569,7 @@ template <class charT> struct formatter<std::complex<double>, charT> {
|
||||
basic_format_parse_context<charT>& ctx) {
|
||||
auto end = parse_format_specs(ctx.begin(), ctx.end(), specs_, ctx,
|
||||
detail::type::float_type);
|
||||
detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_, detail::error_handler());
|
||||
detail::parse_float_type_spec(specs_);
|
||||
return end;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -539,9 +587,9 @@ template <class charT> struct formatter<std::complex<double>, charT> {
|
||||
fmt::runtime("{:" + specs + "}"), c.imag());
|
||||
auto fill_align_width = std::string();
|
||||
if (specs_.width > 0) fill_align_width = fmt::format(">{}", specs_.width);
|
||||
return format_to(ctx.out(), runtime("{:" + fill_align_width + "}"),
|
||||
c.real() != 0 ? fmt::format("({}+{}i)", real, imag)
|
||||
: fmt::format("{}i", imag));
|
||||
return fmt::format_to(ctx.out(), runtime("{:" + fill_align_width + "}"),
|
||||
c.real() != 0 ? fmt::format("({}+{}i)", real, imag)
|
||||
: fmt::format("{}i", imag));
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
FMT_END_NAMESPACE
|
||||
@ -554,17 +602,14 @@ TEST(locale_test, complex) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(locale_test, chrono_weekday) {
|
||||
auto loc = get_locale("ru_RU.UTF-8", "Russian_Russia.1251");
|
||||
auto loc = get_locale("es_ES.UTF-8", "Spanish_Spain.1252");
|
||||
auto loc_old = std::locale::global(loc);
|
||||
auto mon = fmt::weekday(1);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", mon), L"Mon");
|
||||
auto sat = fmt::weekday(6);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(fmt::format(L"{}", sat), L"Sat");
|
||||
if (loc != std::locale::classic()) {
|
||||
// {L"\x43F\x43D", L"\x41F\x43D", L"\x43F\x43D\x434", L"\x41F\x43D\x434"}
|
||||
// {L"пн", L"Пн", L"пнд", L"Пнд"}
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT(
|
||||
(std::vector<std::wstring>{L"\x43F\x43D", L"\x41F\x43D",
|
||||
L"\x43F\x43D\x434", L"\x41F\x43D\x434"}),
|
||||
Contains(fmt::format(loc, L"{:L}", mon)));
|
||||
// L'\xE1' is 'á'.
|
||||
auto saturdays = std::vector<std::wstring>{L"s\xE1""b", L"s\xE1."};
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT(saturdays, Contains(fmt::format(loc, L"{:L}", sat)));
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::locale::global(loc_old);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user